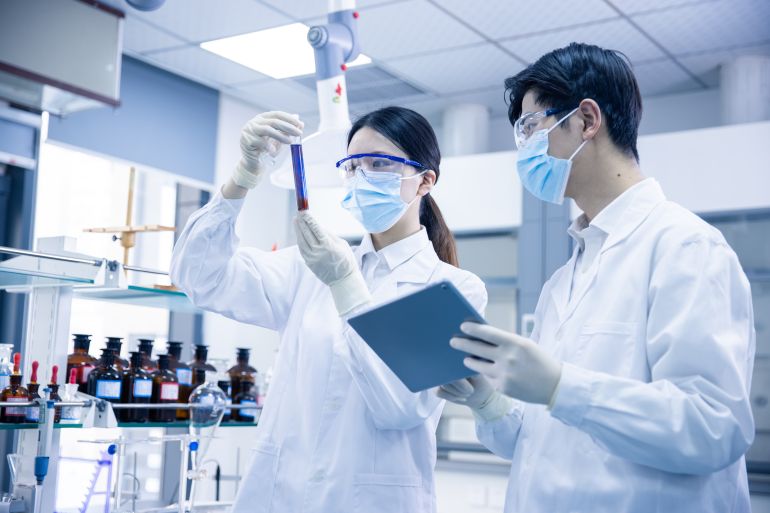
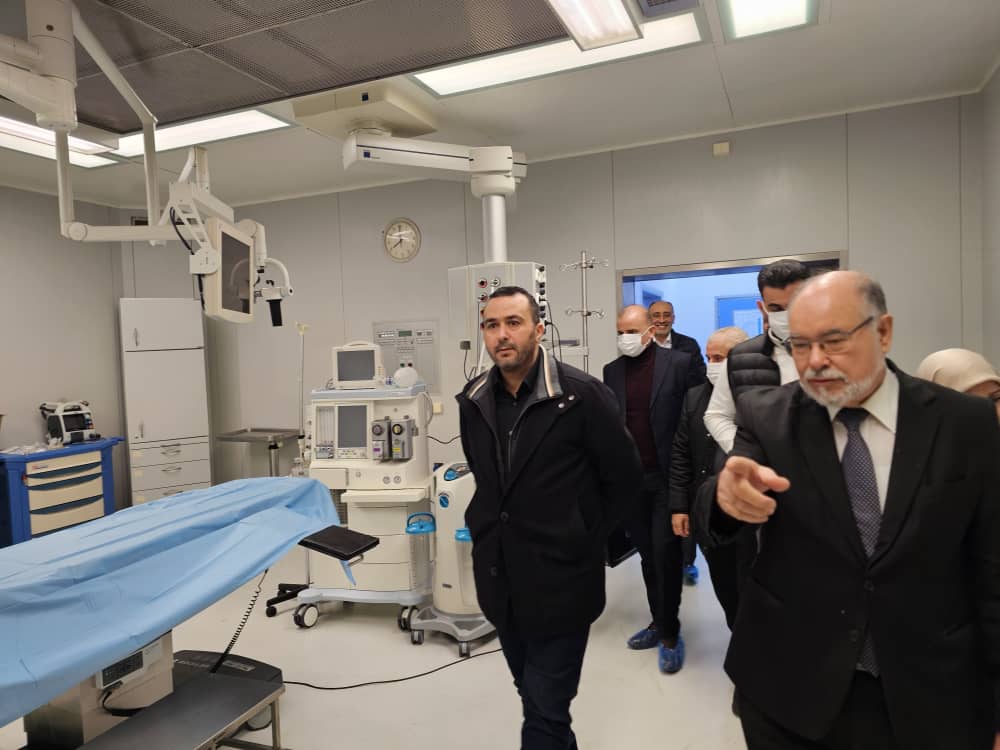
Tripoli, December 02, 2025 – The National Integrated Fruit Fly Control Project, affiliated with the Libyan Center for Biotechnology Research, organized a training course on the use of immunological techniques for detecting bacterial and viral diseases affecting plants.
The course covered the scientific foundations of plant diseases, the characteristics of pathogens, and immune response mechanisms, emphasizing the importance of the specific binding between antigens and antibodies in improving diagnostic accuracy.
It was also noted that serological techniques play a role in the early detection of plant pathogens, contributing to increased laboratory test efficiency and enhancing researchers’ capabilities in supporting plant disease prevention and control efforts.
…

National Integrated Fruit Fly Control Project
Here’s a breakdown of what such a project generally involves:
—
### **1. Objectives**
– **Reduce crop losses** caused by fruit fly infestations.
