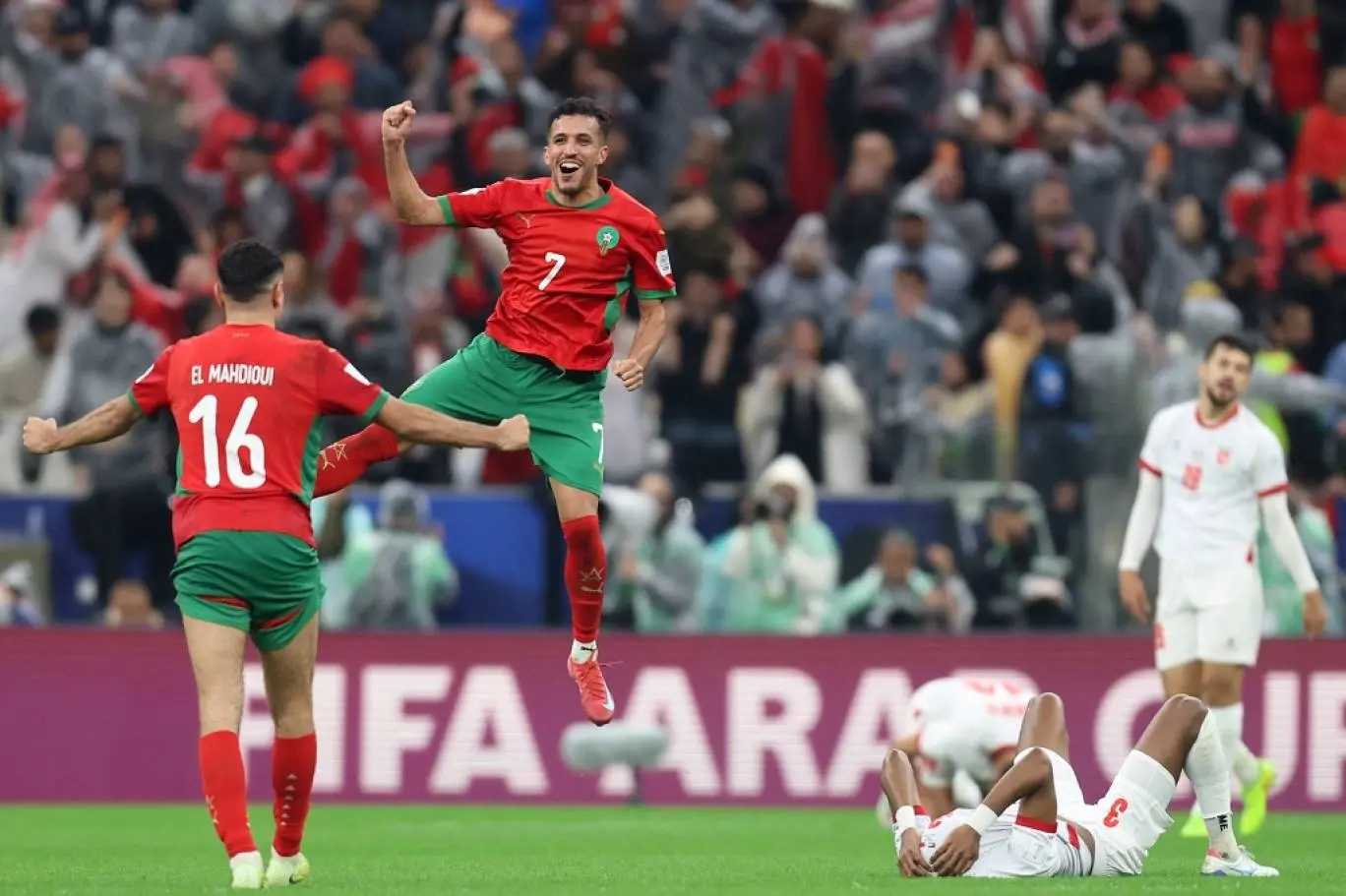
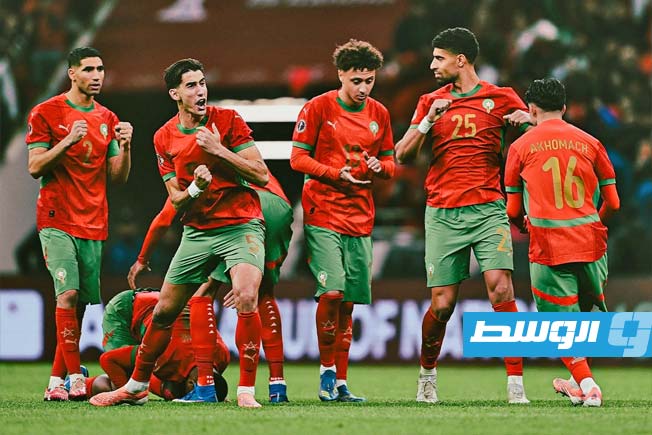
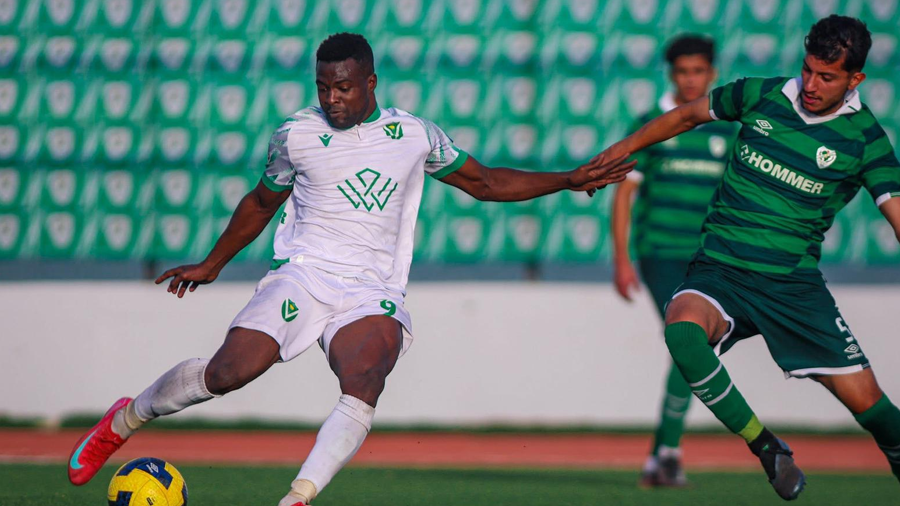
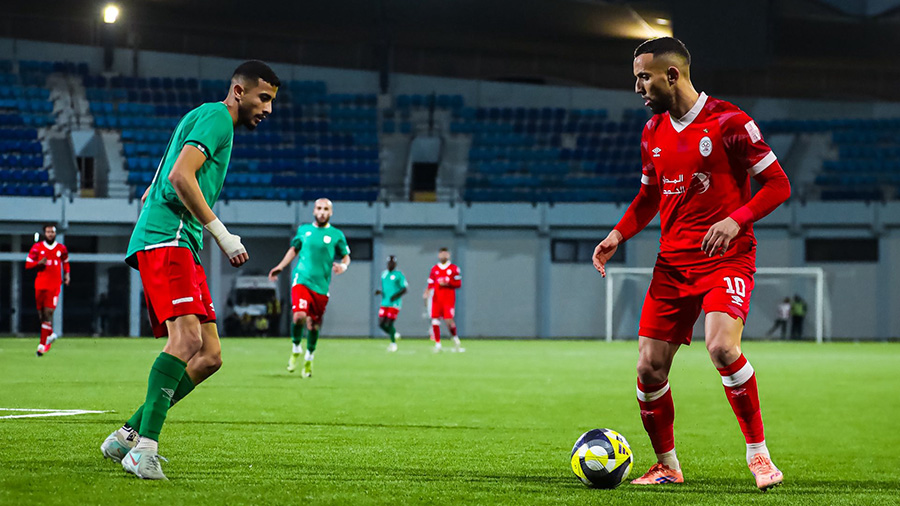
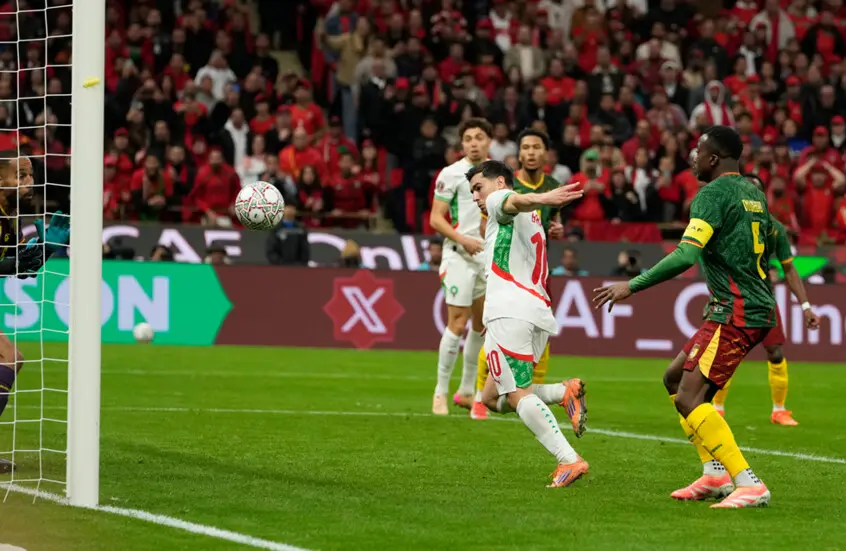
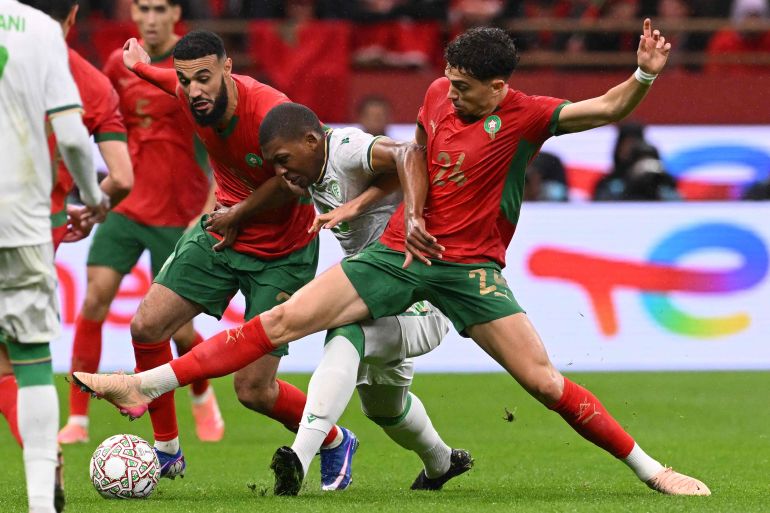
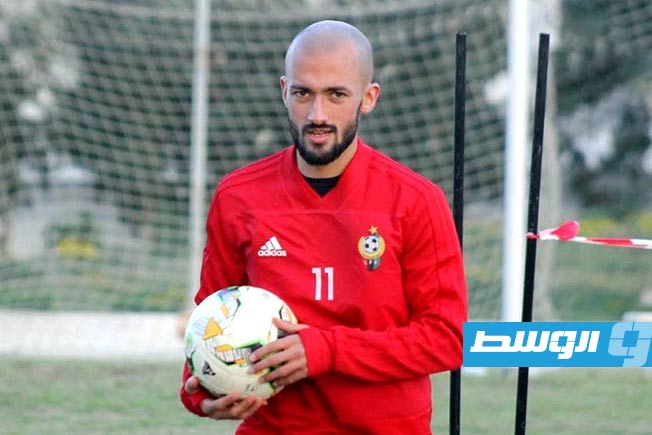
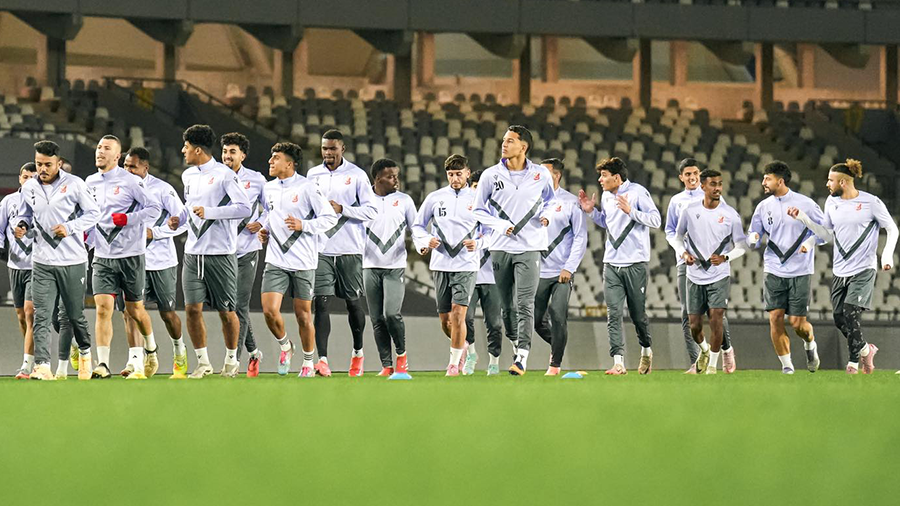
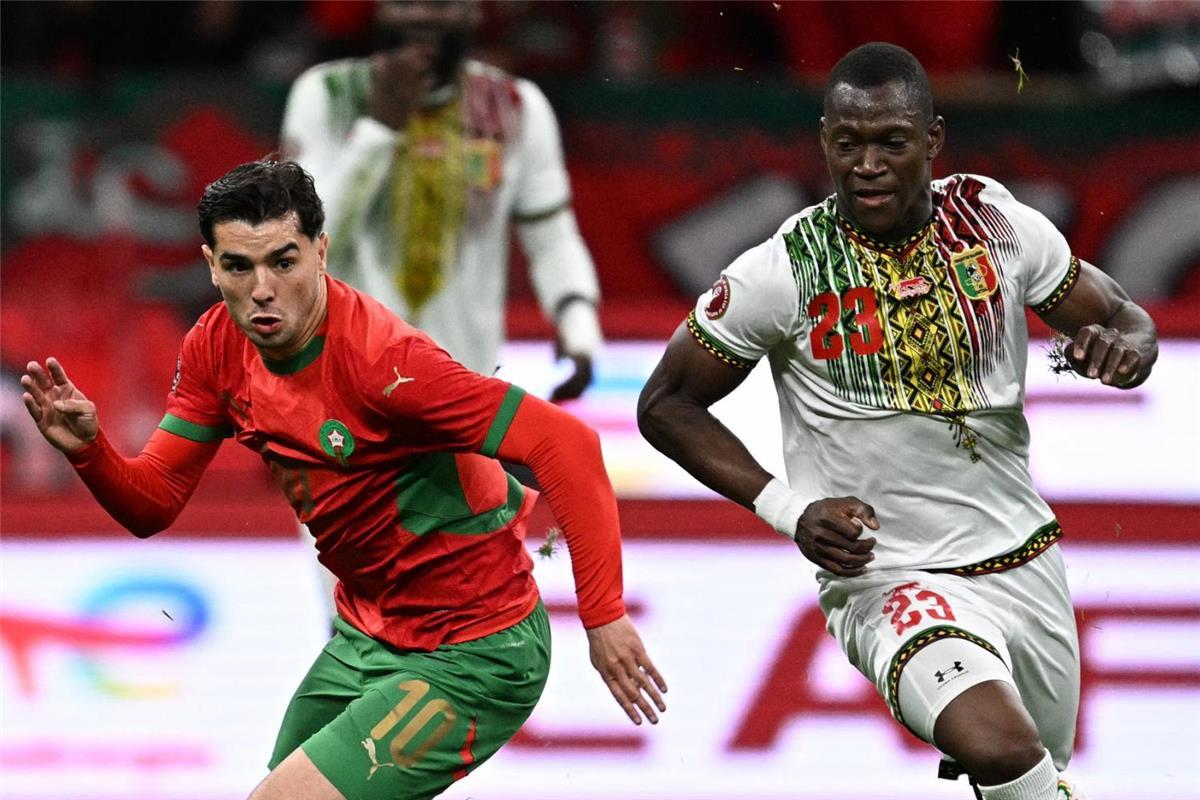
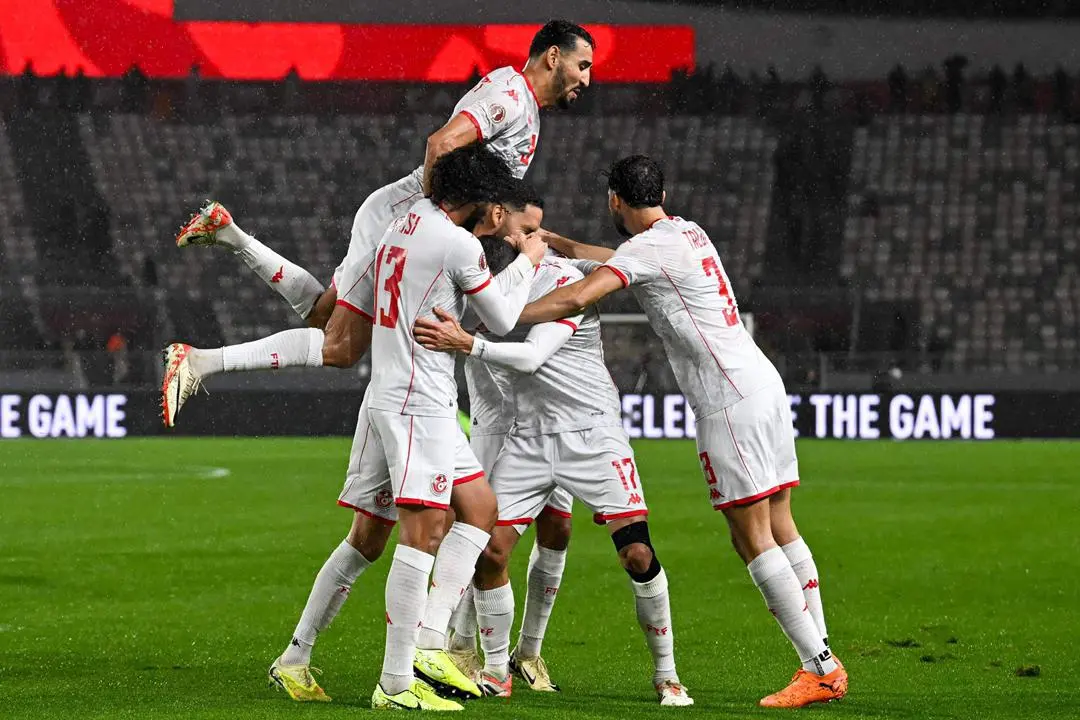
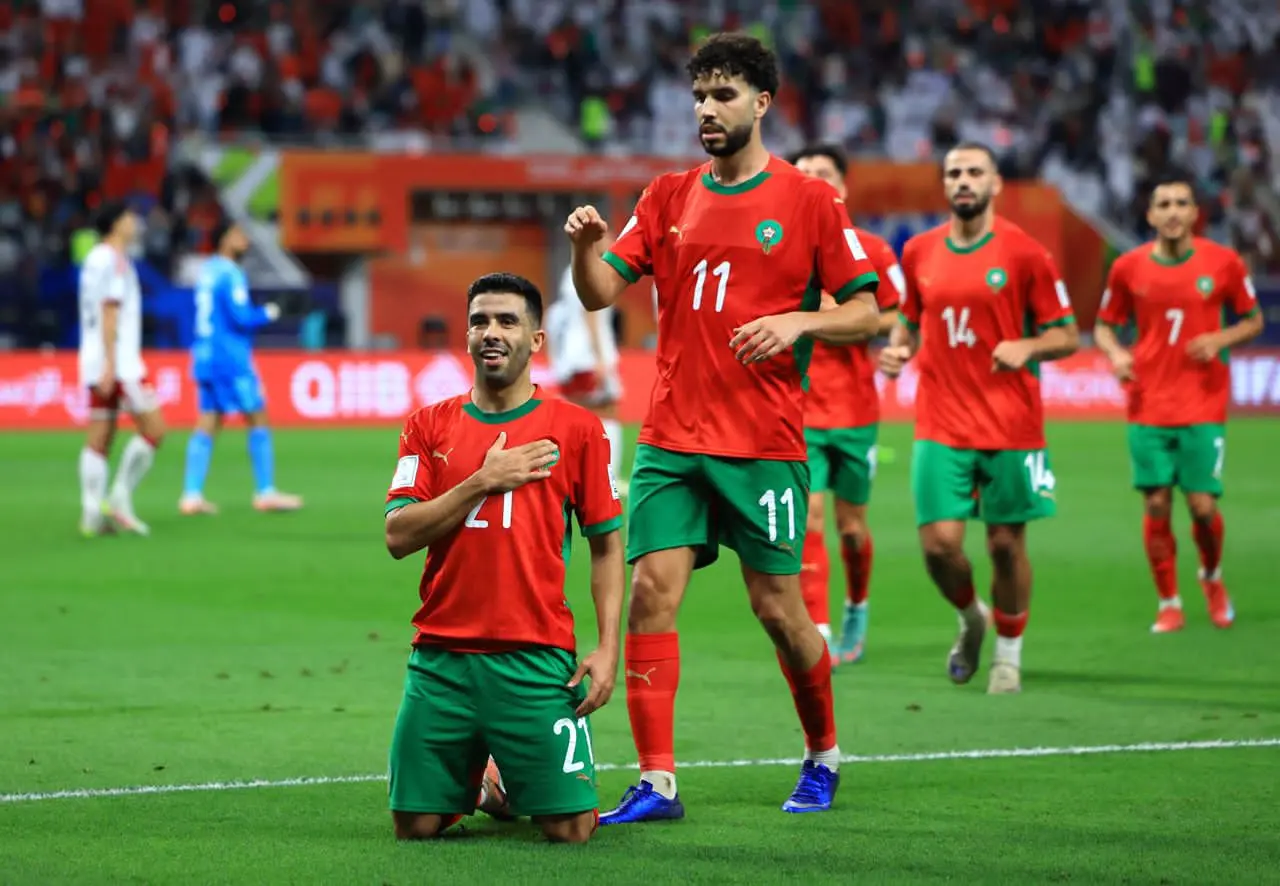
