Although raw and cooked vegetables “offer unique health benefits,” most people believe that “raw vegetables are best,” even though there are “additional nutritional benefits to some varieties when cooked properly.” The most important benefits include:
Making some nutrients more available. Research published in 2022 indicated that “cooking vegetables and legumes at home is important for preserving nutritional quality and reducing nutrient loss.”
The role of cooking in reducing calcium oxalate. According to a 2005 study, about 75% of kidney stones “are composed of water-soluble calcium oxalate,” which is found in high levels in most raw vegetables. Cooking processes—especially steaming—reduce their levels by “30 to 87%.”
It is true that some vitamins and minerals begin to break down when vegetables are cooked due to their sensitivity to heat, but cooking vegetables like carrots, tomatoes, peas, leafy greens, mushrooms, and onions can improve their nutritional value and make it easier for your body to absorb their nutrients.
Not to mention that cooking vegetables “can make them tastier by softening them and imparting a distinctive flavor, which increases the likelihood of eating more of them to meet your daily needs.” Here are the top 7 vegetables experts recommend cooking:
-
Carrots
Cooked carrots provide more nutrients than raw carrots.
Carrots are rich in carotenoids, plant pigments that give them their orange color. They are known for their antioxidant properties that protect cells from damage and are linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and some cancers.
The body also converts them into vitamin A, which supports eye health and boosts the immune system.
Cooking carrots increases the availability of these carotenoids, helping the body absorb a greater amount. Research published in 2020 found that “beta-carotene absorption was 6.5 times higher in cooked carrots compared to raw carrots.”
-
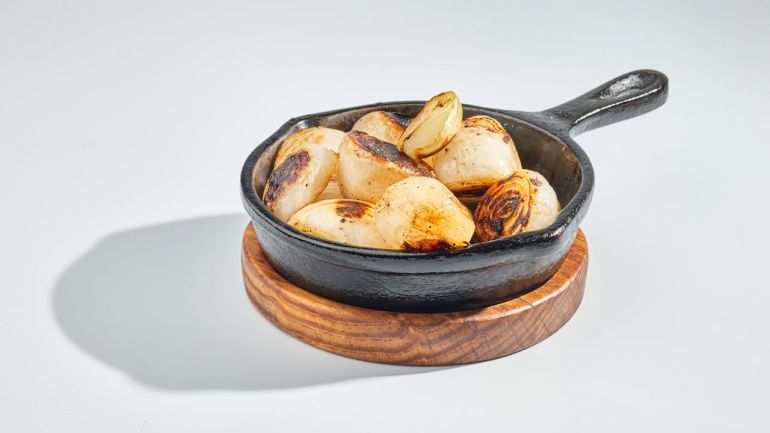
Onions
Onions are known for their strong flavor and pungent smell that causes tears, two factors that make eating them raw less appealing. In contrast, “cooking increases the availability of quercetin found in onions, which has anti-inflammatory benefits.” Grilling or sautéing onions can lead to a 7% to 25% increase in free quercetin content.

-
Mushrooms
Mushrooms are vegetables rich in antioxidants. Their nutritional value and antioxidant activity increase when quickly steamed or microwaved. It should be noted that “cooking them for long periods may reduce their benefits.”
-
Asparagus
Asparagus is a tough vegetable rich in antioxidants, usually served cooked to become tender and easier to eat. To preserve its vitamin C content, it is recommended to choose “a quick cooking method, such as steaming or stir-frying.”

-
Dark Leafy Greens
Most dark leafy greens, such as spinach and chard, may be better for your health after cooking. “The cooking process helps reduce oxalates and makes calcium and iron more beneficial for the body.”
Although leafy greens lose a lot of vitamin C when cooked, the cooking process may increase their absorption of beta-carotene and vitamins E and K. To preserve the maximum amount of vitamin C, it is recommended to quickly sauté