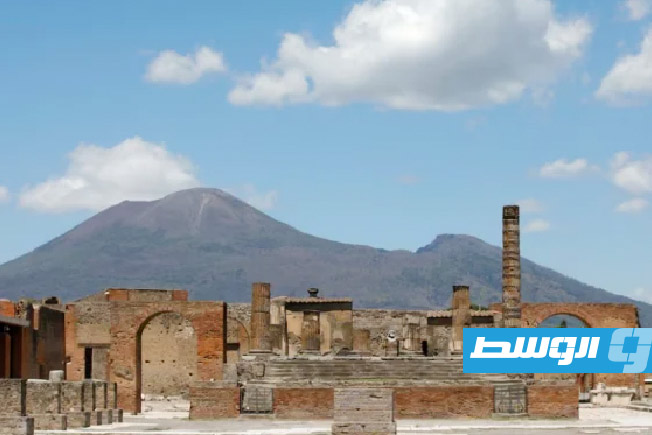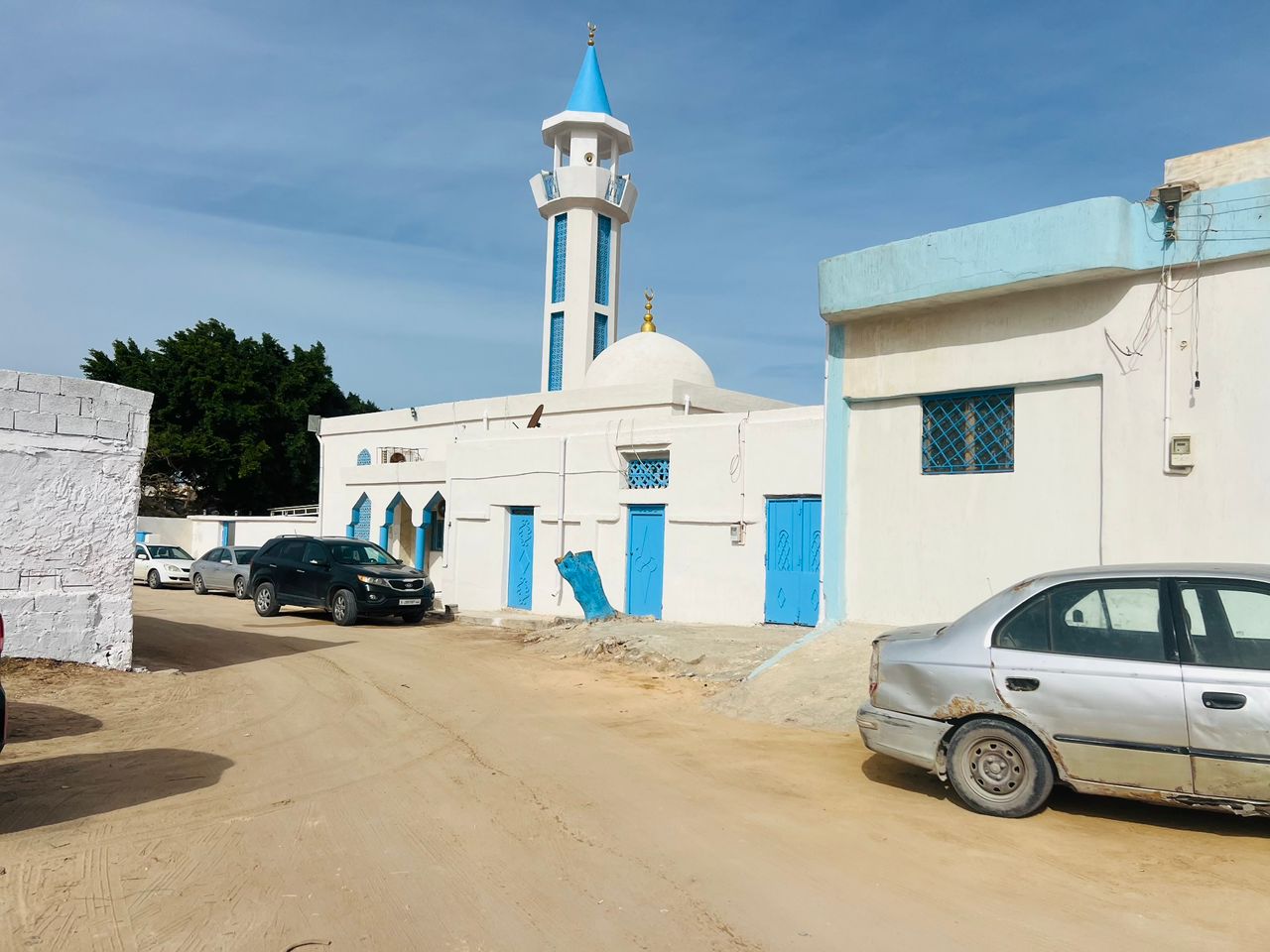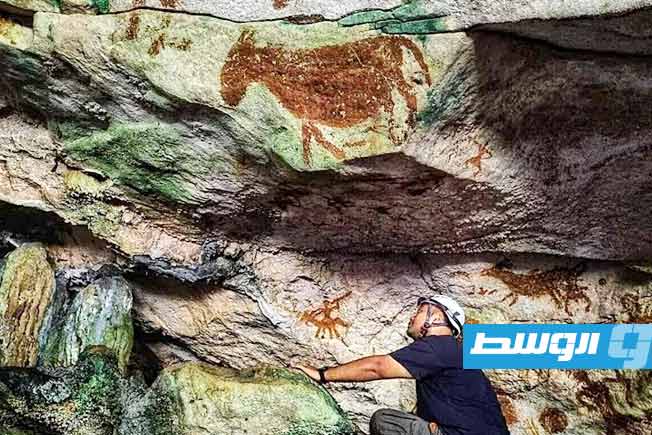