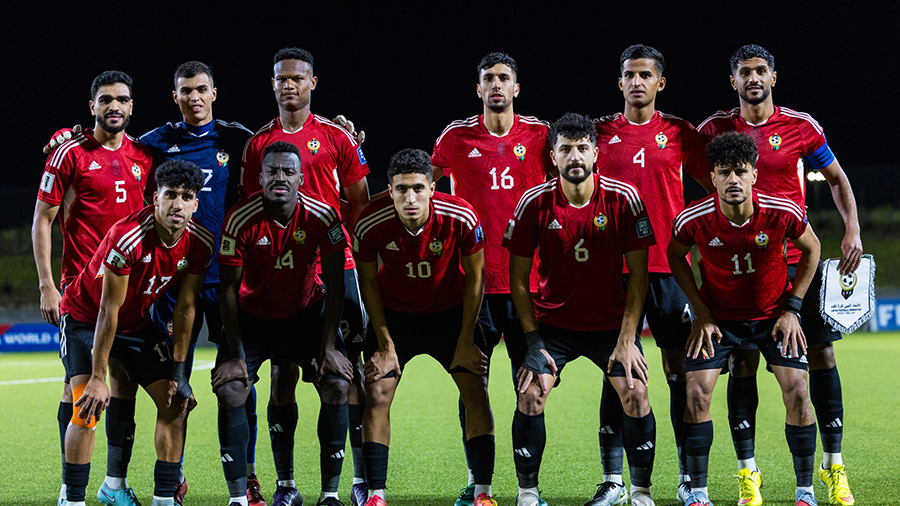
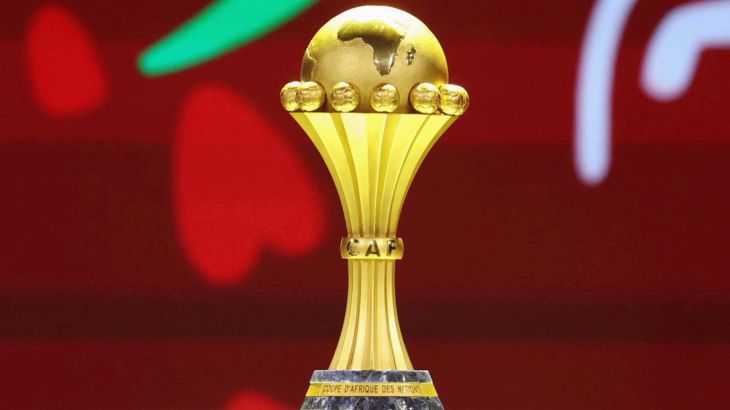
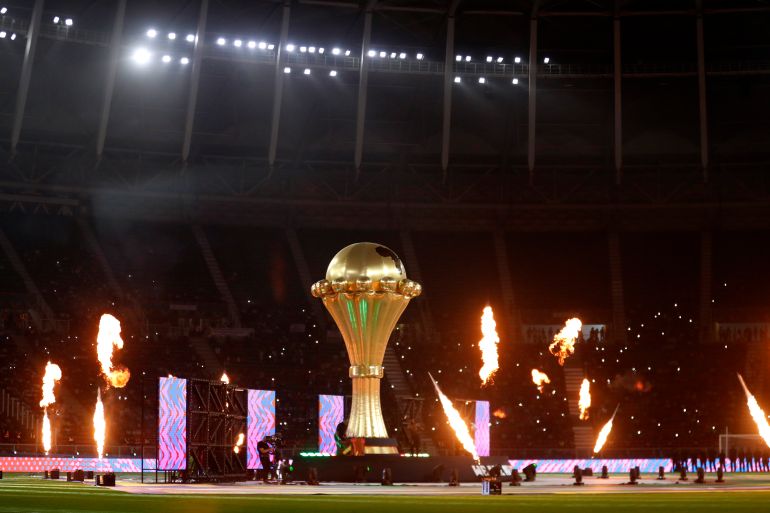
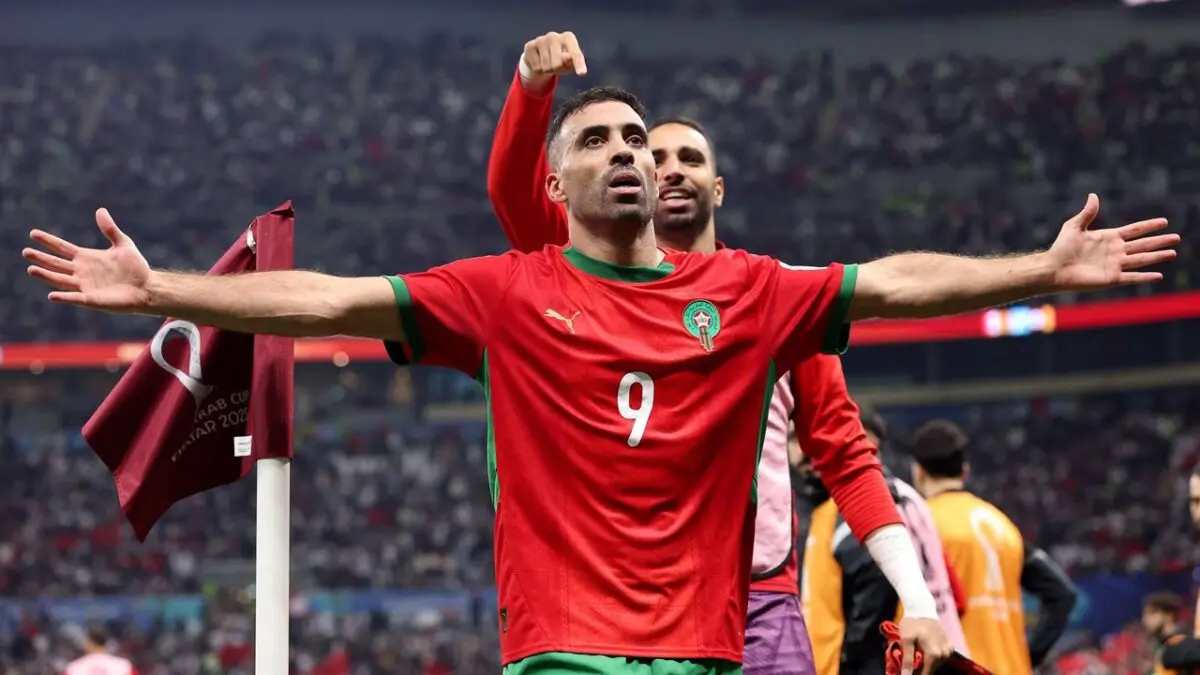
All eyes are on Morocco as the Atlas Lions embark on a journey to win a long-awaited African title. The Africa Cup of Nations finals kick off on Moroccan soil starting Sunday, December 22nd, until January 18th next year. The Moroccan national team, led by its coach, holds the top African spot in the FIFA rankings