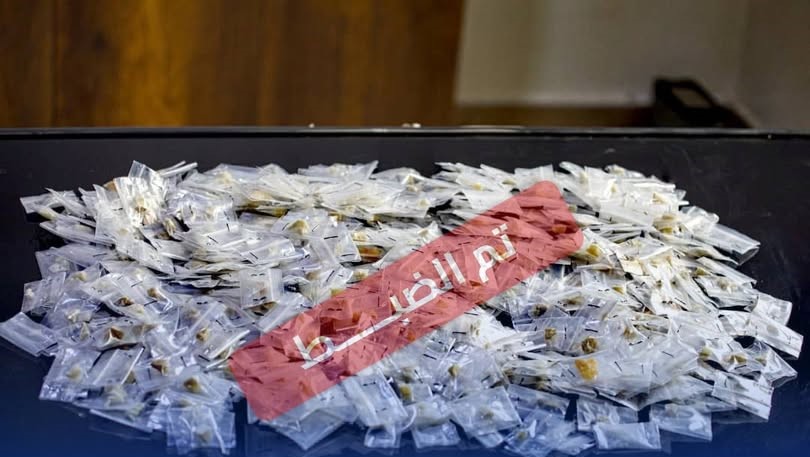
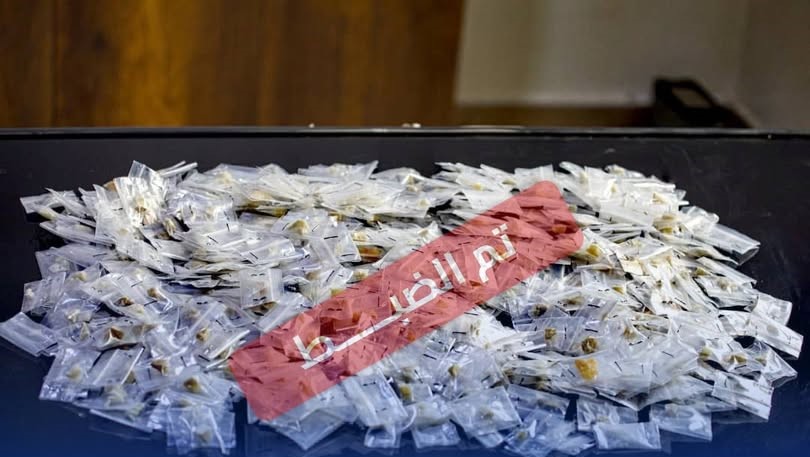
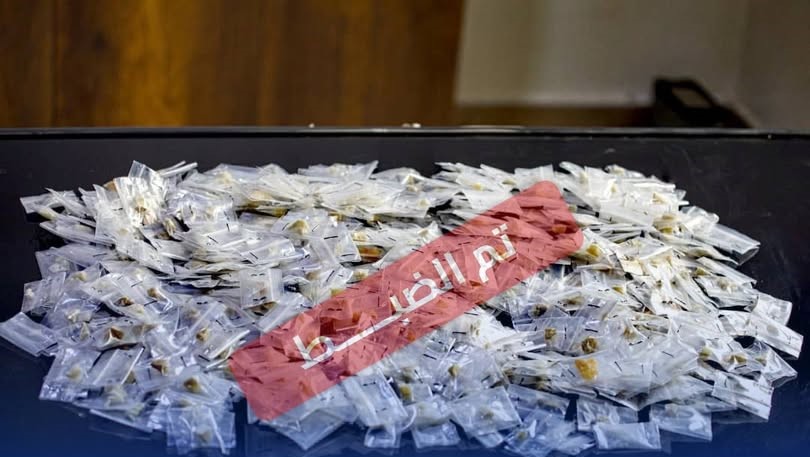
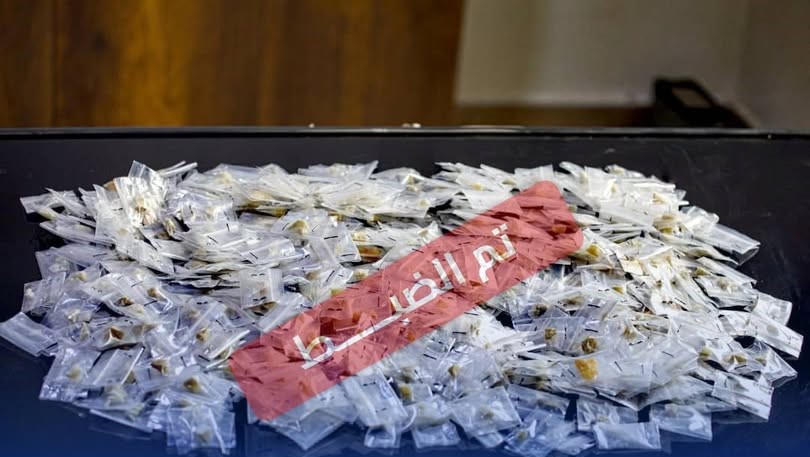
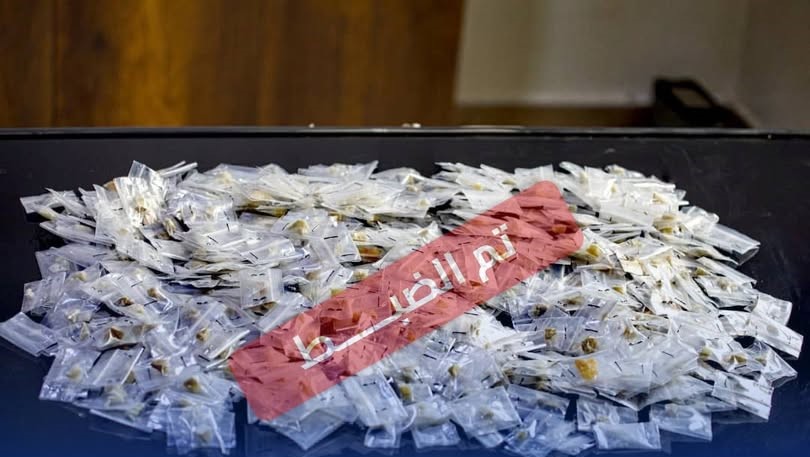
Tripoli, December 17, 2025 – The Investigation Authority of the Public Prosecutor’s Office has halted forged family records at the Civil Registry Office in central Sirte, which resulted in the issuance of 598 national identification numbers for foreigners. This action is part of its measures to curb tampering with citizenship data and to address the resulting severe impacts on economic, social, and political rights.
The Public Prosecutor’s Office stated that investigators into the forgery of civil status data uncovered a breach of responsibility in managing the data system at the Civil Registry Office in central Sirte. They documented irregularities involving the forgery of family records, which led to the issuance of 598 national identification numbers for foreigners. These individuals used documents based on these forged records and national numbers to obtain full citizenship rights.
It clarified that the investigation necessitated signing an order to suspend the national numbers under review, evaluating related administrative transactions, and taking the necessary steps to file criminal charges against those responsible for the forgery.

Investigation Authority of the Public Prosecutor’s Office
Here is a breakdown of its meaning and context:
### Core Meaning
It signifies that the Public Prosecutor’s Office (or State Prosecutor) does not merely decide whether to charge a suspect after police investigation. Instead, it has the **direct authority to lead, direct, or conduct criminal investigations itself.**
### Key Functions Typically Included:
1. **Directing Police Investigations:** Prosecutors give binding instructions to the police on how to proceed with an investigation.
2. **Conducting Independent Investigations:** Prosecutors may have their own corps of investigative judges or judicial police under their direct command to gather evidence, question witnesses, and execute searches.