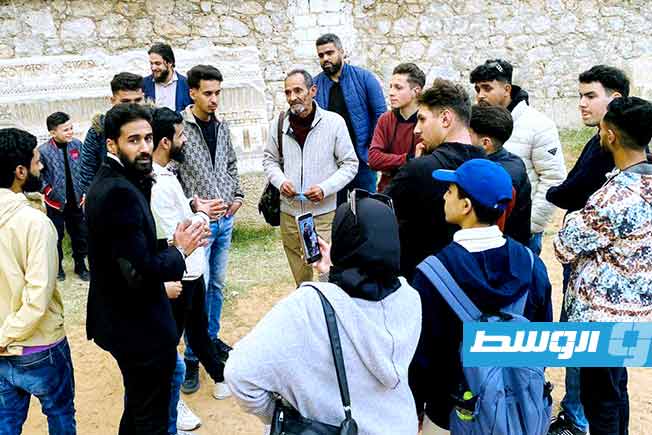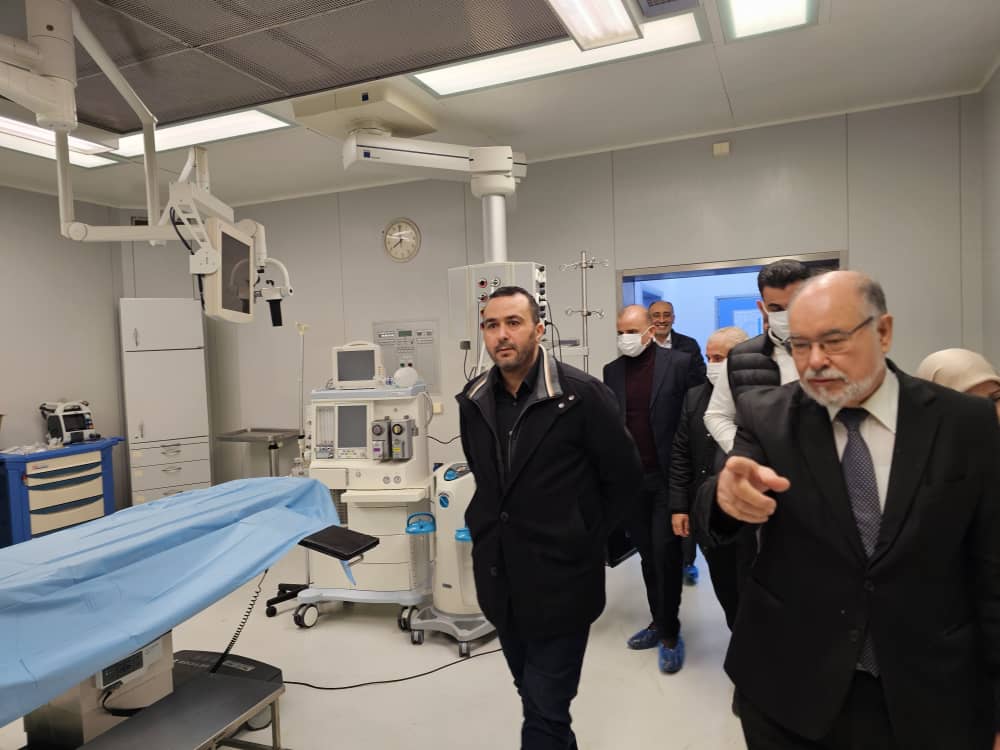