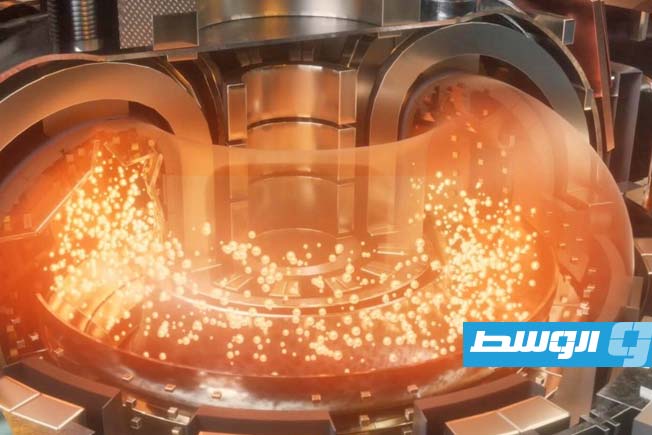
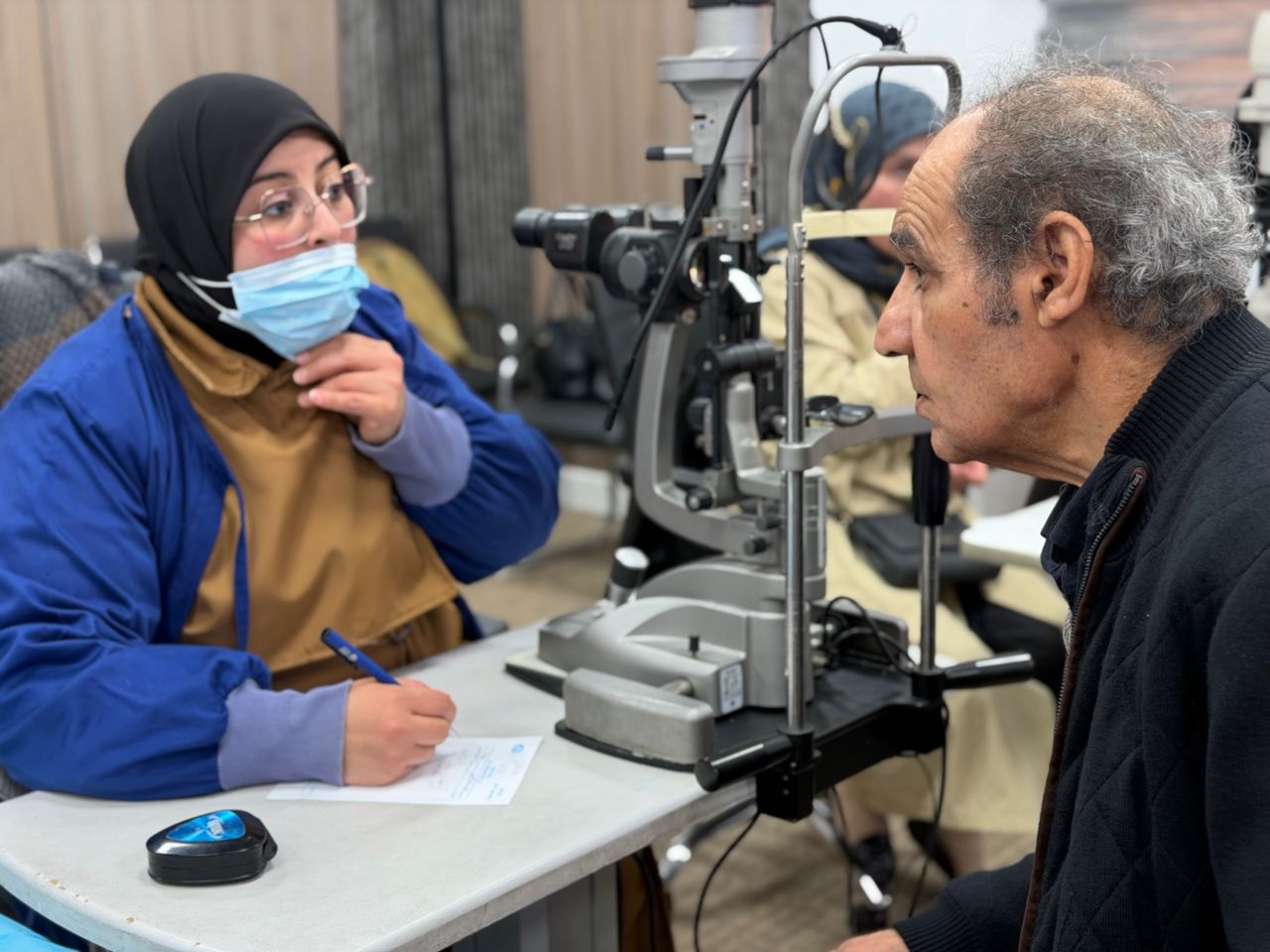
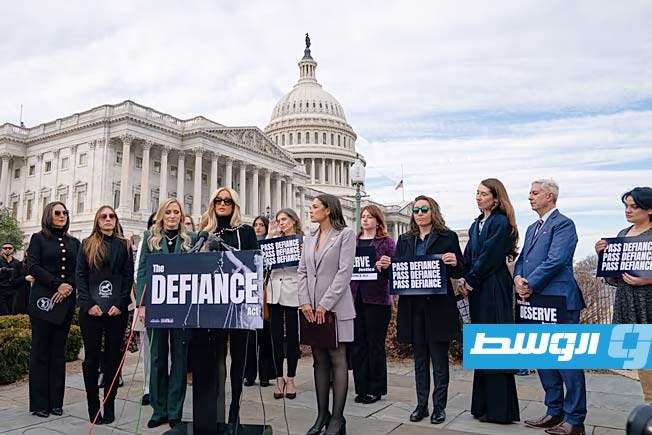
Chinese researchers have achieved a significant scientific breakthrough in the field of nuclear fusion, successfully overcoming a long-standing practical limitation on fusion reactor performance known as the “Greenwald limit” within the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST).
The Greenwald limit is a practical ceiling for plasma density inside tokamak reactors. Exceeding this limit often leads to plasma instability and sudden collapse, posing risks to reactor components. For decades, this limit has been considered a given in the design and operation of fusion reactors, according to a published study.
However, new experiments have shown that precise control over how plasma forms and interacts with the reactor walls can push the system into what physicists call a “density-limit-free regime.” This concept is based on reducing negative interactions between the plasma and the reactor walls during the initial operational phase.
The team started from the hypothesis that the density limit is heavily influenced by plasma-wall interactions when the reactor starts up.
– Video: NASA mission captures unprecedented footage of massive solar flares
– US laboratory announces achieving ‘historic progress’ in nuclear fusion
– Japanese companies design robots to clean nuclear power plants
Modifying Plasma Behavior
To achieve this, researchers precisely adjusted the fuel gas pressure during startup, along with adding a special heating pulse known as “Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating.”
This method helped modify the behavior of the plasma at its edge, significantly reducing the influx of atomic impurities from the reactor walls into the plasma. These impurities typically cause energy loss and plasma cooling.
As a result, the team was able to achieve plasma densities approximately 65% higher than the traditional Greenwald limit.
While this does not mean density limits have disappeared entirely, it confirms that the Greenwald limit is not a fundamental physical barrier but can be overcome by improving operational methods.
The results indicate a practical and scalable path for extending density limits in tokamak reactors and future fusion devices.