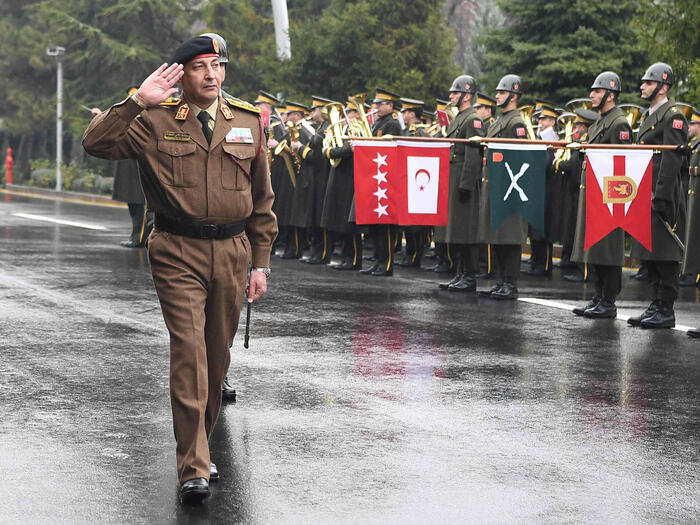
In recent years, the term “alkaline water” has emerged in medical and marketing circles, transforming from a limited scientific topic into a widely promoted product accompanied by many attractive health promises. These range from boosting energy levels and improving body hydration to supporting the body’s ability to fight chronic diseases. But is there any real scientific basis behind these shiny promises, or is it just a marketing trick exploiting people’s desire to improve their health?
Alkaline Water: The Secret Lies in the pH Level
Classifying water as “alkaline” is primarily based on the pH scale of liquids, also known as the “hydrogen ion concentration.” This scale determines the balance of acidity and alkalinity in a liquid. The scale ranges from 0 to 14, where a pH of 7 is considered neutral. A pH higher than 7 indicates the liquid is alkaline, and a pH lower than 7 indicates it is acidic. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency recommends that the pH of drinking water should be between 6.5 and 8.5, with an average of 7.5 for most drinking water.
Water becomes alkaline when it passes over rocks and picks up alkaline minerals, or it can be produced industrially through “electrolysis.” This is a process where filtered water is passed through a device that separates it into two streams: alkaline and acidic. The alkaline stream contains minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. After being treated in this way, the water is sold in bottles.
It has been noted that some proponents of alkaline water believe it balances the body’s pH level, but this claim is not supported by any scientific studies.

Common Health Claims and What Science Says
Advertisements promoting alkaline water claim it has a unique ability to improve body hydration compared to regular water, along with improving digestion or reducing acidity, and even preventing certain diseases.
However, these claims are said to be unjustified.
A 2016 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (JISSN) investigated the effect of alkaline water on body hydration and general vitality after exercise. The results showed that after exercise, blood viscosity decreased more with the consumption of alkaline water. However, key biological measurements of hydration, such as total body water or changes in mass, did not show statistically significant differences between alkaline water and regular water regarding overall hydration. This led the researchers to conclude that there is no convincing evidence that alkaline water hydrates the body better than regular water.
Regarding the reduction of acidity, it has been clarified that a potential benefit of alkaline water is indeed alleviating symptoms of heartburn caused by acid reflux. However, this effect is only temporary, and there are more effective options for dealing with stomach acidity, such as antacids and medications that suppress stomach acid production.
Concerning supporting energy levels, a 2021 study examined the effect of drinking high-mineral alkaline water for 3 consecutive days before anaerobic exercise on reaction speed and some indicators of physical performance in 12 healthy young men.
The results showed no effect of alkaline water on reaction time, an indicator related to performance and cognitive functions. Similarly, there was no effect on other key energy indicators compared to regular water. The study’s results confirmed that no statistically significant improvement was observed in most performance-related variables, except for some aspects of anaerobic performance under limited conditions. This indicates that claims regarding increased energy are not scientifically supported.

Finally, regarding the prevention of chronic diseases, a 2016 scientific review confirmed that there is no strong evidence supporting that alkaline water prevents chronic diseases like cancer. The review examined