and is 11th globally. It possesses the strongest squad in the tournament, backed by massive fan support, and has set a world record for consecutive wins by any national team with 18 victories.
The Moroccan national team seeks to claim the title nearly fifty years after its first and only win in 1976, relying on its star player and its key athletes to achieve the national dream. The team’s president aspires to make the 2025 edition the largest in the tournament’s history and emphasizes the necessity of winning.
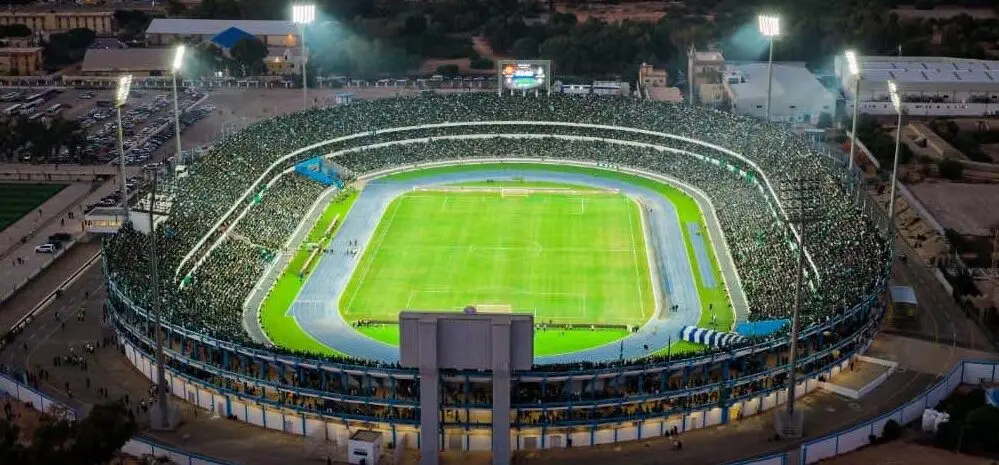
The Moroccan national team maintains a blend of youthful strength and experience, benefiting from widespread fan support across all Moroccan cities. The meticulous organization is highlighted by modern or specially renovated stadiums for this edition, as part of Morocco’s preparations to co-host the 2030 World Cup with Spain and Portugal, following South Africa in 2010.