– **Minimize pesticide use** through integrated pest management (IPM).
– **Enhance market access** by meeting phytosanitary standards for export.
– **Increase farmer awareness** and build capacity for sustainable control.
– **Establish monitoring and surveillance** systems for early detection.
—
### **2. Key Components**
– **Monitoring & Surveillance:**
Use of traps, lures, and field surveys to track fruit fly species and population levels.
– **Control Measures:**
– **Biological control:** Introduction of natural enemies (parasitoids like *Fopius arisanus*).
– **Cultural control:** Field sanitation, removal of infested fruits, crop rotation.
– **Chemical control:** Targeted bait sprays and male annihilation techniques (MAT).
– **Physical/Mechanical control:** Use of fruit bagging and nets.
– **Sterile Insect Technique (SIT):** Releasing sterilized male flies to reduce reproduction.
– **Quarantine & Regulatory Support:**
Restricting movement of infested produce; certification for pest-free areas.
– **Research & Development:**
Studying fruit fly behavior, resistance, and new control methods.
– **Farmer Training & Extension Services:**
Workshops, demonstrations, and information dissemination.
—
### **3. Expected Outcomes**
– Reduced infestation rates and higher crop yields.
– Decreased reliance on broad-spectrum insecticides.
– Establishment of pest-free zones for export crops.
– Improved farmer income and food security.
– Sustainable long-term management of fruit fly populations.
—
### **4. Examples Worldwide**
– **Australia:** *National Fruit Fly Strategy* (prevention, eradication, management).
– **India:** *National Horticulture Mission* includes fruit fly management components.
– **South Africa:** *Fruit Fly Action Plan* for key export fruits.
– **European Union:** Coordination across member states for *Ceratitis capitata* (Mediterranean fruit fly).
—
### **5. Challenges**
– High cost of implementation and maintenance.
– Need for continuous farmer cooperation.
– Risk of pesticide resistance.
– Climate change affecting pest distribution.
—
If you’re looking for details on a **specific country’s project**, let me know, and I can provide more targeted information.
Libyan Center for Biotechnology Research
### Overview
The **Libyan Center for Biotechnology Research (LCBR)** is a leading national scientific institution in Libya, dedicated to research, development, and application of biotechnology. Its primary mission is to address local and regional challenges in healthcare, agriculture, environment, and industry through advanced biotechnological solutions.
### Key Details
* **Arabic Name:** المركز الليبي لبحوث التقنية الحيوية
* **Common Acronym:** LCBR
* **Location:** Tripoli, Libya.
* **Affiliation:** It typically operates under the umbrella of the Libyan government’s higher education or scientific research authority (often linked to the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research).
### Core Objectives & Functions
The center’s work generally focuses on:
1. **Scientific Research:** Conducting fundamental and applied research in various biotechnology fields.
2. **Human Development:** Training scientists, technicians, and students to build national expertise.
3. **Public Service:** Providing specialized diagnostic services, consulting, and technical support to public and private sectors.
4. **Collaboration:** Partnering with national and international research institutions and universities.
### Typical Research Departments/Areas
While its structure may evolve, the LCBR commonly houses laboratories and research groups in areas such as:
* **Medical Biotechnology:** Research on infectious diseases, cancer, genetic disorders, vaccine development, and diagnostic tools.
* **Agricultural Biotechnology:** Improving crop resistance, developing bio-fertilizers, and plant tissue culture for food security.
* **Environmental Biotechnology:** Waste treatment, bioremediation of polluted sites, and biodiversity studies.
* **Industrial Biotechnology:** Enzyme technology, fermentation processes, and production of bio-based products.
* **Molecular Biology & Genetics:** Core services like DNA sequencing, genetic fingerprinting, and genomic studies.
### Importance and Context
* **National Strategic Asset:** The LCBR is crucial for Libya’s efforts to build a knowledge-based economy and achieve self-reliance in critical areas like health and agriculture.
* **Challenges:** Like many institutions in Libya, the LCBR has faced significant operational challenges due to political instability, conflict, and funding constraints over the past decade. This has impacted its infrastructure, research continuity, and international collaborations.
* **Future Potential:** It remains a vital institution with the potential to contribute substantially to Libya’s post-conflict reconstruction and development by providing scientific solutions to pressing national problems.
### Contact & Further Information
For the most current information—such as exact leadership, active projects, or partnership opportunities—it is best to search for recent publications or official announcements from Libyan government portals related to scientific research.
**In summary, the Libyan Center for Biotechnology Research is the cornerstone of Libya’s national biotechnology strategy, aiming to harness modern biological sciences for the country’s development, despite operating in a challenging environment.**