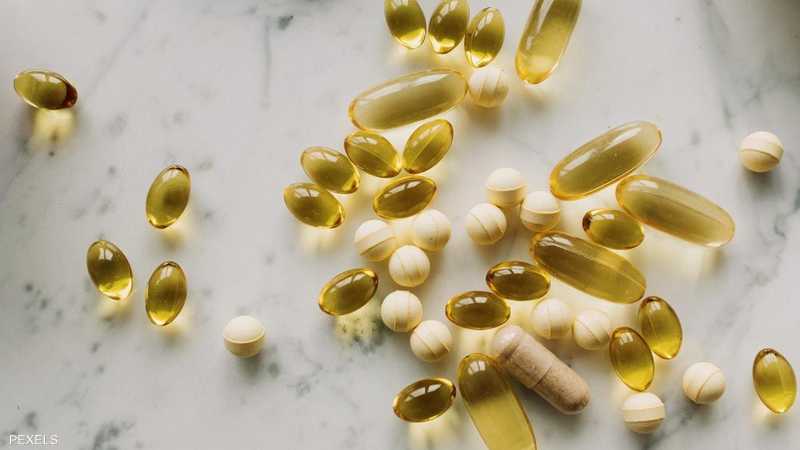
Omega-3 supplements, also known as fish oil, contain a type of fat found in fatty fish and seafood such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna.
Scientific study results on the effect of daily omega-3 supplement intake on blood sugar levels show mixed outcomes, generally pointing towards a limited or almost negligible effect.
Unclear Impact on Blood Sugar
High blood sugar levels, resulting from a dysfunction in insulin production or the body’s response to it, are the main characteristic of diabetes, a chronic disease that, if not controlled, can lead to serious complications affecting the eyes, kidneys, heart, and nervous system.
Given the severity and chronic nature of the disease, extensive research has been conducted to study the role of certain dietary supplements, including omega-3 fatty acids, both in preventing diabetes and as a supplement to traditional drug therapy. However, the results of this research have remained inconsistent.
While some studies have suggested that omega-3 supplements may help lower blood sugar levels, other studies have found no significant effect.
What Do Scientific Studies Say?
One study highlighting this discrepancy was published in 2024 in the scientific journal “Current Nutrition Reports” and reviewed 30 randomized clinical trials involving adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
Participants received omega-3 supplements in various doses and types for periods ranging from 6 weeks to 12 months.
The results showed a decrease in fasting blood sugar in some participants, while no change occurred in others.
This variation was attributed to several factors, including the number of participants, study duration, patient age, duration of diabetes, and supplement dosage.
Is It Recommended to Take Omega-3 Supplements?
There is insufficient evidence to support the use of omega-3 supplements for improving blood sugar control. Therefore, the American Diabetes Association does not generally recommend their use for people with diabetes or those with prediabetes.
However, some evidence suggests that omega-3 may be beneficial for improving heart health in people with diabetes, especially in those with high cholesterol or other cardiac risk factors. For this reason, a doctor may recommend them based on individual circumstances.
Consulting a Doctor is Essential
It is always advised to consult a doctor before starting to take omega-3 supplements, as they may interact with certain medications like blood thinners. Their side effects are often mild and include:
- An unpleasant taste.
- Bad breath.
- Digestive issues such as nausea, diarrhea, or heartburn.