Competing Teams
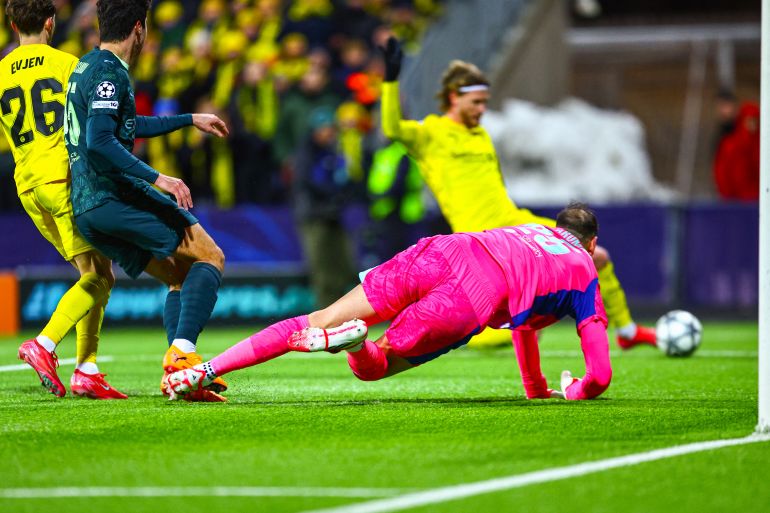
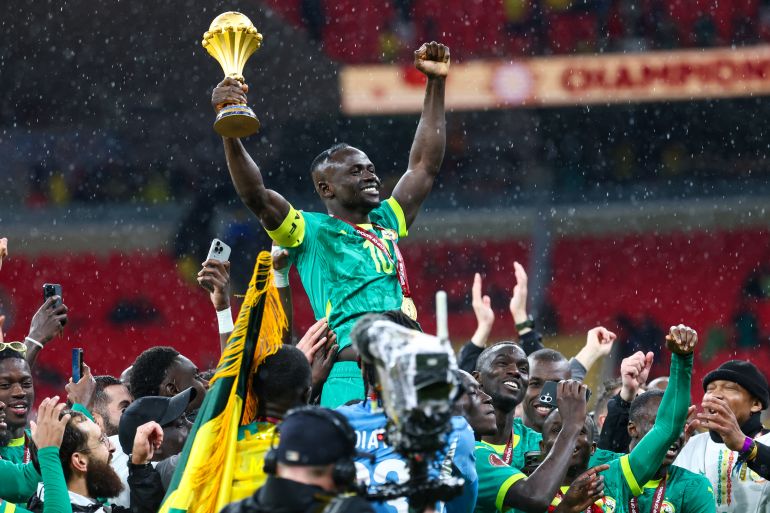
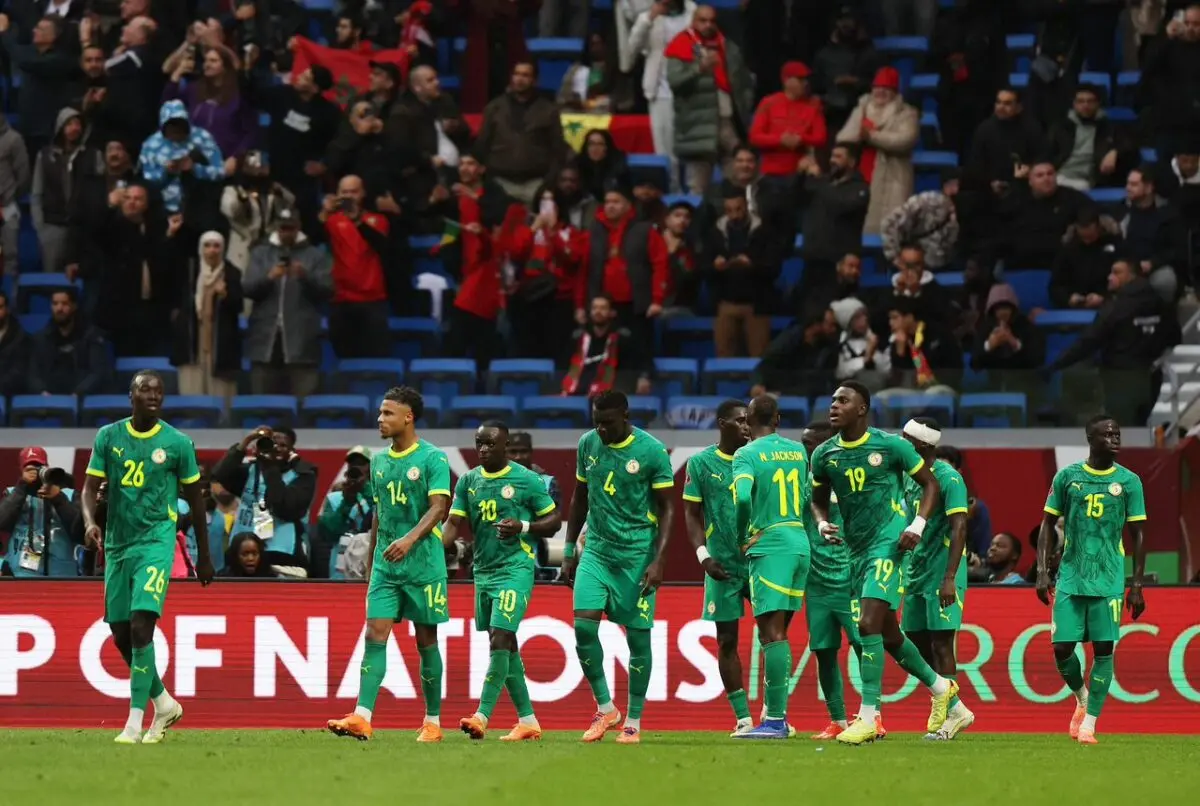
The Senegalese national team, under its coach’s leadership, is seen as a fierce competitor for the title. The squad includes world-class players and relies on professionals from the French league. Despite an early exit in the 2023 edition and the difficulty of the previous tournament in the Maghreb, Senegal remains a strong contender.
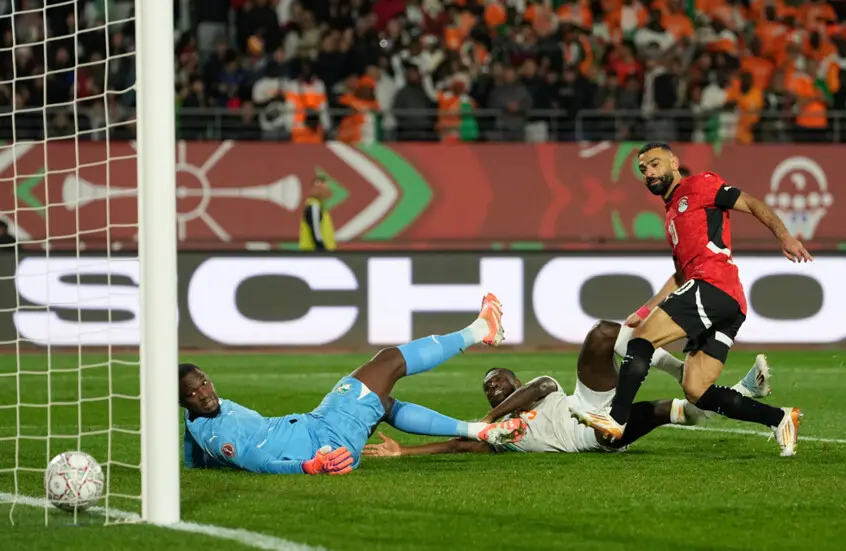
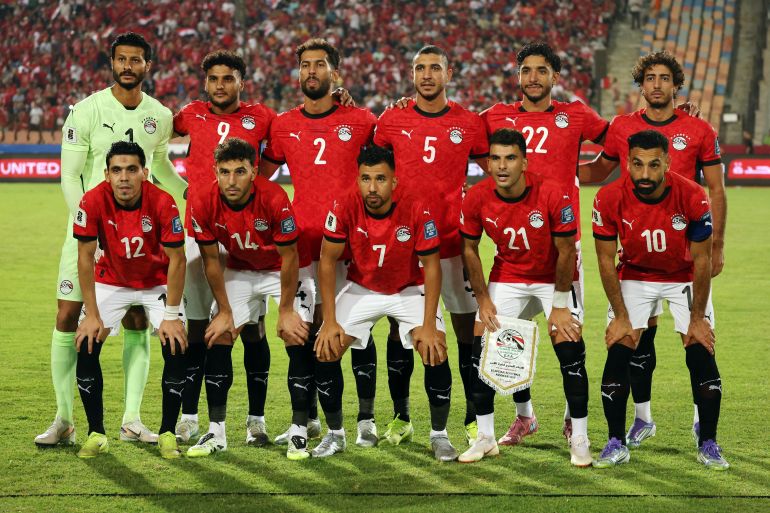
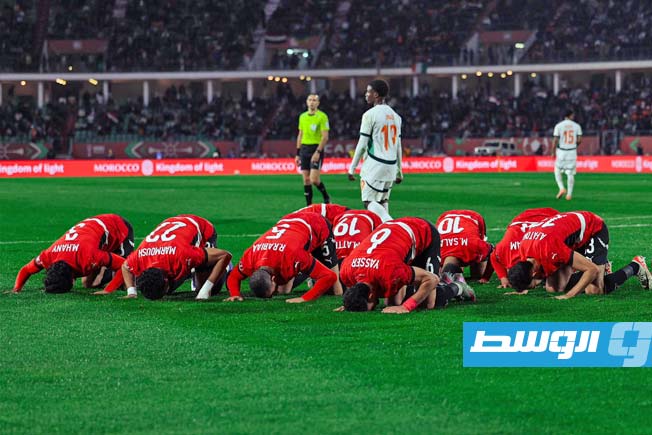