3. **Supervising Legality:** Ensuring that the investigation respects legal procedures and the rights of all parties.
4. **Deciding on Charges:** Based on the evidence gathered under their authority, they decide whether to bring the case to court.
### Jurisdictional Context
* **Common in:** Many European countries (like Germany, France, Italy, Spain), Latin America, Japan, and South Korea.
* **Contrast with Common Law Systems:** In countries like the U.S. and U.K., the police generally conduct investigations independently, and the prosecutor’s role is primarily to review the completed case file and decide on prosecution. The term “investigation authority” in this sense is less prominent.
### Purpose
The main rationale is to ensure that investigations are conducted from a **neutral, legal perspective from the very beginning**, aiming to uncover the truth objectively (not just to secure a conviction) and to protect suspects’ rights early in the process.
**In summary, “Investigation Authority of the Public Prosecutor’s Office” describes a system where the prosecutor is an active, directing chief of the criminal investigation, not just a passive recipient of a police case file.**
Civil Registry Office in central Sirte
### **Primary Location: Sirte Central Civil Registry Office**
* **General Function:** This is the main government office in Sirte responsible for issuing and managing all **national identification documents** for Libyan citizens.
* **Key Services Provided:**
1. **Issuance of National ID Number (رقم تعريف وطني):** The foundational ID number for all citizens.
2. **Family Book (السجل العائلي):** The primary family civil status document.
3. **Birth Certificates (شهادات الميلاد).**
4. **Death Certificates (شهادات الوفاة).**
5. **Marriage & Divorce Certificates (شهادات الزواج والطلاق)** – often linked to the court, but registered here.
6. **Extraction of Civil Records (استخراج السجلات المدنية):** Getting official copies of any of the above documents.
