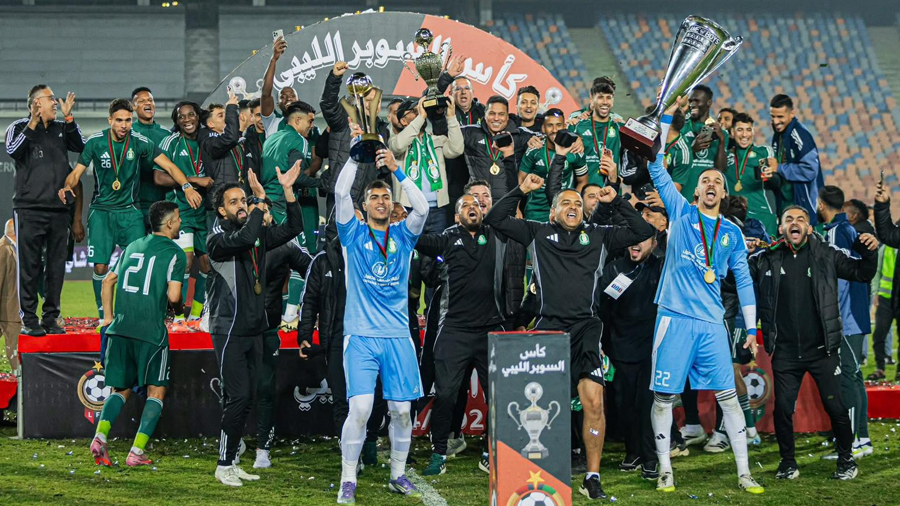
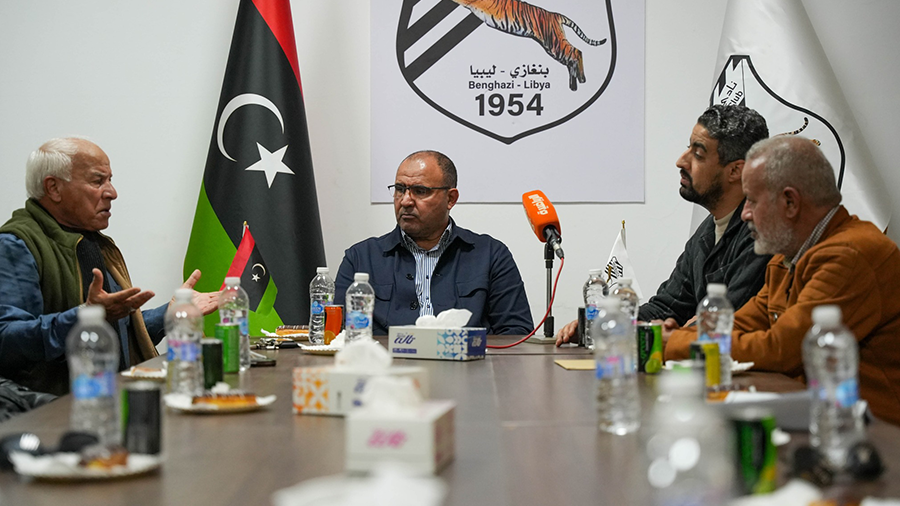
Four matches will be held on Wednesday as part of the competitions for Groups Two and Four of the Premier League.
The matches kick off from Derna Municipal Stadium, which hosts a strong encounter at 3:00 PM between Al-Afriqi, the runner-up of Group Four, and the group leader, Al-Nasr. At the same time, Al-Wefaq hosts Ajdabiya at their home ground, Al-Muruj Stadium.
Within the competitions of Group Two, a match between the neighboring teams, Al-Tirsana and Abi Al-Ashhar, will be held at 3:30 PM on the pitch of Al-Nahr Al-Sina’i Stadium. The Wednesday matches conclude with the encounter between Shabab Al-Ghar and their guest, Al-Shumou’, at 7:00 PM on the same stadium.