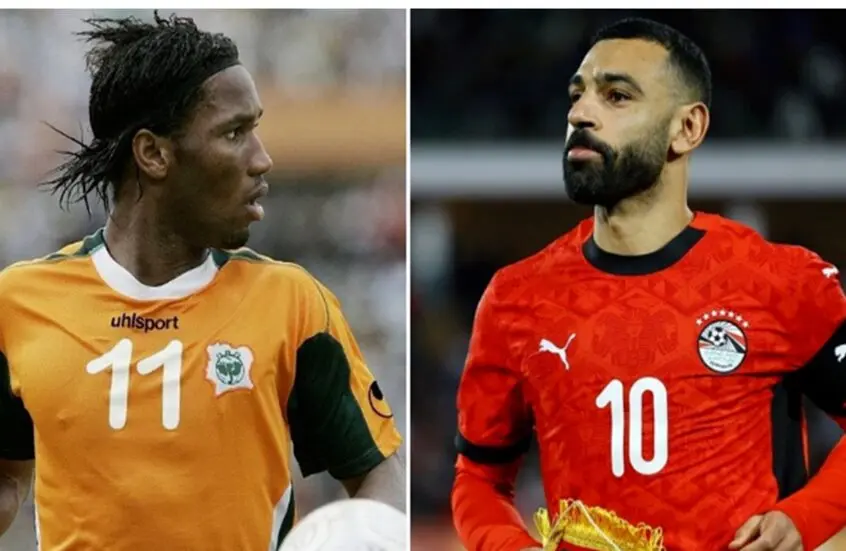
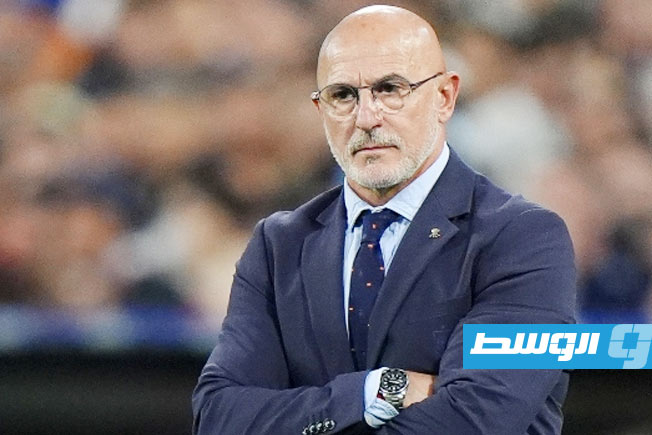
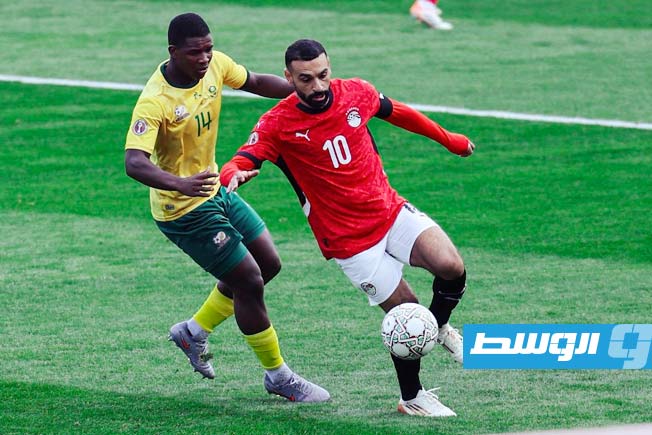
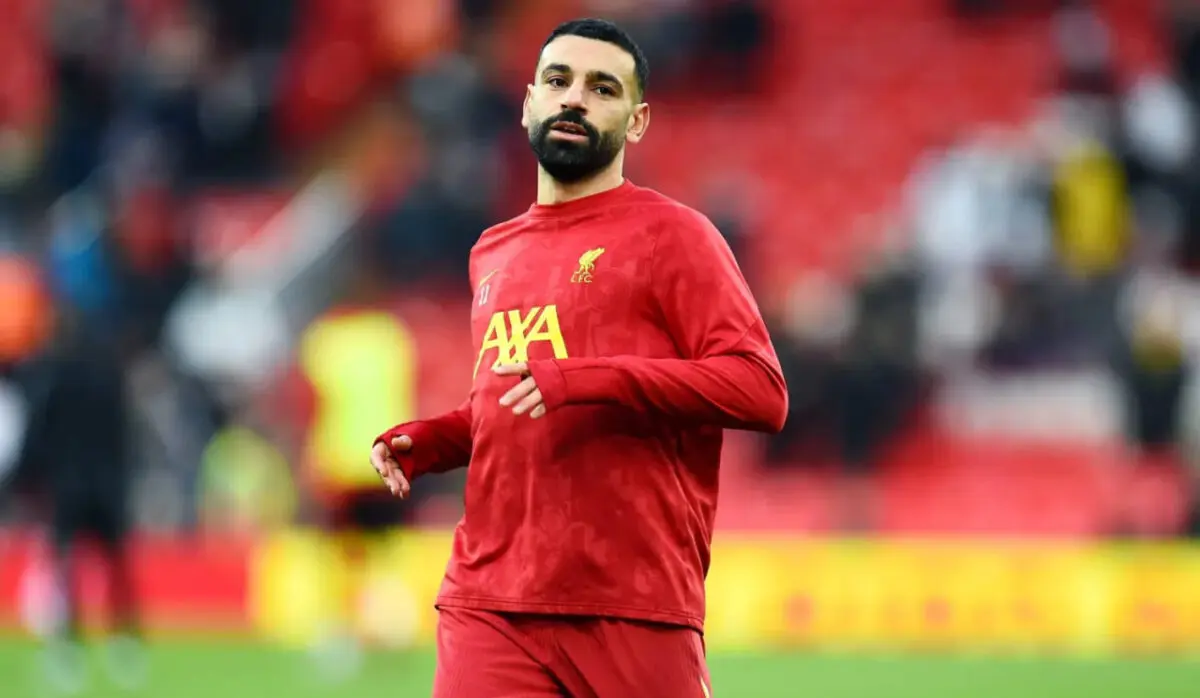
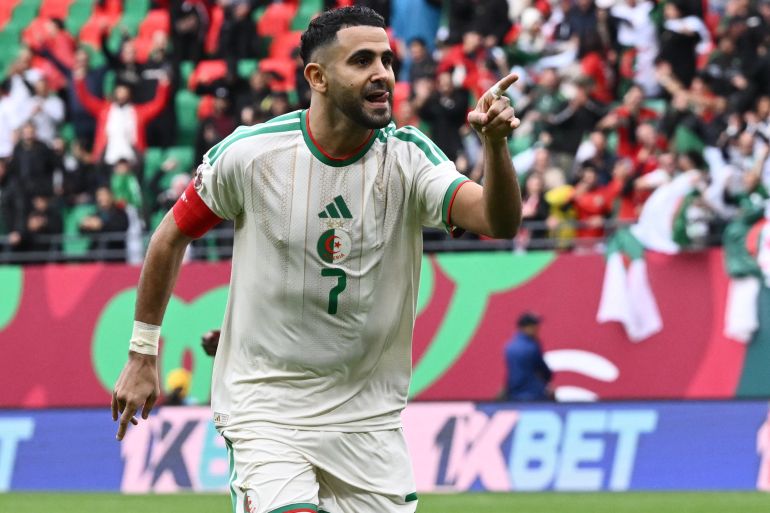
Egypt calls upon its historical experience and competes for an eighth title, led by its coach and its star player, alongside other key attackers. The participation and performance of its star player will define the team’s path in the tournament.
The Ivory Coast, the defending champion from the 2023 edition, aims to repeat the achievement but faces challenges after the absence of some of its key players.