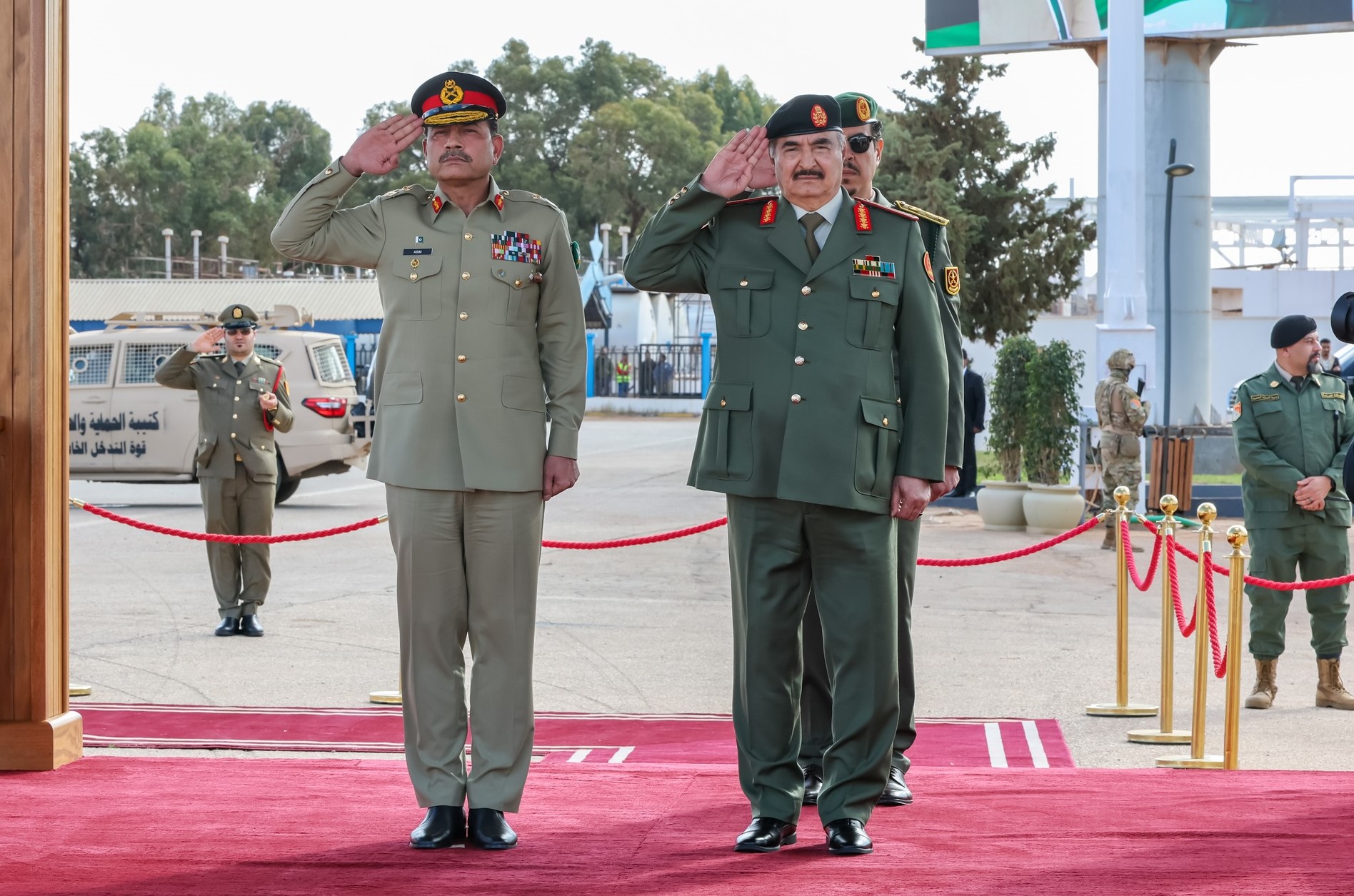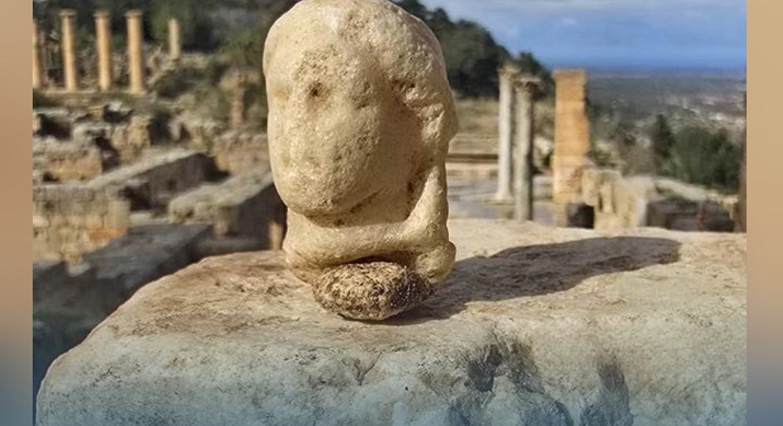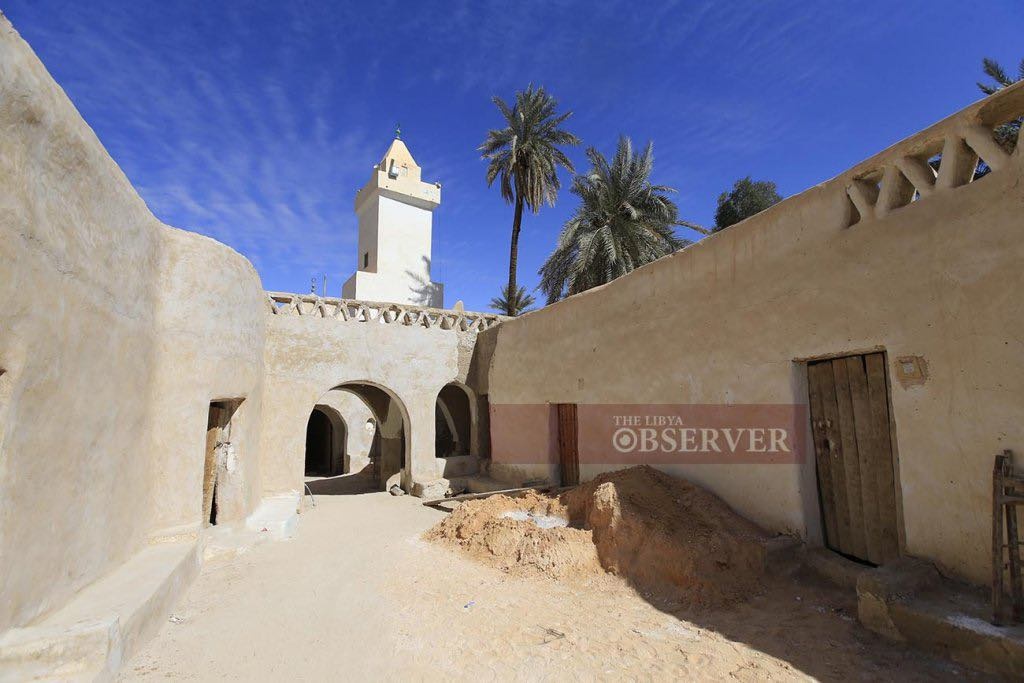