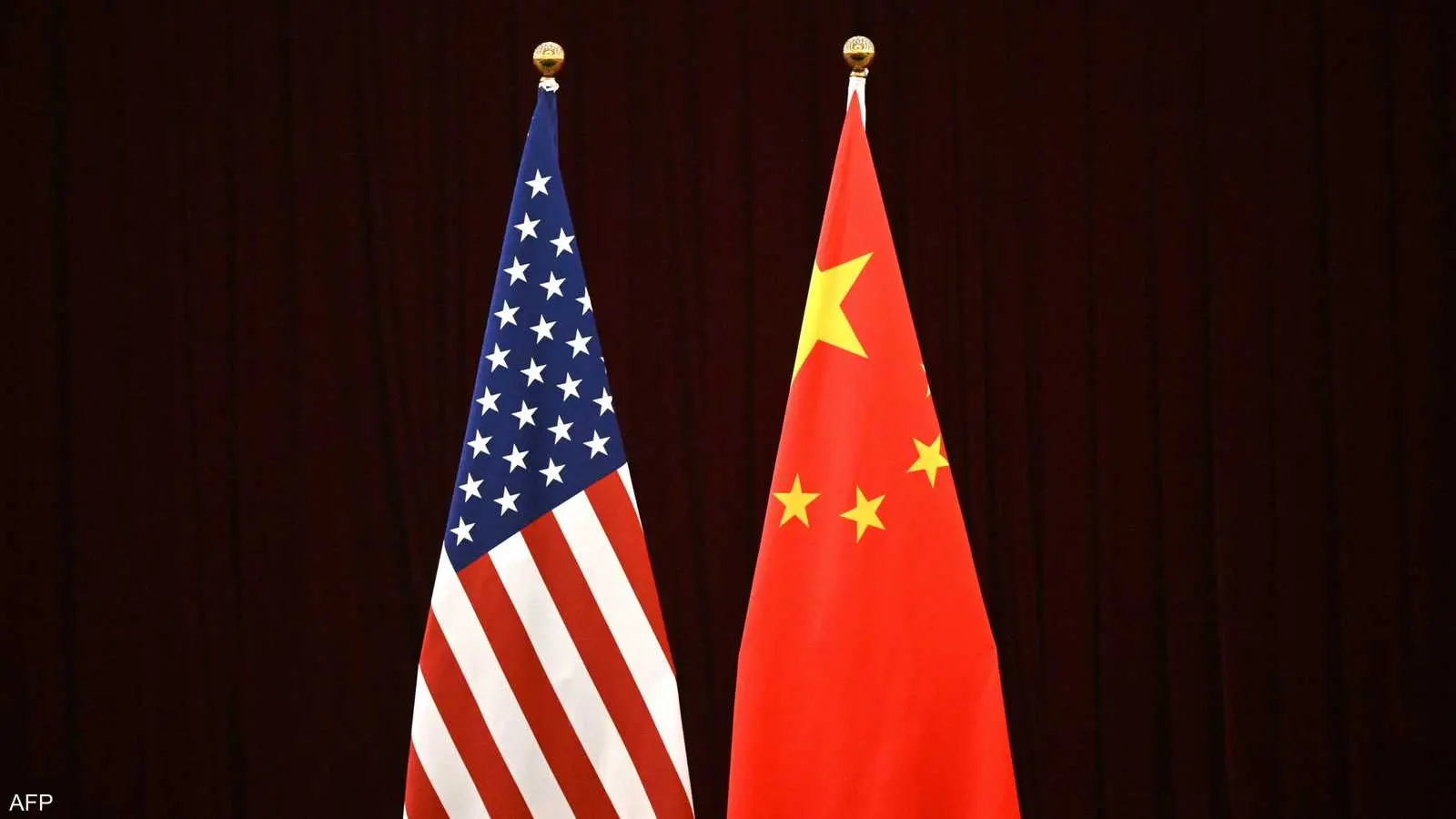
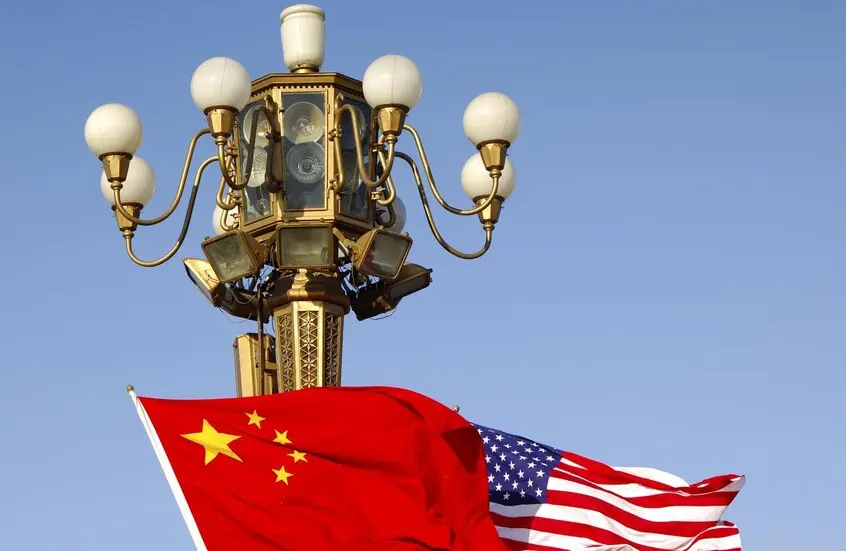
On Thursday, it was revealed that the email accounts of U.S. Congressional staffers working on influential committees were breached, likely by Chinese sources, as part of a cyber espionage campaign named “Salt Typhoon.”