—
### **Important Considerations & Current Context**
Due to the political and administrative situation in Libya, here is crucial practical advice:
1. **Location & Security:** The main office is typically located on or near **Giza Street (شارع الجيزة)** or in the main government complex area in central Sirte. **Always confirm the exact location and accessibility locally**, as security conditions can change.
2. **Dual Administration:** Libya has had rival governments. While Sirte is under the control of the Government of National Stability (based in the east), its documents are **not always recognized** by the rival Government of National Unity in Tripoli (west), and vice-versa. This is a critical issue for legal and travel purposes.
3. **Process and Requirements:** The process can be bureaucratic. You will typically need:
* Existing family documents.
* Supporting documents from other offices (e.g., court for marriage).
* Witnesses for certain procedures.
* **Patience and time.** Hiring a local facilitator (“مُسَاعِد” or “مُكَاتِب”) is very common to navigate the process.
—
### **Practical Steps & Alternatives**
* **Before You Go:** Contact the office directly if possible. Ask a local resident or relative in Sirte for the most current information on operating hours, required paperwork, and any specific procedures.
* **Alternative for Diaspora:** Libyans abroad should contact the **Libyan embassy or consulate** in their country of residence. They can often initiate the process or provide official documents, though final issuance usually requires coordination with the central registry in Libya.
* **Language:** All official business is conducted in **Arabic**. You will need an Arabic speaker to assist if you are not fluent.
### **Summary**
The Civil Registry Office in central Sirte is the key institution for civil documentation. However, navigating its services requires an understanding of the complex Libyan political landscape, which directly affects the validity and recognition of the documents it issues. **Local knowledge and verification of the current situation are absolutely essential.**
Would you like guidance on a specific procedure, such as obtaining a Family Book or a birth certificate?
Public Prosecutor’s Office
### Core Definition
A **Public Prosecutor’s Office** (often called the Prosecutor’s Office, District Attorney’s Office, Crown Prosecution Service, or State’s Attorney’s Office depending on the country) is a governmental body responsible for representing the state in criminal proceedings against an accused person. Its primary role is to act as the legal representative of **”the people”** or **”the state”** in court, ensuring that justice is served by prosecuting those who violate the law.
### Key Functions and Responsibilities
1. **Criminal Prosecution:** This is its central function. Prosecutors decide whether to file criminal charges based on evidence gathered by the police, and then present the case in court.
2. **Case Investigation:** In many legal systems (especially civil law/inquisitorial systems), prosecutors direct or supervise police investigations to ensure they are lawful and thorough.
3. **Discretion and Charging Decisions:** Prosecutors have significant discretion. They can:
* **Charge** an individual with a crime.
* **Drop or dismiss** charges if evidence is insufficient.
* **Negotiate plea bargains** with the defense.
4. **Representation in Court:** Prosecutors present evidence, examine witnesses, make legal arguments, and recommend sentences to the judge or jury.
5. **Upholding Justice:** Their duty is not simply to secure convictions, but to **ensure justice**. This means they must disclose exculpatory evidence (evidence favorable to the defense) and act as “ministers of justice.”
6. **Appeals:** They handle appeals if a case is lost or if they believe a sentence was too lenient.
7. **Victim Support:** Often, they serve as a point of contact for victims, keeping them informed about case progress and advocating for their rights.
### How It Differs from Police and Defense
* **vs. Police:** The police **investigate crimes and gather evidence**. The Prosecutor’s Office **evaluates that evidence, applies the law, and decides on prosecution**. They provide legal guidance to police.
* **vs. Defense Attorney:** The defense attorney represents the **individual accused** and protects their rights. The prosecutor represents **society and the state’s interest** in enforcing the law.
### Structure and Names Around the World
The structure and name vary significantly:
* **United States:** Often called the **District Attorney’s (DA) Office** (county level) or **United States Attorney’s Office** (federal level). They are typically elected officials.
* **United Kingdom:** **Crown Prosecution Service (CPS)** for England and Wales. It is a public agency headed by the Director of Public Prosecutions (DPP).
* **Canada:** **Crown Attorney’s Office** or **Public Prosecution Service of Canada** (federal).
* **Many Civil Law Countries (e.g., France, Germany, Italy, Japan):** The office is often part of a hierarchical, national judiciary system. Prosecutors (like *procureurs* or *Staatsanwälte*) are typically career magistrates, not elected.
* **International:** The **International Criminal Court (ICC)** has an **Office of the Prosecutor**, which investigates and prosecutes genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes.
### Important Principles
* **Independence:** Prosecutors should exercise their functions independently, free from improper political or other influence.
* **Impartiality:** They must act objectively and fairly.
* **Proportionality:** They should only bring charges that are proportionate to the alleged offense and the available evidence.
In summary, the **Public Prosecutor’s Office** is the cornerstone of the criminal justice system, bridging the gap between police investigation and court adjudication, with the ultimate goal of maintaining public order and justice under the law.