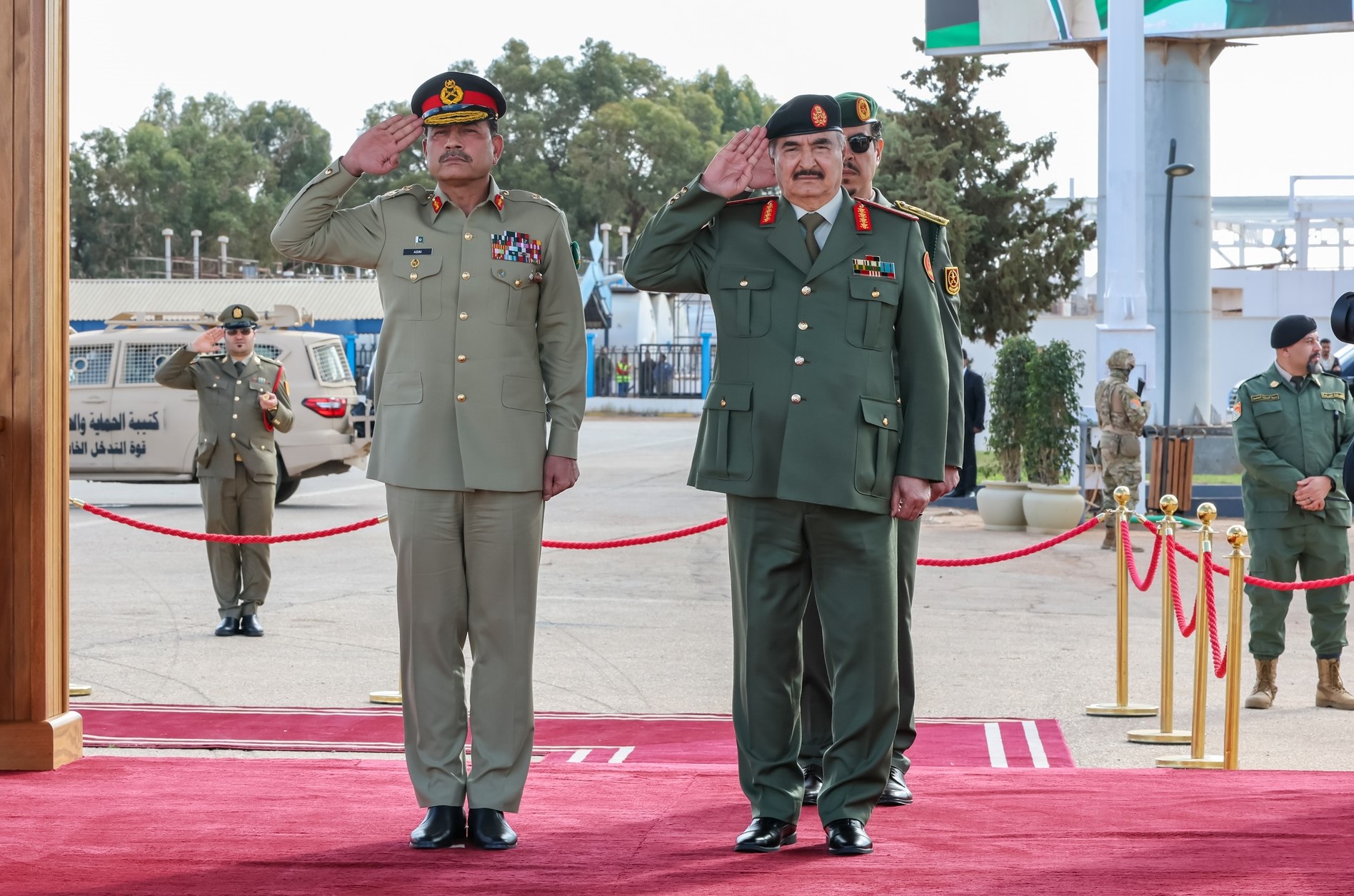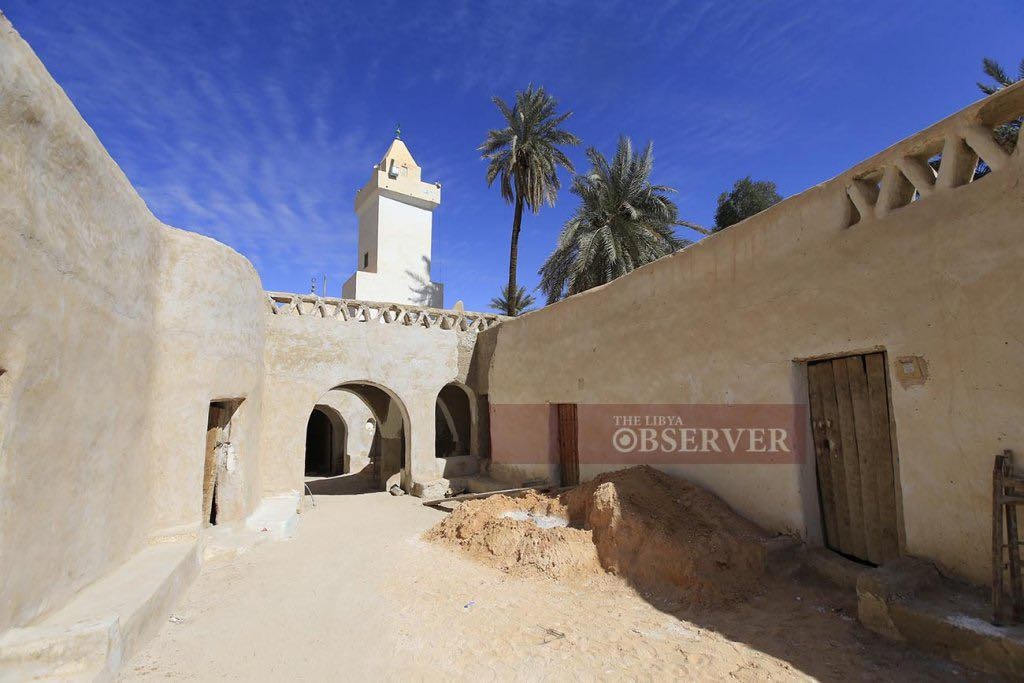