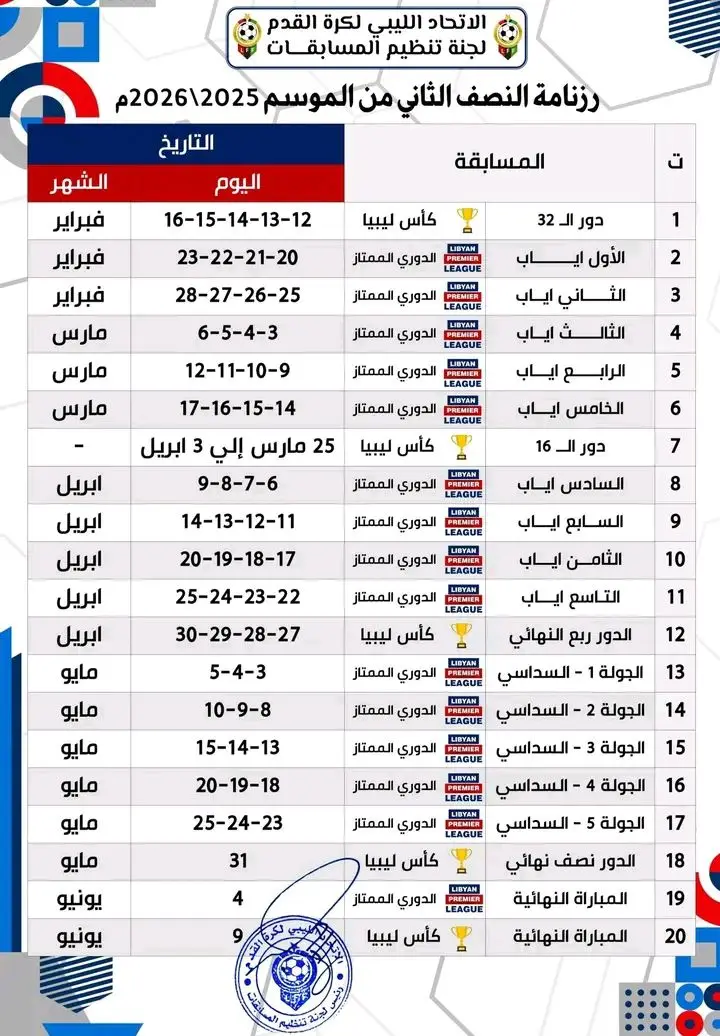
Four matches from the third round will be held on Thursday, for the teams in Groups Two and Four.
The competition begins with Group Two, where the Zintan Stadium will host the first match between Ittihad Gharyan and its guest, Ittihad Misrata. In the second match, Ittihad will be a guest to Al-Shumo’ at Misrata Stadium.
In the Group Four competitions, Al-Afriqi will host Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya at Derna Municipal Stadium, and Thursday’s matches will conclude with a match between Al-Akhdar and its guest, Al-Murooj.
The third round matches will conclude on Friday with four matches. Abi Al-Ashhar will host its guest, Shab Al-Ghar, in the first match at the Artificial River Stadium. In the second match at the same stadium, Al-Majd will face Al-Tarsana.
In the Group Four competitions, Khalij Sirt will host Al-Tahadi at its stadium. The round’s matches will conclude with a meeting between Al-Nasr and Al-Andalus at Benghazi International Stadium.
Zintan Stadium
Zintan Stadium is a football stadium located in the city of Zintan, Libya. It was constructed in the early 2000s and has primarily served as the home ground for the local football club, Al-Nasr Zintan. The stadium’s history is tied to the post-Gaddafi era, reflecting a period of local development and community focus on sport.
Ittihad Gharyan
Ittihad Gharyan is a Libyan football club based in the city of Gharyan, founded in 1954. The club has historically been a significant part of the local sports culture in the Jabal al Gharbi region. Its name, “Ittihad,” meaning “union” in Arabic, reflects its community roots.
Ittihad Misrata
Ittihad Misrata is a prominent Libyan football club based in the city of Misrata, founded in 1944. It is historically one of the country’s most successful clubs, having won multiple national league and cup titles. The club has a strong local fanbase and has been a significant part of Libya’s sporting culture for decades.
