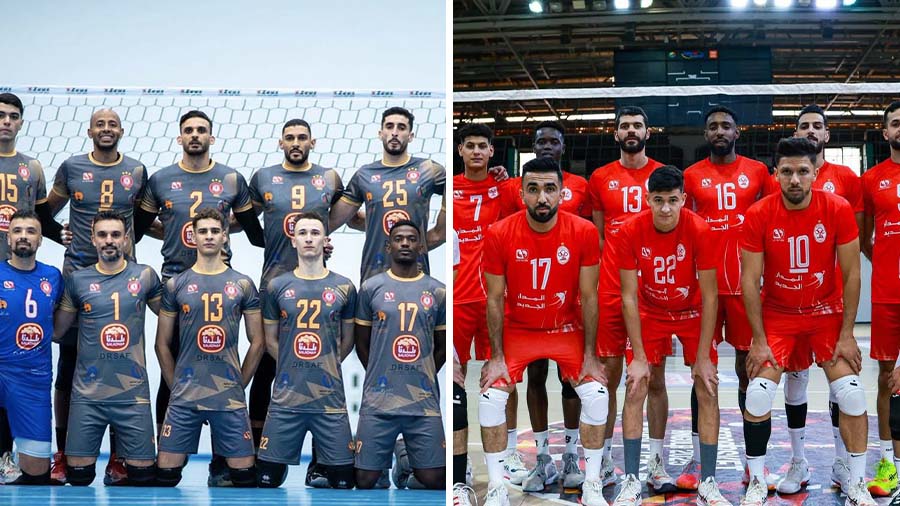
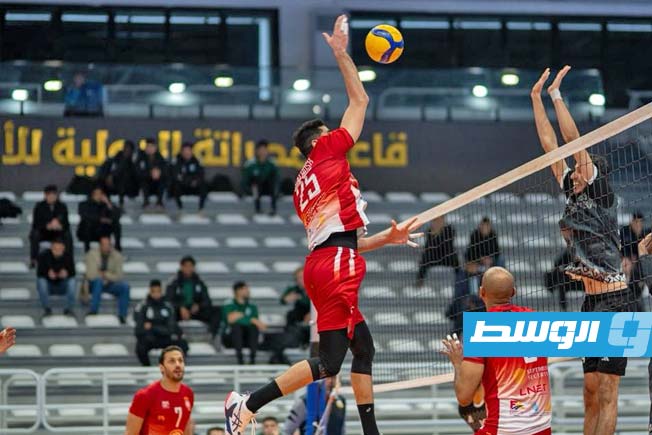
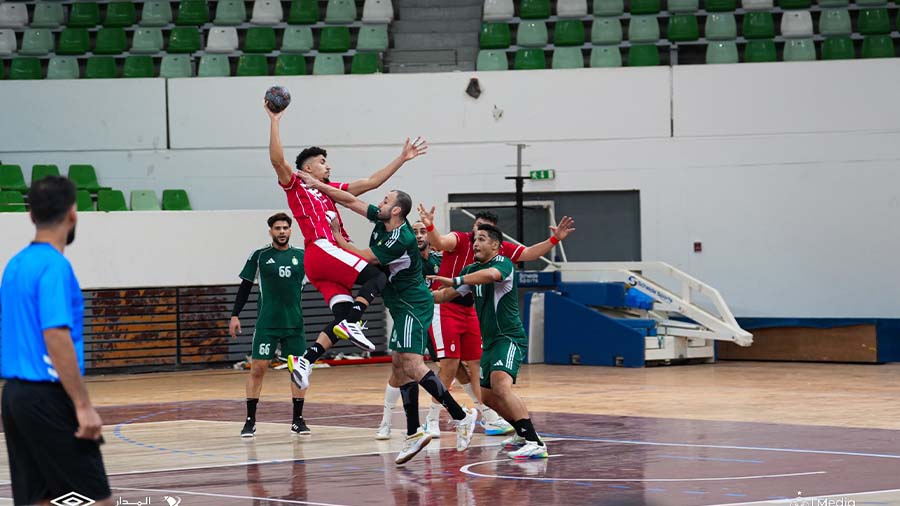
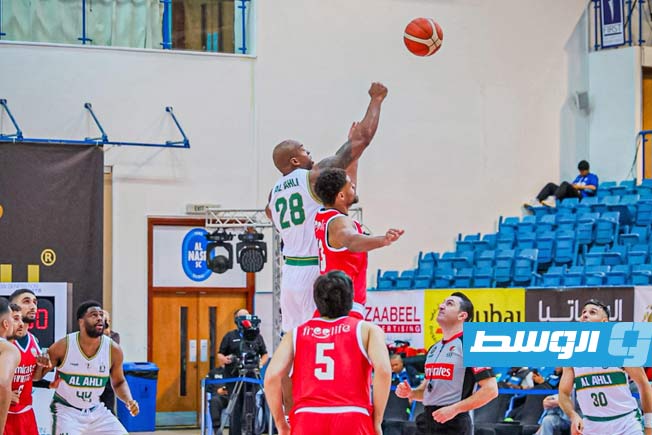
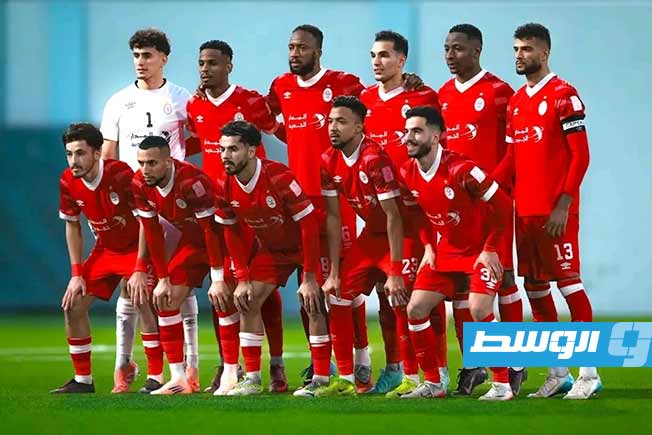
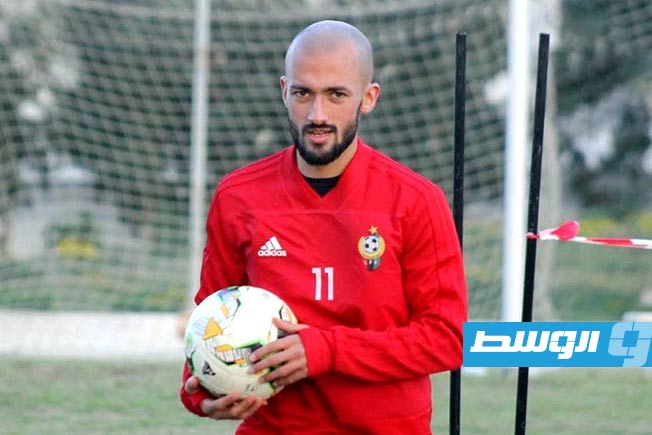
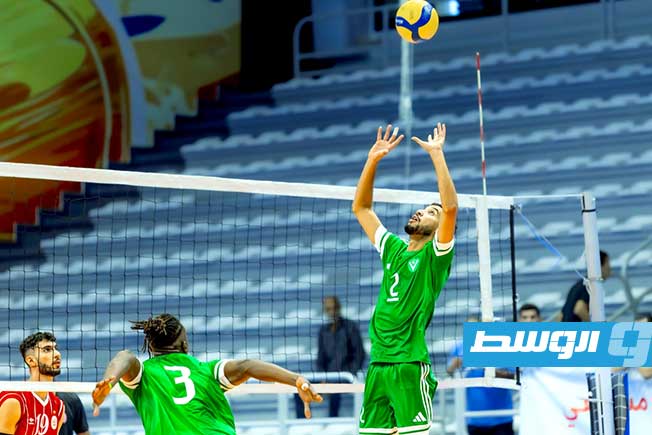
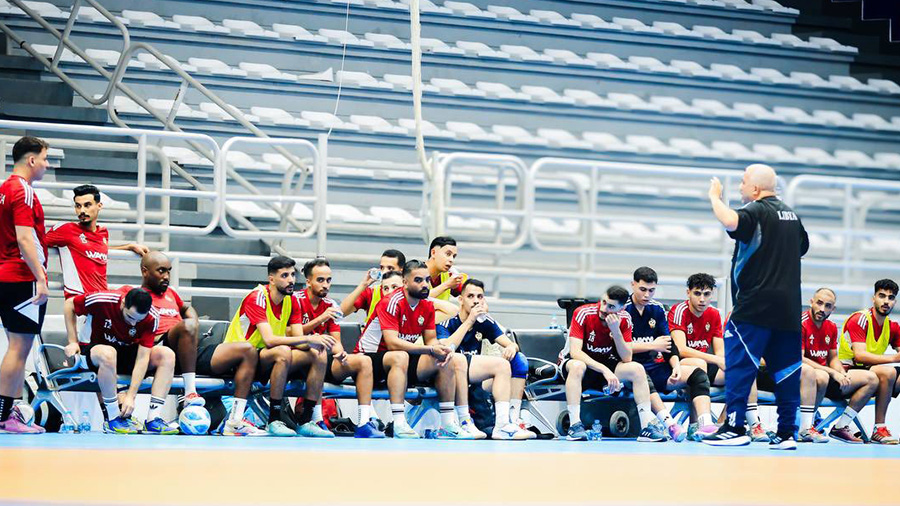
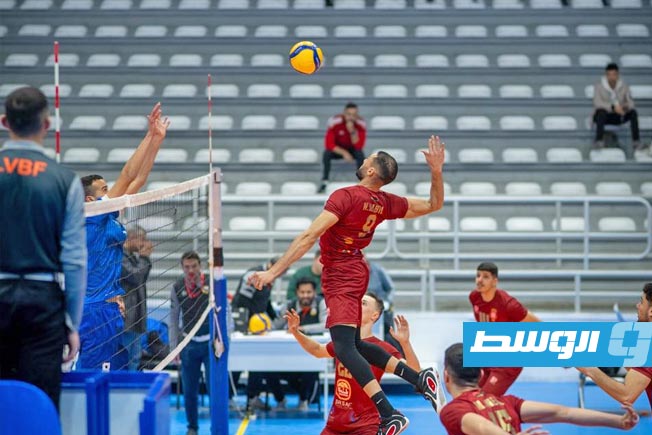
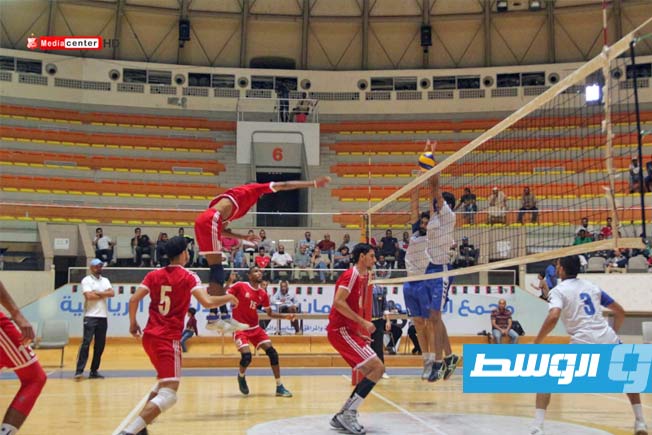
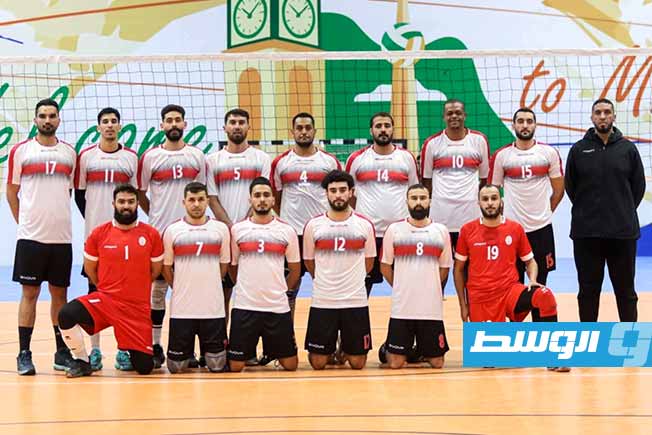
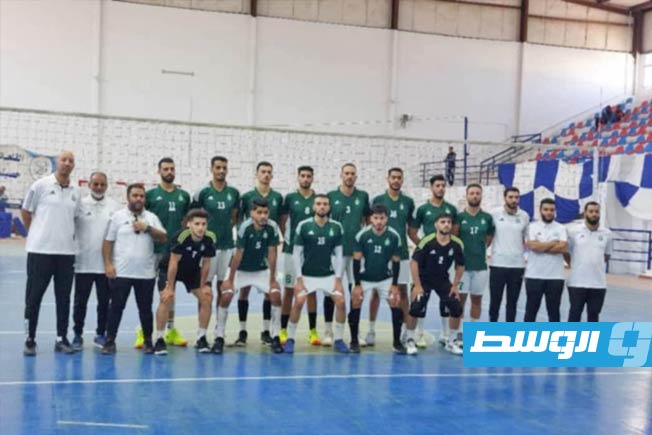
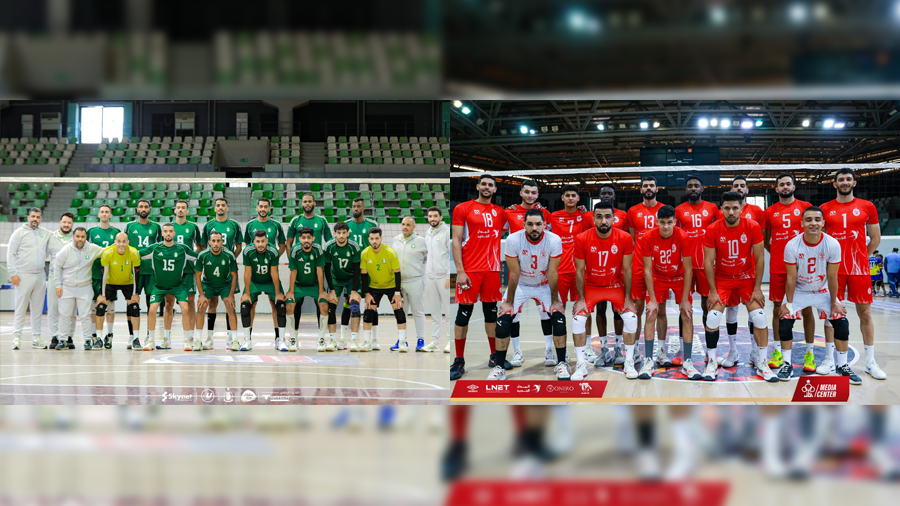
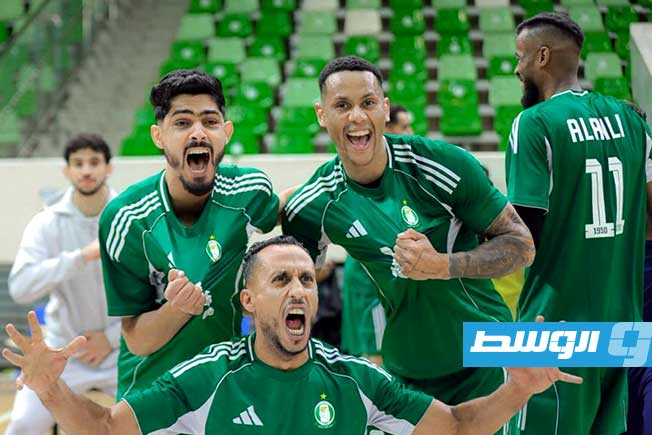
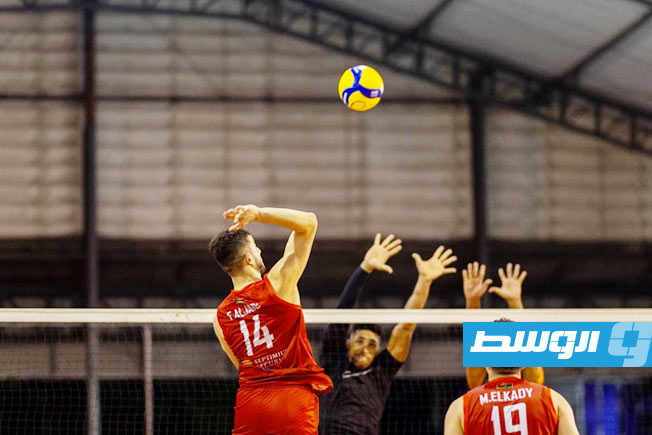
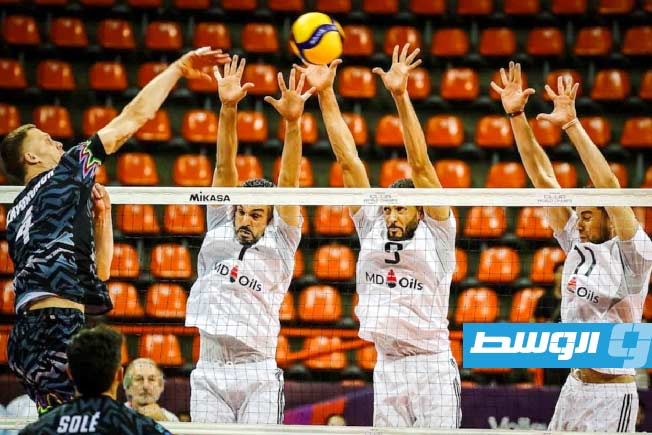
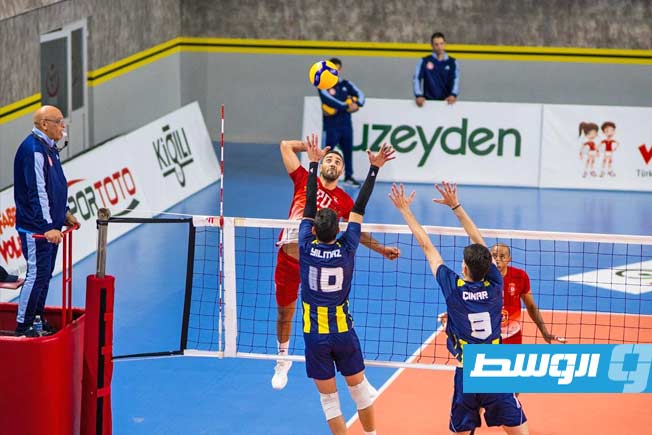