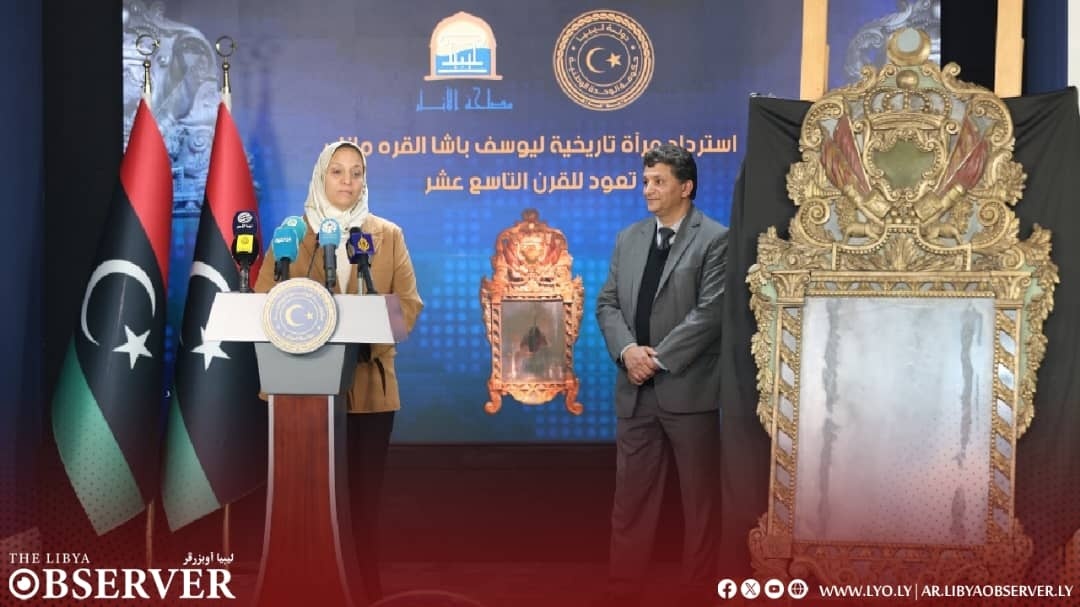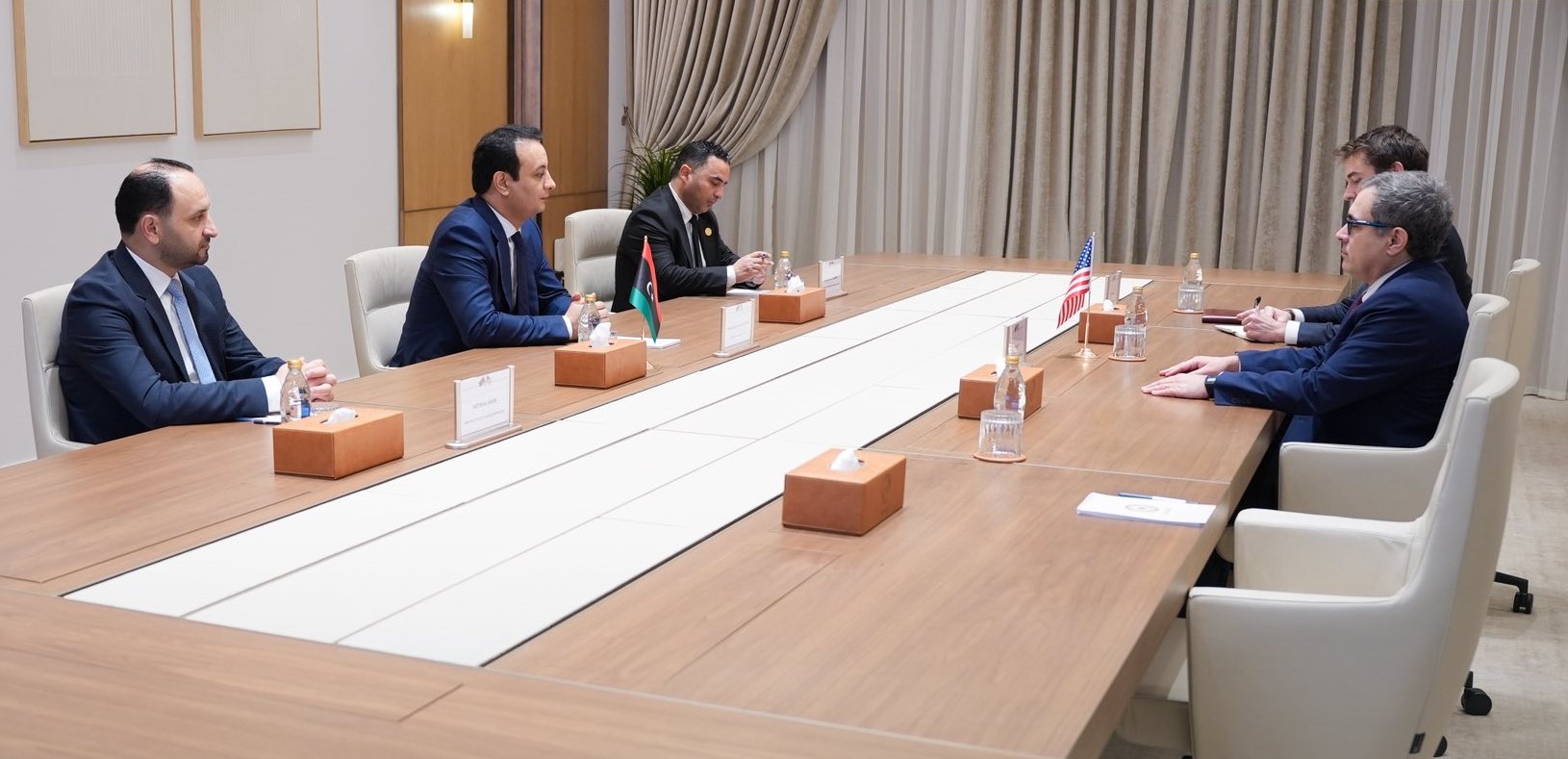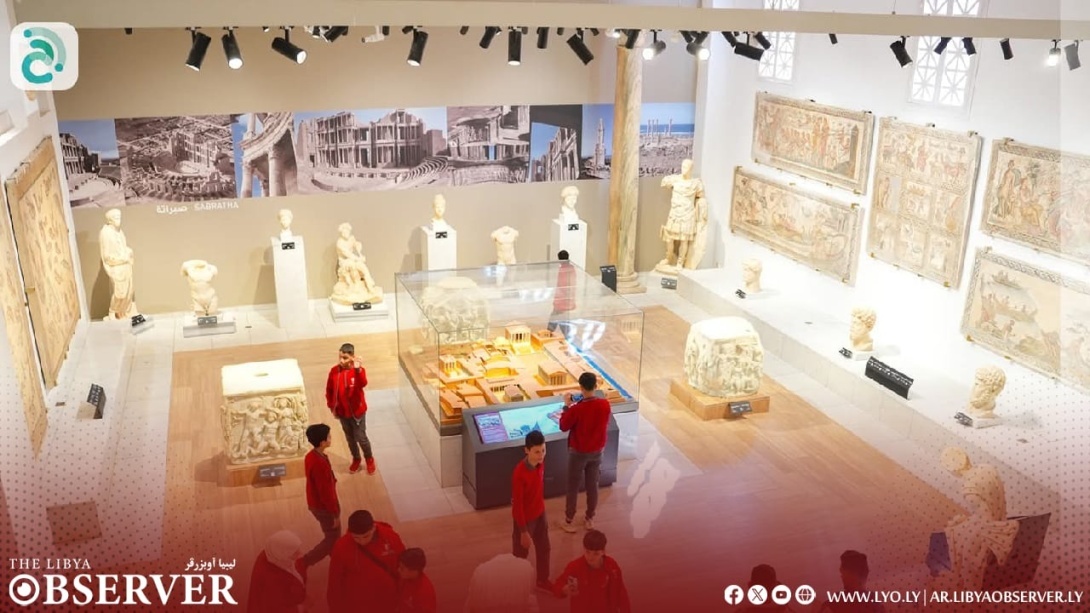
The Benghazi Antiquities Authority has announced the discovery of a significant archaeological site in the Boudrissa area of Benghazi, now added to the city’s official antiquities records.