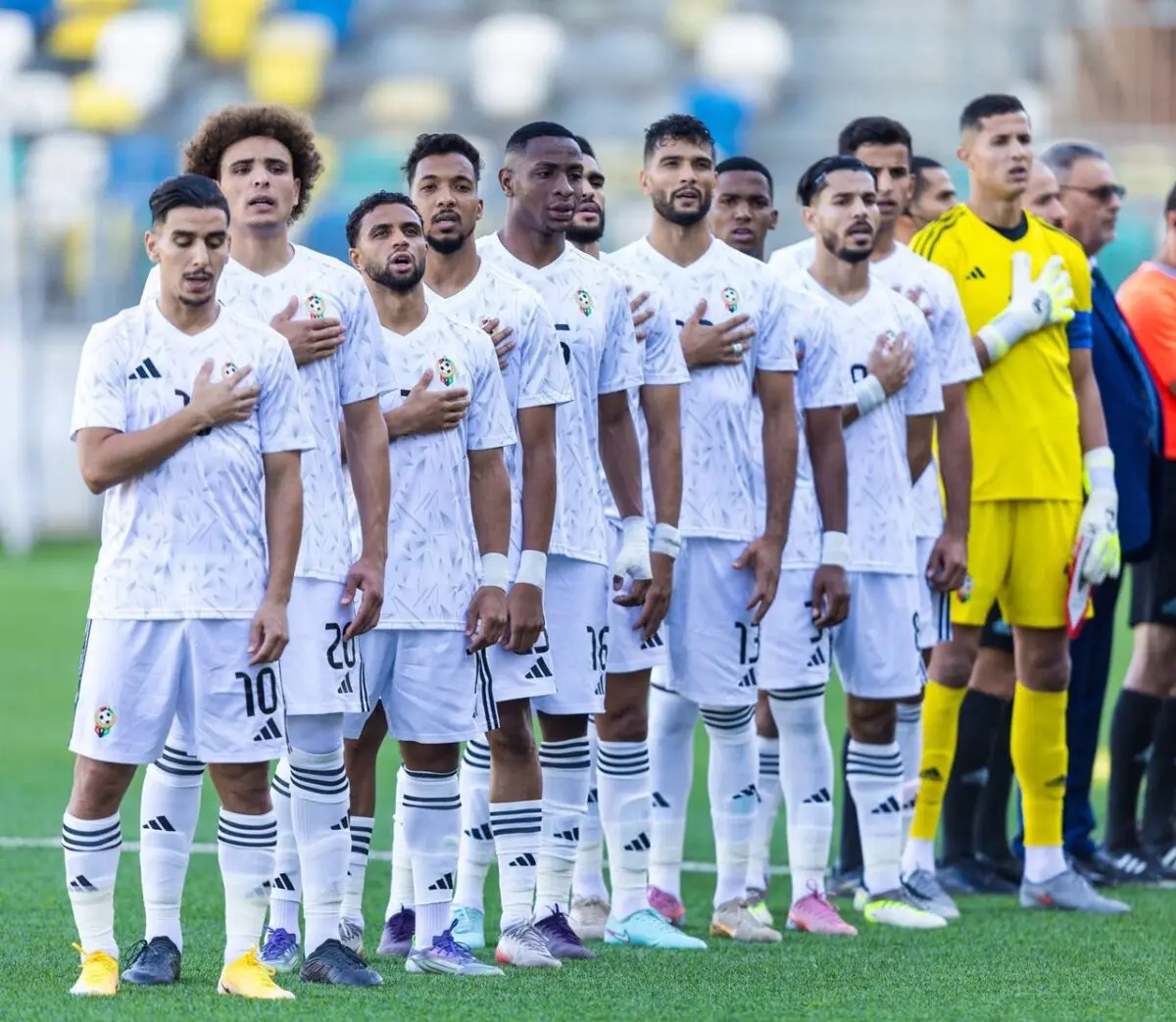
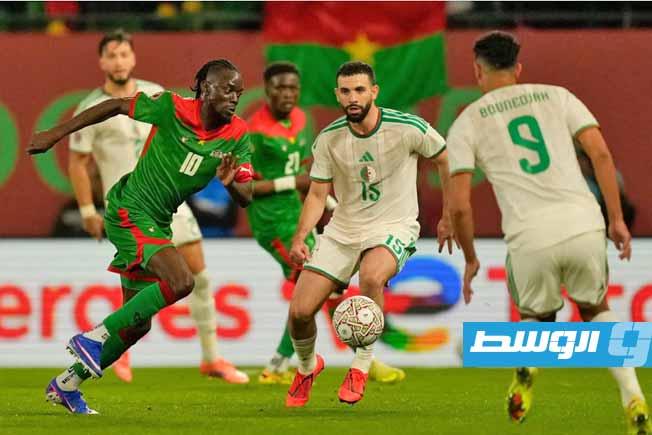
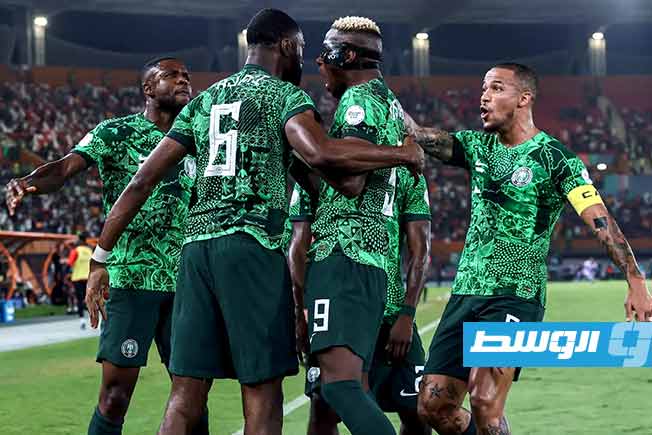
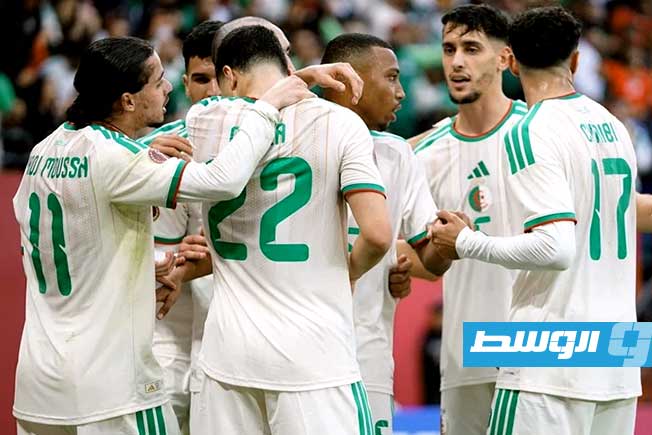
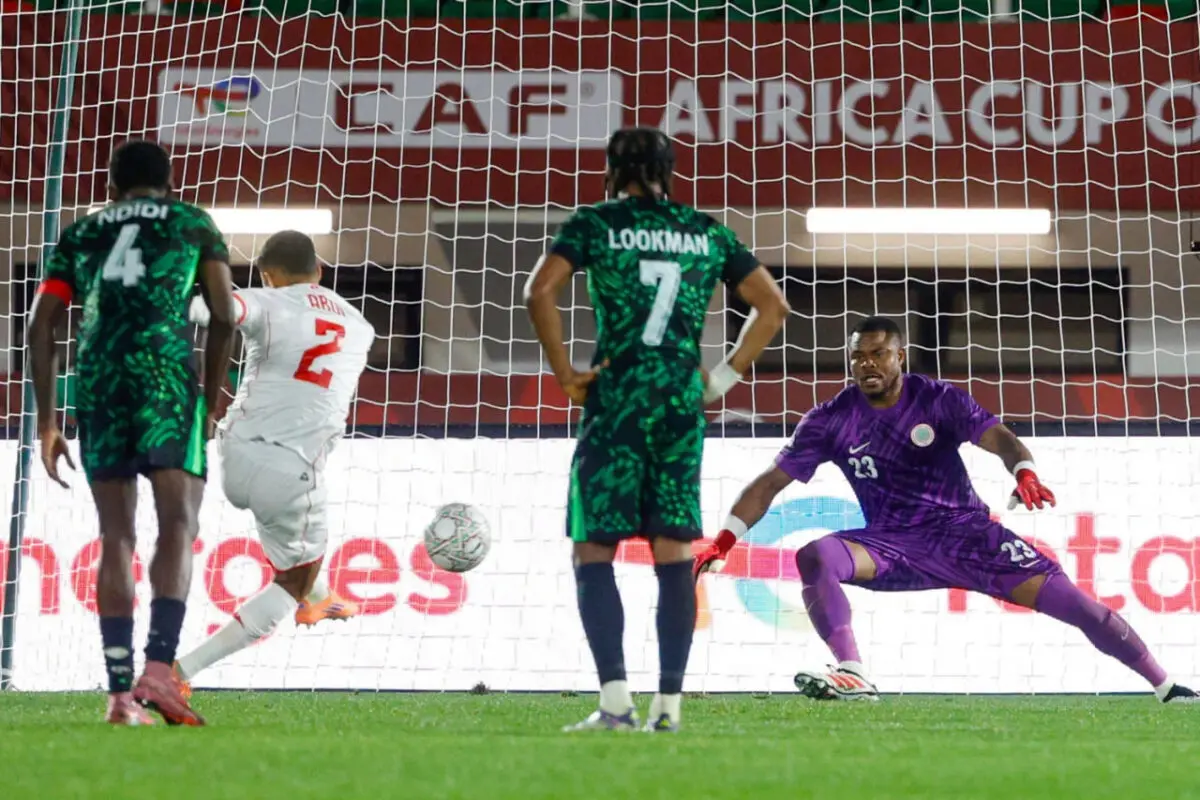
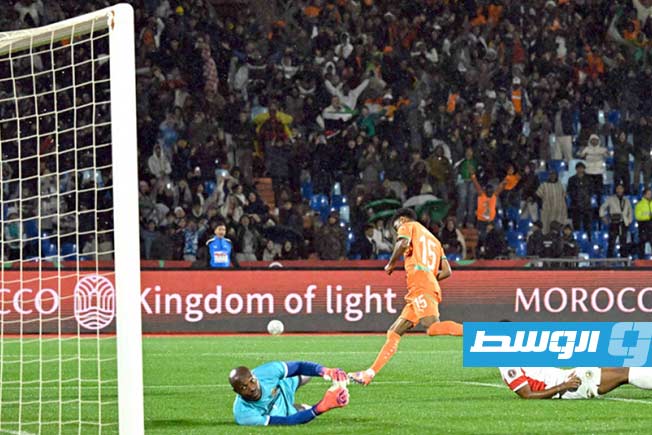
Algeria, Nigeria, and Cameroon remain formidable opponents, despite some early exits in previous editions. Algeria retains its solidity under the leadership of its coach.