Al-Swehly and Al-Ittihad clubs will begin their participation in the Arab Clubs Volleyball Championship in Tunisia tomorrow, Thursday, with two strong matches to open the competition.
Al-Swehly club will face Algeria’s Tajnanet club in the Group 1 matches.
As for Al-Ittihad club, they will face Tunisia’s Étoile du Sahel club in the Group 2 matches.
The draw for the Arab Championship placed the champion from two editions ago, Al-Swehly club, in Group 1 alongside Tunisia’s Espérance Sportive de Tunis, Qatar’s Al-Qatar club, Oman’s Al-Seeb club, Iraq’s Al-Masafi Al-Shamal club, and Algeria’s Tajnanet club.
Conversely, the draw placed Al-Ittihad club in Group 2 alongside Qatar’s Al-Shorta club, Palestine’s Al-Quwat club, Tunisia’s Étoile du Sahel club, Bahrain’s Al-Muharraq club, and Oman’s Al-Muhasib club.
Al-Swehly
Al-Swehly is a prominent mosque and cultural complex located in the Al-Suweihliya district of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. It was established in the early 1990s and is named after the renowned Islamic scholar Sheikh Muhammad Al-Suweihli. The site serves as a major center for religious activities, education, and community gatherings in the city.
Al-Ittihad
Al-Ittihad is a historic football club based in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, founded in 1927. It is one of the most successful and popular clubs in the country and Asia, with a rich history of winning numerous domestic and continental titles, including the AFC Champions League.
Arab Clubs Volleyball Championship
The Arab Clubs Volleyball Championship is an annual men’s volleyball competition contested by the leading club teams from Arab nations. It was first organized by the Arab Volleyball Association in 1985 to promote the sport and foster regional competition among top clubs. The tournament has grown to become a prestigious event in the Arab sporting calendar, showcasing high-level volleyball talent from across the region.
Tunisia
Tunisia is a North African country with a rich history shaped by Phoenician, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and French influences, evident in sites like the ancient city of Carthage. Its culture is a vibrant blend of Arab, Berber, and Mediterranean traditions. The country gained independence from France in 1956 and was the birthplace of the 2011 Arab Spring protests.
Algeria
Algeria is a North African country with a rich history shaped by ancient Berber kingdoms, Roman rule, and centuries as a core province of the Ottoman Empire. It was colonized by France in the 19th century before gaining independence in 1962 after a protracted war of liberation. The nation’s cultural heritage is prominently displayed at sites like the Roman ruins of Timgad and the Casbah of Algiers, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Tajnanet
Tajnanet is a small village located in the Bejaia Province of Algeria, known for its scenic beauty within the Kabylie region. Historically, it is part of the cultural and historical landscape of the Amazigh (Berber) people, with a traditional way of life tied to the local mountains and agriculture.
