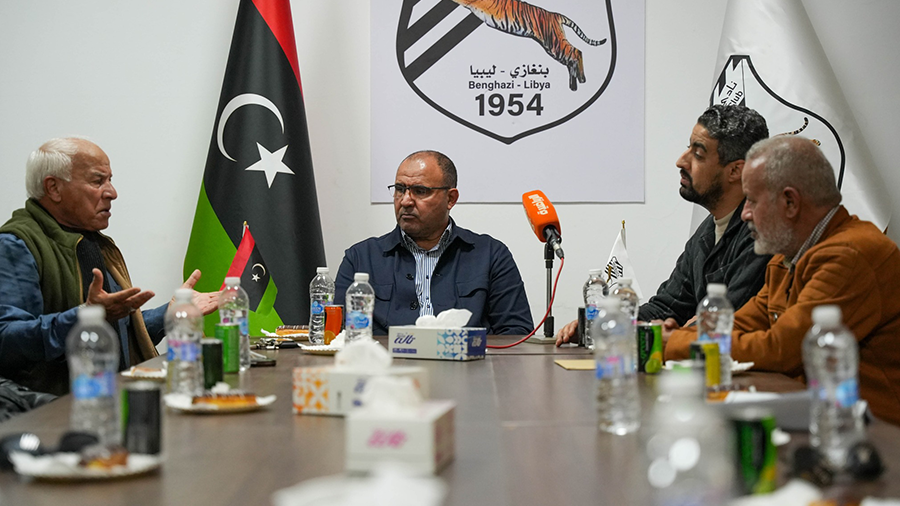
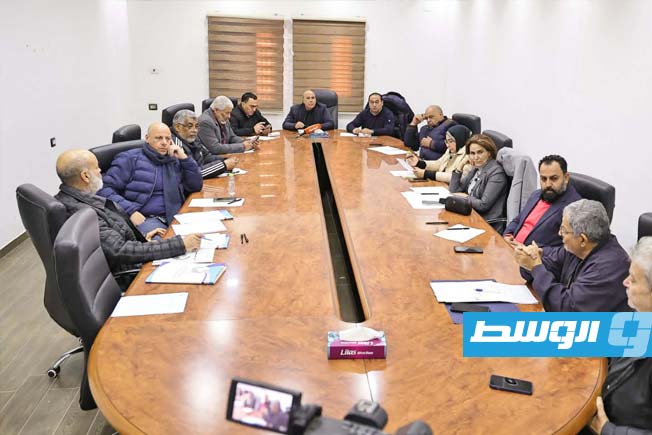
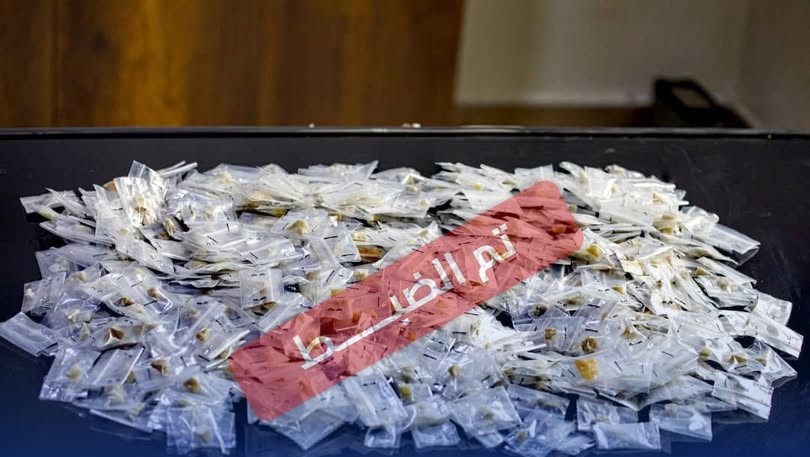
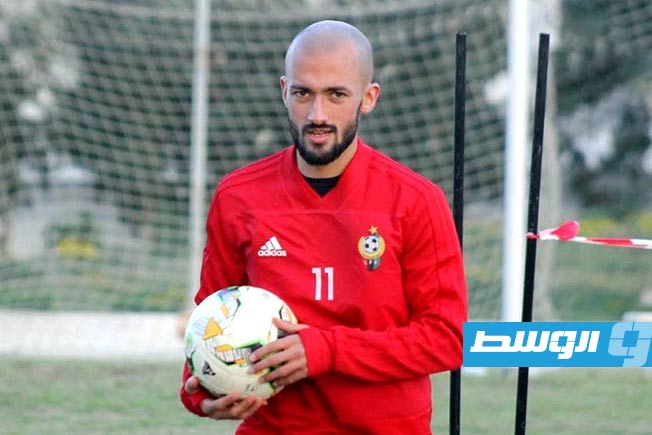
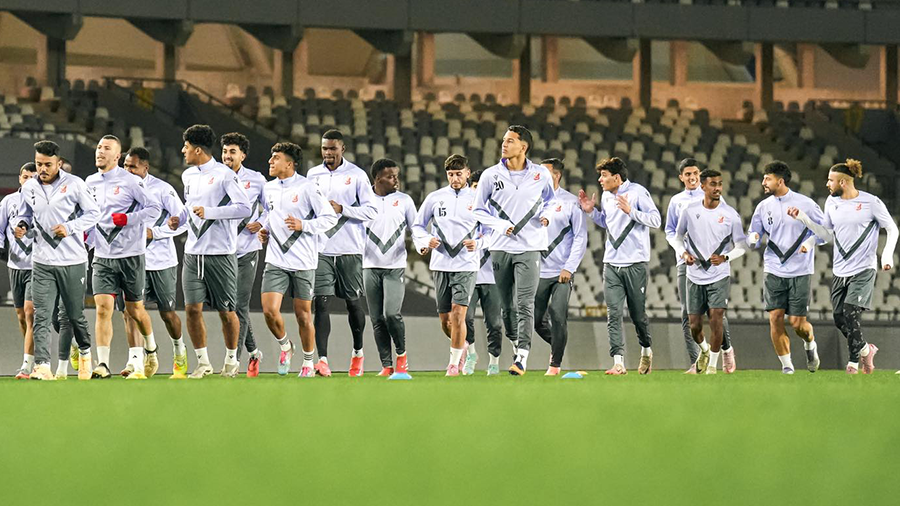
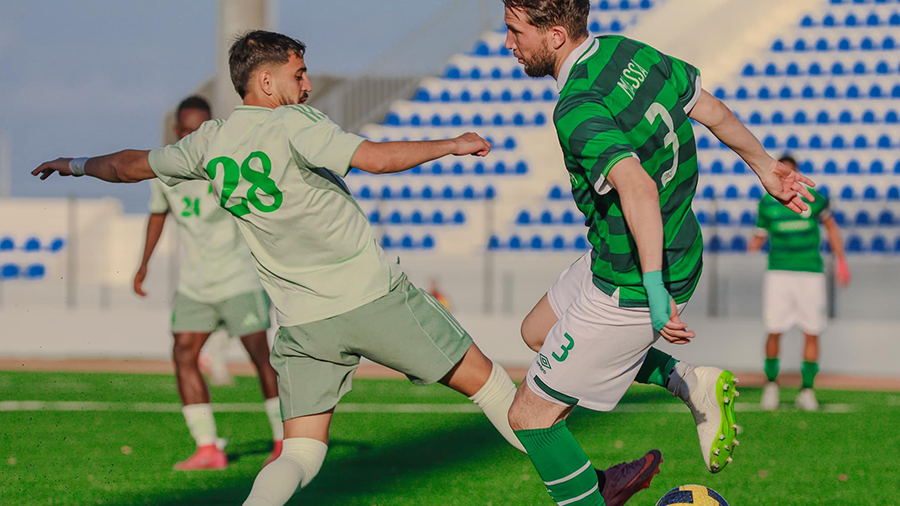
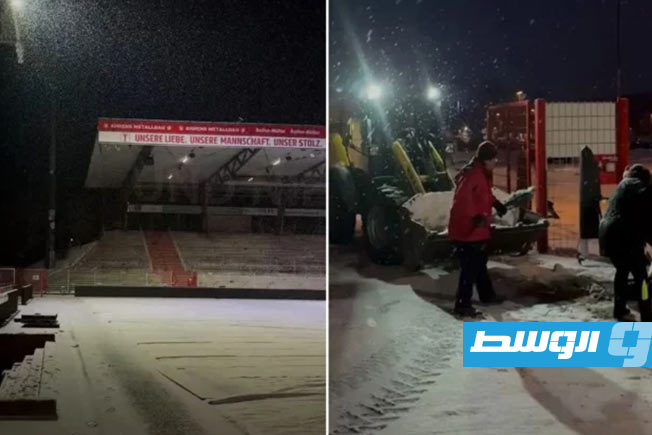
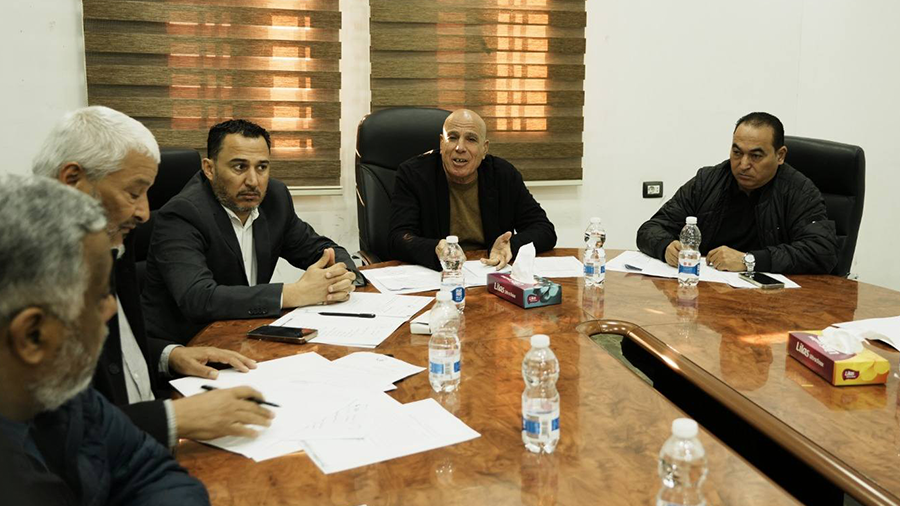
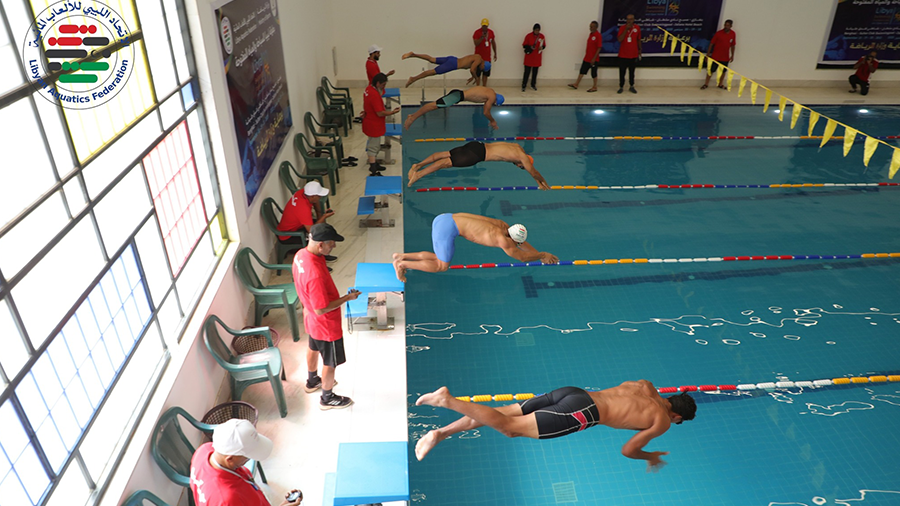
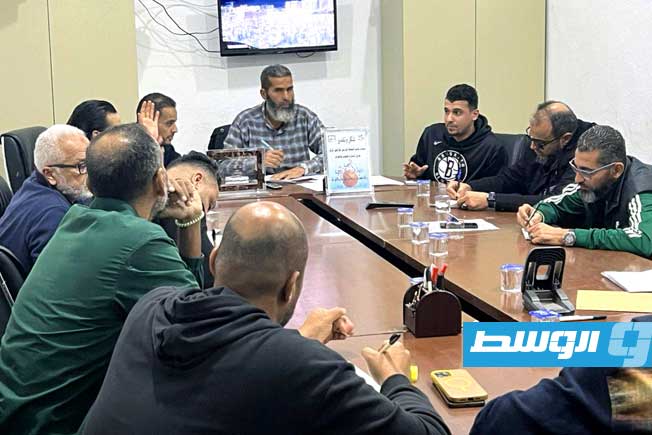
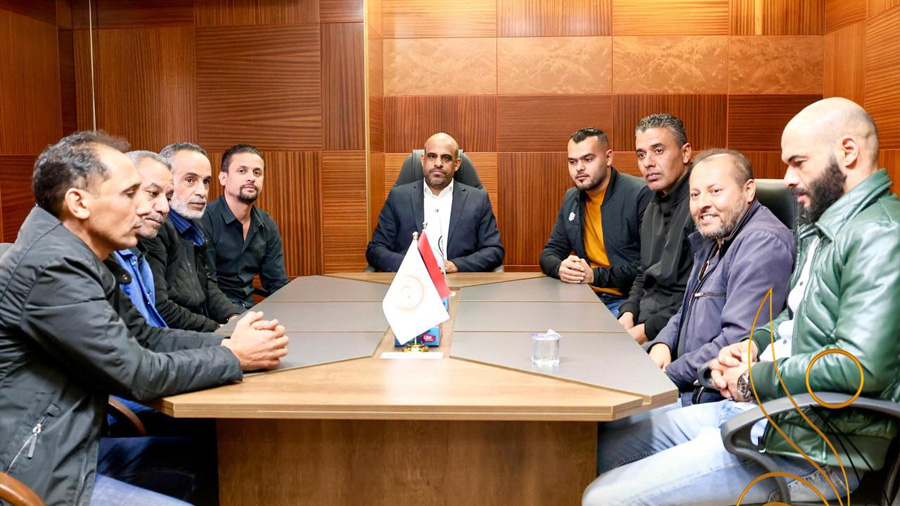
Thirteen clubs from the Premier League’s third and fourth groups announced they will not participate in the fourth round if they do not receive appropriate financial support.