Morocco forms an important platform to enhance its sporting stature on both the continental and international levels, following the achievements of its national teams in youth categories, women’s football, and the Arab Cup. This edition of the Africa Cup of Nations contributes to enhancing the Kingdom’s readiness to host the 2030 World Cup, proving its capacity for organization and excellence in major tournaments.
Morocco
Morocco is a North African country with a rich history shaped by indigenous Amazigh (Berber) cultures, Arab influence from the 7th century, and successive dynasties like the Almoravids and Almohads. Its cultural sites, such as the ancient city of Fez and the Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech, reflect this blend of Arab, Islamic, and Amazigh heritage. The country is also known for its well-preserved medieval medinas and historic kasbahs.
Atlas Lions
The Atlas Lions is the nickname for the Moroccan national football team, derived from the Barbary lion that historically inhabited the Atlas Mountains. The team’s history includes becoming the first African and Arab nation to reach a World Cup semi-final in 2022.
Africa Cup of Nations
The Africa Cup of Nations (AFCON) is the premier men’s international football competition in Africa, first contested in 1957. It was founded to foster unity and sporting excellence among African nations, with its history reflecting the continent’s post-colonial era and the growth of football as a major cultural force.
FIFA
FIFA (Fédération Internationale de Football Association) is the international governing body for association football, founded in Paris in 1904 to oversee international competition. It is best known for organizing the FIFA World Cup, a global tournament first held in 1904 to oversee international competition. It is best known for organizing the FIFA World Cup, a global tournament first held in 1930, which has become the world’s most widely viewed sporting event.
Spain
Spain is a country in southwestern Europe with a rich and diverse cultural history shaped by Roman, Moorish, and Christian influences. Its historical sites range from Roman aqueducts and Islamic palaces like the Alhambra to Gothic cathedrals and modernist architecture, reflecting centuries of complex social and political evolution.
Portugal
Portugal is a country in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula, with a rich history as a global maritime power during the Age of Discoveries in the 15th and 16th centuries. Its cultural heritage is marked by Manueline architecture, traditional Fado music, and historic sites like the Belém Tower and Jerónimos Monastery in Lisbon, which reflect its seafaring past.
South Africa
South Africa is a country located at the southern tip of the African continent, known for its diverse cultures, languages, and dramatic landscapes. Its modern history is profoundly shaped by colonialism and the institutionalized racial segregation of apartheid, which ended in 1994 with the establishment of a constitutional democracy. The country is renowned for sites like Robben Island, where Nelson Mandela was imprisoned, and the Cradle of Humankind, a UNESCO site containing significant hominid fossils.
Senegal
Senegal is a West African nation known for its rich cultural heritage and history as a center of several pre-colonial empires and later French colonial rule. It gained independence in 1960 and is renowned for its tradition of “Teranga” (hospitality), vibrant music like mbalax, and significant sites such as Gorée Island, a UNESCO World Heritage site that memorializes the Atlantic slave trade.
French league
The French league, commonly known as Ligue 1, is the top professional football division in France. It was founded in 1932 under the name National before being renamed Division 1 and later Ligue 1, with AS Saint-Étienne and Paris Saint-Germain among its most successful clubs.
Maghreb
The Maghreb is a region in North Africa encompassing the countries of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania. Historically, it was home to ancient Berber kingdoms, later became part of the Roman Empire, and was profoundly shaped by the Arab-Islamic conquests beginning in the 7th century. The term itself means “place of the setting sun” in Arabic, reflecting its position west of the Arab heartlands.
Egypt
Egypt, home to one of the world’s oldest civilizations, is famed for its ancient monuments along the Nile River, including the Pyramids of Giza and the Great Sphinx, which were built as tombs for pharaohs over 4,500 years ago. Its long history encompasses the Pharaonic, Ptolemaic, Roman, and Islamic periods, with Cairo later becoming a major center of the Arab world. Modern Egypt gained independence in 1922 and remains a pivotal cultural and political hub in the Middle East and North Africa.
Ivory Coast
The Ivory Coast, officially known as Côte d’Ivoire, is a West African nation whose history includes powerful pre-colonial kingdoms, French colonization from the late 19th century, and independence in 1960. A major cultural site is the Basilica of Our Lady of Peace in Yamoussoukro, which is one of the largest churches in the world and was completed in 1989. The country is also renowned for its diverse cultural traditions, including music genres like *coupé-décalé* and its status as one of the world’s leading producers of cocoa.
Algeria
Algeria is a North African nation with a rich history shaped by indigenous Berber cultures, successive empires, and a pivotal modern struggle for independence from France, achieved in 1962. It is home to diverse cultural sites, including the ancient Roman ruins of Timgad and Djémila, as well as the historic Casbah of Algiers, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Nigeria
Nigeria is a West African country with a rich history shaped by ancient kingdoms like the Nri and Benin, as well as the Yoruba city-states. It gained independence from British colonial rule in 1960 and is now Africa’s most populous nation, known for its diverse cultures, vibrant arts, and significant oil reserves.
Cameroon
Cameroon is a Central African country known for its diverse geography, ranging from beaches and rainforests to savannas and mountains. Historically, it was a German protectorate in the late 19th century before being divided into French and British administrative zones after World War I, achieving full independence in 1960. Its culture is exceptionally varied, with over 250 ethnic groups and linguistic influences from both French and English, making it one of Africa’s most culturally rich nations.
Arab Cup
The Arab Cup is a regional international football tournament contested by national teams from the Arab world, first organized in 1963. It has been held intermittently, with its most recent edition in 2021 serving as a test event for the FIFA World Cup in Qatar.
Kingdom
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a modern nation-state founded in 1932 by King Abdulaziz Al Saud, who unified the regions of the Arabian Peninsula. Its history is deeply rooted in the birthplace of Islam, with its territory containing the holy cities of Mecca and Medina, which have been central to Islamic faith and culture for over fourteen centuries.
2030 World Cup
The 2030 FIFA World Cup will be a unique, multi-continental event co-hosted by Spain, Portugal, and Morocco, with three opening matches also taking place in Uruguay, Argentina, and Paraguay. This format commemorates the tournament’s 100th anniversary, as the first World Cup was held in Uruguay in 1930.