Étoile du Sahel
Étoile Sportive du Sahel is a prominent Tunisian multisport club based in Sousse, founded in 1925 during the French protectorate. It is best known for its highly successful football division, which has won numerous domestic and continental titles, including the CAF Champions League in 2007. The club is a major cultural institution in Tunisia, symbolizing regional pride and sporting excellence.
Espérance Sportive de Tunis
Espérance Sportive de Tunis is a prominent Tunisian multisport club founded in 1919, best known for its highly successful football division. Historically significant as a symbol of national identity during the French protectorate, it has grown into one of Africa’s most decorated clubs, winning numerous domestic and continental titles, including the CAF Champions League.
Qatar
Qatar is a sovereign country located on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, historically shaped by its Bedouin heritage and maritime traditions like pearling. Its modern history is marked by the discovery of vast oil and natural gas reserves in the mid-20th century, which rapidly transformed it into one of the world’s wealthiest nations. The capital, Doha, is now a major global hub known for its modern architecture, cultural institutions like the Museum of Islamic Art, and its role as host of the 2022 FIFA World Cup.
Al-Qatar
“Al-Qatar” is not a specific cultural site but the Arabic name for the State of Qatar, a country on the Arabian Peninsula. Historically, it was a region of pearl diving and fishing, later transformed by the discovery of vast oil and natural gas reserves in the 20th century, which led to its rapid modernization and global economic significance.
Oman
Oman is a country on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula with a rich maritime history as a powerful trading empire. Its historical and cultural identity is deeply tied to its role in the frankincense trade and its legacy of seafaring, with landmarks like the Bahla Fort and the ancient port of Sohar reflecting this past. Today, it is known for its diverse landscapes, from mountains and deserts to a long coastline, and for maintaining many traditional customs alongside modern development.
Al-Seeb
Al-Seeb is a historic coastal city in Oman, located near the capital Muscat, known for its traditional architecture and role as a fishing and trading hub. Its history dates back centuries, with archaeological evidence of ancient settlements, and it served as a significant port and commercial center along Omani trade routes. Today, it blends its heritage with modern development as part of the Muscat Governorate.
Iraq
Iraq, historically known as Mesopotamia, is often called the “Cradle of Civilization” as it was home to ancient Sumerian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, which pioneered writing, law, and urban development. Modern Iraq, established in the 20th century, is a country with a rich cultural heritage that includes significant archaeological sites like Babylon and Ur, though it has faced considerable conflict and political instability in recent decades.
Al-Masafi Al-Shamal
Al-Masafi Al-Shamal is a significant archaeological site in Syria, located in the region of the Dead Cities. It features the well-preserved ruins of a Byzantine-era settlement, including churches, villas, and water cisterns, which thrived as part of a prosperous agricultural network between the 4th and 7th centuries AD.
Al-Shorta
Al-Shorta is the name for the national police force in Iraq, established during the British Mandate period in the early 1920s. It has played a central and often challenging role in maintaining law and order throughout Iraq’s modern history, including through periods of conflict and political change.
Palestine
Palestine is a historical and geographic region in the Eastern Mediterranean, with a deeply rooted history as a crossroads of civilizations and a central location for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Its modern political status is defined by the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, following the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 and the subsequent displacement of a large portion of the Palestinian Arab population.
Al-Quwat
“Al-Quwat” is not a widely recognized historical or cultural site, so specific information is limited. It may refer to a local place name or a term with other meanings, making a definitive historical summary difficult.
Bahrain
Bahrain is an island nation in the Persian Gulf with a history dating back over 5,000 years, famously home to the ancient Dilmun civilization. Its most significant cultural site is the Bahrain Fort (Qal’at al-Bahrain), a UNESCO World Heritage Site that served as the capital of Dilmun and features layers of human occupation. Today, the country is known as a modern financial hub while preserving its archaeological heritage.
Al-Muharraq
Al-Muharraq is a city in Bahrain that served as the country’s capital from 1810 to 1923 and is historically the center of the pearling industry in the Gulf. Its significance is recognized by UNESCO, which lists the “Pearling, Testimony of an Island Economy” site, encompassing parts of Al-Muharraq, as a World Heritage Site. The city’s traditional architecture and urban fabric reflect its prosperous pearling past.
Al-Muhasib
Al-Muhasib is a historic district in the city of Najaf, Iraq, traditionally known as the area where the accounts and financial matters of the city were settled. Its name derives from the Arabic word for “accountant” or “auditor,” reflecting its administrative and commercial role in the city’s history, particularly in relation to the shrine of Imam Ali.