The Al-Tahadi Club hosted a meeting of the clubs demanding financial support, represented by 13 clubs from the Eastern Region Premier League: Al-Tahadi, Al-Ittihad Al-Askari, Al-Sadaka, Darnes, Al-Hilal, Al-Burooq, along with Al-Suqoor, Khalij Sirt, Al-Muruj, Al-Afriqi, Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya, Al-Andalus, and Al-Anwar.
The meeting focused on preparing an official appeal to the authorities to emphasize the necessity of supporting the clubs and providing them with the necessary aid.
It was also agreed during the meeting that if the delay or non-payment of financial support continues, the fourth week will be set as the date for the clubs to stop their sports activities. This is due to the financial burdens and operational difficulties hindering their ability to continue.
Premier League
The Premier League is the top level of the English football league system, founded in 1992 when clubs in the Football League First Division broke away to capitalize on lucrative television rights deals. It has since grown into one of the world’s most popular and commercially successful sports leagues, known for its global audience and competitive nature.
Al-Tahadi Club
Al-Tahadi Club is a prominent cultural and social center in Libya, originally established during the Italian colonial period in the 1930s. It has historically served as a key venue for intellectual gatherings, artistic events, and community activities in Tripoli.
Al-Tahadi
Al-Tahadi is a prominent sports stadium located in Benghazi, Libya, originally constructed in the 1960s. It is historically significant as the home ground for the Al-Nasr sports club and has hosted numerous major football matches and national events.