It was reported that in December of last year, Chinese intelligence gained access to the email systems of staffers on the House Select Committee on China, as well as aides on committees for Foreign Affairs, Intelligence, and Armed Services, under the oversight of China’s Ministry of State Security.
It remains unclear whether the attack reached the messages of the members of Congress themselves, but it represents the latest episode in a series of Chinese cyberattacks targeting vital American networks.
Sources indicate that the “Salt Typhoon” campaign sometimes grants Beijing the ability to access unencrypted phone calls, text messages, voicemails, and email accounts, and China has previously intercepted calls of prominent U.S. officials over the past two years.
Warnings were issued about the weak response to this threat, with American telecommunications companies being described as “extremely vulnerable” to this type of attack.
This attack follows the FBI’s 2024 disclosure of another Chinese hacking campaign known as “Volt Typhoon,” which targeted American energy, transportation, and communications systems, potentially serving Beijing in the event of a conflict with Washington.
The U.S. Treasury Department had considered imposing sanctions on entities linked to China’s Ministry of State Security over “Salt Typhoon,” but stepped back for fear that these sanctions could affect efforts to ease tensions between the leaders of the two countries.
In response, the Chinese Embassy in Washington denied all accusations, with a spokesperson stating: “China firmly opposes groundless accusations and the use of cybersecurity to smear China’s reputation and spread misinformation about the so-called Chinese threat.”
U.S. Congressional staffers
U.S. Congressional staffers are the professional employees who work for members of Congress and congressional committees, providing essential research, administrative, and legislative support. The role and number of staff have grown significantly since the early 20th century, particularly after the Legislative Reorganization Act of 1946, which formally recognized their importance in managing the increasing complexity of the federal government.
House Select Committee on China
The House Select Committee on the Strategic Competition Between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party, commonly called the House Select Committee on China, is a bipartisan committee of the U.S. House of Representatives established in January 2023. Its primary purpose is to investigate and provide policy recommendations concerning the economic, technological, and security challenges posed by the People’s Republic of China to U.S. national interests.
Foreign Affairs
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is a government department responsible for managing a country’s diplomatic relations and foreign policy. Its history is tied to the development of the modern nation-state, evolving from the royal courts and chancelleries of early monarchies into a formalized executive department.
Intelligence
“Intelligence” is not a specific place or cultural site, but a concept. In a historical context, the development of intelligence as a measurable human attribute is often traced to the early 20th century with the creation of IQ tests by psychologists like Alfred Binet. The study and application of intelligence have since become central fields in psychology, education, and technology.
Armed Services
The Armed Services refers collectively to a nation’s military branches, such as the army, navy, and air force, which are responsible for national defense. Historically, modern armed services evolved from professional standing armies and navies, with their structure and roles often formalized in the 19th and 20th centuries. They operate under civilian control and are governed by a distinct legal and disciplinary framework.
China’s Ministry of State Security
China’s Ministry of State Security (MSS) is the principal civilian intelligence, security, and secret police agency of the People’s Republic of China, established in 1983. It is responsible for counter-intelligence, foreign intelligence, and political security to safeguard the state. Its functions and history are closely tied to maintaining national security and stability under the leadership of the Communist Party of China.
Beijing
Beijing is the capital of China, with a history spanning over three millennia as a significant political and cultural center. It served as the seat of imperial power during several dynasties, most notably the Ming and Qing, and is home to UNESCO World Heritage Sites like the Forbidden City and the Great Wall. Today, it stands as a major global metropolis blending ancient historical architecture with modern urban development.
American telecommunications companies
American telecommunications companies have played a central role in the nation’s technological and economic development since the invention of the telegraph and telephone in the 19th century. Historically dominated by the Bell System monopoly, the industry was transformed by antitrust regulation and the Telecommunications Act of 1996, leading to today’s competitive landscape of major providers like AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile. These companies are now pivotal in building and operating the infrastructure for modern mobile, broadband, and data services.
FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the United States’ primary federal law enforcement and domestic intelligence agency. It was established in 1908 as the Bureau of Investigation to address interstate crime and has since evolved to counter threats including organized crime, terrorism, and cybercrime.
American energy
“American energy” broadly refers to the United States’ historical and ongoing development of its energy resources, including fossil fuels like oil and coal as well as modern renewables. Its history is marked by periods such as the 19th-century coal boom, the 20th-century rise of the petroleum industry, and a 21st-century expansion into natural gas and alternative energy. This sector has been fundamental to the nation’s industrial growth and remains a central economic and geopolitical factor.
American transportation
American transportation has evolved from early canals and railroads in the 19th century to the development of the interstate highway system and commercial aviation in the 20th century. This infrastructure network has been fundamental to the country’s economic growth and cultural identity, emphasizing mobility and connectivity.
American communications systems
American communications systems, such as the telegraph and later the telephone, revolutionized long-distance interaction in the 19th century. This infrastructure, which expanded to include radio, television, and the internet, has been foundational to the country’s economic growth and cultural influence.
Washington
Washington, D.C., is the capital city of the United States, founded in 1790 and named after the nation’s first president, George Washington. It is renowned for its iconic national monuments, museums, and federal buildings, including the White House, the U.S. Capitol, and the Smithsonian Institution.
U.S. Treasury Department
The U.S. Department of the Treasury is a federal executive department established by Congress in 1789 to manage the government’s revenue. It is responsible for producing currency, collecting taxes, and advising on economic policy, with its history deeply intertwined with the financial foundations of the United States.
Chinese Embassy in Washington
The Chinese Embassy in Washington, D.C., serves as the primary diplomatic mission of the People’s Republic of China in the United States. It was established in 1979 following the normalization of diplomatic relations between the two countries. The embassy complex is located on International Place and functions as a central hub for diplomatic, consular, and cultural exchanges.