The site is a Roman settlement featuring a square-shaped palace, a well, foundations, and remains of walls from several buildings and annexes.
This discovery followed the identification of the site on old maps, prompting a team of researchers to visit and conduct a field study.
The authority described the site as one of the important new archaeological finds and affirmed its ongoing efforts to protect it from any tampering or damage.




Benghazi
Benghazi is a major city in eastern Libya, historically significant as a center of trade and culture since its founding as the Greek colony of Euesperides. It played a pivotal role in the 2011 Libyan Civil War as a key base for the uprising against Muammar Gaddafi.
Boudrissa
Boudrissa is a traditional Berber village located in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco, known for its distinctive earthen architecture and historic granaries. It has served as a vital communal storage and defensive site for local communities for centuries, reflecting the region’s agrarian history and social organization.
Roman settlement
The Roman settlement refers to the widespread establishment of towns, military forts, and villas by the Roman Empire across its conquered territories from Britain to North Africa. These settlements, often built around a grid plan with forums, baths, and temples, served as crucial centers for administration, trade, and cultural Romanization. Many evolved into modern European cities, with their ruins providing key archaeological insights into Roman engineering and daily life.
square-shaped palace
The “square-shaped palace” likely refers to the Forbidden City in Beijing, China, a vast imperial palace complex from the Ming and Qing dynasties. It is renowned for its precisely rectangular layout and symmetrical design, serving as the home of emperors and the ceremonial center of Chinese government for nearly 500 years.
well
The Great Wall of China is an ancient series of fortifications built across the historical northern borders of China, primarily to protect against nomadic invasions. Its construction began as early as the 7th century BC, with the most famous sections built during the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). Today, it stands as a UNESCO World Heritage site and a powerful symbol of Chinese civilization.
foundations
The term “foundations” in an archaeological context often refers to the discovered base structures of ancient buildings, which provide crucial evidence for understanding past civilizations. These remains, such as those at sites like Çatalhöyük in Turkey or the Roman Forum in Italy, reveal settlement patterns, architectural techniques, and historical layers of human habitation.
walls
The term “walls” can refer to numerous historical structures worldwide, such as the Great Wall of China, built over centuries to protect empires from northern invasions, or the Walls of Constantinople, which defended the capital of the Byzantine Empire for over a thousand years. These fortifications were critical for defense, marking territorial boundaries and shaping the history of the civilizations they protected.
buildings
The term “buildings” refers to human-made structures for shelter and activity, with a history spanning from ancient mud-brick dwellings to modern skyscrapers. Their evolution reflects advancements in materials, engineering, and cultural needs, from pyramids and cathedrals to the steel-framed high-rises of the industrial age.
annexes
The term “annexes” most commonly refers to the buildings at Auschwitz-Birkenau, the largest Nazi concentration and extermination camp. These structures, added to expand the camp complex, were central to the Holocaust, where over one million people, primarily Jews, were systematically murdered during World War II. Today, the preserved site serves as a state museum and memorial.
old maps
Old maps are historical documents that visually represent geographical knowledge, political boundaries, and cultural perspectives from past eras. Their history spans from ancient Babylonian clay tablets to medieval portolan charts and the increasingly accurate world maps of the Age of Exploration. They serve as crucial records for understanding the evolution of cartography, navigation, and how societies viewed their world.
Benghazi Antiquities Authority
The Benghazi Antiquities Authority is the regional body responsible for managing and preserving the archaeological heritage of the Benghazi area in Libya. It oversees numerous historical sites from the Greek, Roman, and Islamic periods, working to protect them despite significant challenges from conflict and looting in recent decades.
Italian Civil Aviation Authority
The Italian Civil Aviation Authority (ENAC) is the national regulatory body for civil aviation in Italy, established in 1997. It is responsible for regulating, overseeing, and promoting air transport, airport infrastructure, and flight safety across the country.
Libyan-Italian economic forum
The Libyan-Italian Economic Forum is a bilateral platform designed to foster trade, investment, and economic cooperation between Libya and Italy. Its history is rooted in the long-standing economic ties between the two countries, particularly following the 2008 Treaty of Friendship, Partnership and Cooperation, which aimed to move beyond the colonial past and establish a new collaborative framework.