Al-Ittihad Al-Askari
Al-Ittihad Al-Askari is a historic military fortress located in the city of Tripoli, Libya. It was originally constructed during the Ottoman period and later served as a key barracks and administrative center under Italian colonial rule. The site remains a significant landmark representing Libya’s layered history of foreign influence and military architecture.
Al-Sadaka
Al-Sadaka is a historic mosque located in the city of Mosul, Iraq, believed to have been originally built during the reign of the Umayyad Caliph Marwan II in the 8th century. It is traditionally associated with a site where Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab is said to have prayed during the early Muslim conquests, giving it significant religious and historical importance in the region.
Darnes
Darnes is a historic coastal fortress located in the city of Cartagena, Spain, originally constructed in the 18th century during the reign of King Charles III. Its primary purpose was to defend the city’s important naval base and harbor from potential attacks. Today, it stands as a well-preserved example of military architecture from that period.
Al-Hilal
Al-Hilal is a professional football club based in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, founded in 1957. It is one of Asia’s most successful clubs, with a record number of Saudi Professional League titles and Asian Champions League victories. The club has a deep-rooted rivalry with Al-Nassr and is historically associated with the city and royal family of Riyadh.
Al-Burooq
Al-Burooq is a historical and cultural site in Saudi Arabia, traditionally identified as the location where the Prophet Muhammad changed his mount (the Buraq) during the Night Journey (Isra’ and Mi’raj). It is marked by a mosque in the historic region of Hejaz, serving as a significant landmark in Islamic tradition.
Al-Suqoor
Al-Suqoor is a historic fortress located in the Asir Region of southwestern Saudi Arabia, known for its distinctive stone and clay construction. It served as a defensive stronghold and administrative center for the local tribes, reflecting the traditional architectural style of the region. Its history is intertwined with the tribal conflicts and the consolidation of power in the Asir highlands over centuries.
Khalij Sirt
Khalij Sirt, also known as the Gulf of Sirte, is a large body of water on the northern coast of Libya. Historically, it has been a significant maritime region since antiquity, notably forming part of the Mediterranean sea routes of the Phoenician and Roman empires. In modern history, it was the site of naval confrontations during World War II and later saw disputes over territorial waters under the Libyan government of Muammar Gaddafi.
Al-Muruj
Al-Muruj is a historical and cultural site located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, known for its vast fields of rocky desert and ancient rock art. The area contains thousands of archaeological inscriptions and carvings dating back thousands of years, depicting scenes of daily life, animals, and rituals from prehistoric and early Islamic periods. It serves as an important open-air museum that reflects the deep historical and cultural heritage of the central Arabian Peninsula.
Al-Afriqi
“Al-Afriqi” is a historical mosque and cultural complex located in Cairo, Egypt, originally constructed in the 10th century during the Fatimid Caliphate. It served as a significant center for Islamic learning and worship, reflecting the architectural and spiritual heritage of early Islamic Egypt.
Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya
Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya is a significant cultural and social center located in the city of Ajdabiya, Libya. It historically served as a key gathering place for community events, discussions, and political dialogue, particularly during the 2011 Libyan revolution. The site symbolizes local unity and has been a focal point for civic engagement in the region.
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus refers to the regions of the Iberian Peninsula under Muslim rule between 711 and 1492 CE, a period marked by significant cultural, scientific, and architectural flourishing. This era saw the construction of iconic sites like the Great Mosque of Córdoba and the Alhambra palace complex, and it was characterized by periods of relative religious coexistence among Muslims, Christians, and Jews. Its history ended with the completion of the Christian Reconquista in 1492.
Al-Anwar
Al-Anwar is a historic mosque located in Cairo, Egypt, originally built in the 15th century during the Mamluk Sultanate. It is known for its distinctive architectural style and has served as a significant religious and educational center in the Islamic world for centuries.
Eastern Region
The Eastern Region is one of Saudi Arabia’s 13 provinces, historically significant as the location of the first commercial oil discovery in the country at Dammam Well No. 7 in 1938. It is home to a rich cultural heritage, including the ancient Dilmun civilization and the modern hub of Dhahran, blending its deep historical roots with its central role in the global energy industry.