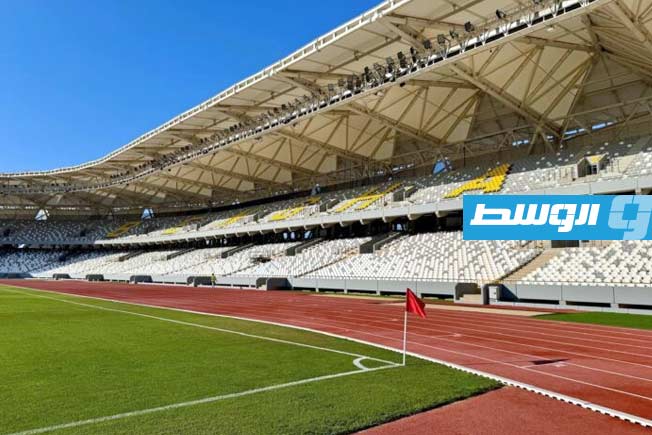
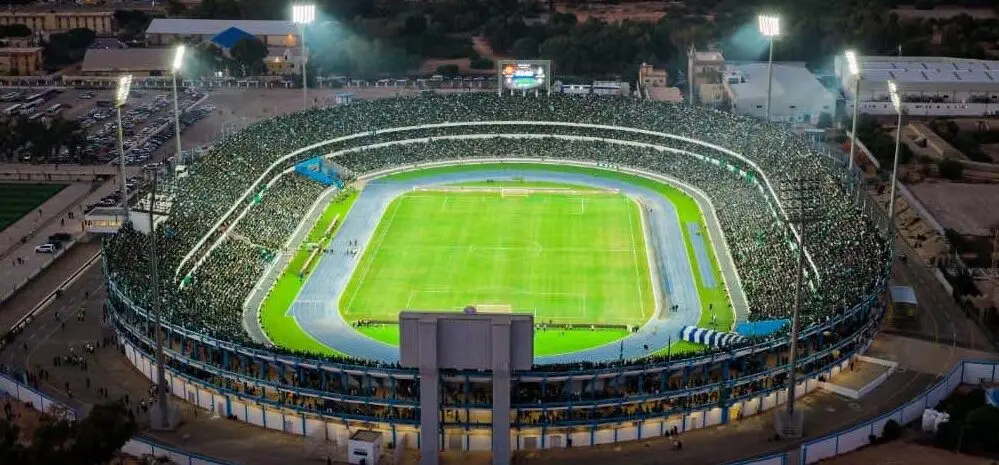
Derna Municipal Stadium
Derna Municipal Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium located in Derna, Libya, primarily used for football matches. It historically served as the home ground for Derna-based clubs and has been a focal point for local sporting events. The stadium has faced significant damage and disruption due to the conflicts in Libya during the 2010s.
Al-Afriqi
“Al-Afriqi” is a historical name for the continent of Africa, derived from the Latin “Africus.” It was notably used by medieval Arab geographers like Al-Idrisi, who wrote a seminal work called “Kitab Rujar” or “The Book of Roger,” which described the world known to the Islamic civilization at the time.
Al-Nasr
Al-Nasr is a common Arabic name meaning “The Victory,” often used for monuments, sports clubs, or neighborhoods across the Arab world. Historically, it is most famously associated with the Al-Nasr Mosque in Medina, Saudi Arabia, which is traditionally believed to mark the location where the Prophet Muhammad celebrated a key military victory.
Al-Wefaq
Al-Wefaq is a Shiite political society in Bahrain that was founded in 2001 and became the largest bloc in the country’s parliament. It historically advocated for greater political reform and representation for the Shiite majority but was dissolved by a court order in 2016 after years of government tension.
Ajdabiya
Ajdabiya is a city in northeastern Libya, historically significant as a major crossroads for trans-Saharan trade routes and caravans. It gained prominence during the Italian colonial period and later served as a key strategic location during the 2011 Libyan Civil War.
Al-Muruj Stadium
Al-Muruj Stadium is a multi-purpose sports venue located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, primarily used for football matches. It was constructed in the 1970s and has historically served as a home ground for several local clubs, most notably Al-Nassr FC for many years before they moved to a larger arena.
Al-Tirsana
Al-Tirsana is a historic village located in Syria’s Homs Governorate, known for its well-preserved traditional stone architecture. Its history dates back centuries, serving as an important agricultural and residential community in the region, with many of its structures reflecting Ottoman-era influences.
Abi Al-Ashhar
Abi Al-Ashhar is a historical archaeological site located in Jordan, believed to be an ancient Nabataean settlement. It features ruins that include tombs, water channels, and structures indicative of the advanced engineering of the Nabataean civilization, which flourished from around the 4th century BC to the 1st century AD.
Al-Nahr Al-Sina’i Stadium
Al-Nahr Al-Sina’i Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium located in the city of Homs, Syria. It was originally constructed in 1976 and has historically served as the home venue for the Al-Karamah sports club.
Shabab Al-Ghar
“Shabab Al-Ghar” is a prominent cultural and sports club based in the city of Hebron in the West Bank, Palestine. Founded in 1974, it has played a significant role in Palestinian society, particularly through its football team, which has been a mainstay in the Palestinian Premier League. The club serves as an important community institution, fostering local talent and civic pride in the region.
Al-Shumou’
Al-Shumou’ is a prominent cultural and literary magazine founded in Syria in 1930, known for its influential role in promoting Arab literature and intellectual thought during the mid-20th century. It served as a key platform for poets, writers, and thinkers, contributing significantly to the Arab cultural renaissance (Al-Nahda) of that era.