Misrata Stadium
Misrata Stadium is a multi-purpose sports venue located in Misrata, Libya, primarily used for football matches. It was constructed in the 1970s and has since served as a home ground for local clubs. The stadium also gained historical significance as a site of conflict and a gathering point during the 2011 Libyan Civil War.
Al-Afriqi
“Al-Afriqi” is a historical name for the continent of Africa, derived from the Latin “Africus.” It was notably used by medieval Arab geographers like Al-Idrisi, who wrote a seminal work called “The Book of Roger” (Kitab Rujar) which described the world, including the African continent. This term reflects the early Islamic world’s geographical knowledge and cartographic contributions.
Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya
Al-Wefaq Ajdabiya is a prominent cultural and social organization based in the city of Ajdabiya, Libya. Historically, it has served as a key gathering place and civil society hub, particularly known for fostering local dialogue and community cohesion, especially during and after the 2011 Libyan revolution.
Derna Municipal Stadium
Derna Municipal Stadium is a football stadium located in Derna, Libya, which historically served as a key sporting venue for the city. It gained international attention during the 2011 Libyan Civil War when it was used as a mass detention site by militias.
Al-Akhdar
Al-Akhdar, also known as the Green Mountain, is a prominent mountain range in eastern Libya, part of the Jabal al Akhdar plateau. Historically, it was a significant region in the ancient Greek colony of Cyrenaica and later a center for early Christianity and Islamic scholarship. Its fertile highlands and forests have long contrasted with the surrounding desert, making it a historically important agricultural and cultural area.
Al-Murooj
Al-Murooj is a modern residential and commercial district located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, developed as part of the city’s contemporary urban expansion. Its name, which translates to “The Meadows,” reflects its design with extensive green spaces and parks integrated into the urban landscape. The area represents the rapid growth and modernization of Riyadh in the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
Abi Al-Ashhar
Abi Al-Ashhar is a historical archaeological site located in Jordan, believed to be an ancient Nabataean settlement. It features ruins including tombs and water channels, reflecting the engineering prowess of the Nabataean civilization that flourished from around the 4th century BC to the 1st century AD.
Shab Al-Ghar
Shab Al-Ghar is a cave located in the Al-Baha Region of Saudi Arabia, known for its historical significance as a natural shelter. It is believed to have been used by ancient tribes and travelers for centuries due to its strategic location along old trade routes.
Artificial River Stadium
The Artificial River Stadium is a modern sports venue located in Tripoli, Libya, built alongside the man-made Great Man-Made River project. It was constructed in the early 2000s and primarily serves as the home stadium for the Al-Ittihad Tripoli football club. Its name and location are directly tied to the massive irrigation system that is a major feat of Libyan engineering.
Al-Majd
“Al-Majd” is a term meaning “The Glory” in Arabic and is commonly used in the names of various modern commercial and residential developments, particularly in the Gulf region. It does not refer to a single, specific historical or cultural site with a unified history, but rather to contemporary projects that symbolize progress and prestige.
Al-Tarsana
Al-Tarsana is a traditional wooden boat-building workshop located in the Old City of Damascus, Syria, preserving the centuries-old craft of constructing *shakhtouras* (Nile barges) and other vessels. Historically, this craft was vital for trade and transport along the Barada River and the region’s waterways, with skills passed down through generations of Damascene artisans. Today, it stands as a cultural heritage site showcasing this intricate craftsmanship to visitors.
Khalij Sirt
Khalij Sirt, also known as the Gulf of Sidra, is a large body of water on the coast of Libya in the Mediterranean Sea. Historically, it has been a significant maritime region since antiquity, known for trade and as the site of naval battles, including a major confrontation during World War II. In modern times, it gained geopolitical prominence due to territorial claims and conflicts in the late 20th century.
Al-Tahadi
Al-Tahadi is a prominent sports stadium located in Benghazi, Libya, primarily used for football matches. It was originally constructed in the 1960s and has since served as a key venue for local and national sporting events. The stadium has undergone several renovations and remains a significant landmark in the city’s cultural and athletic life.
Al-Nasr
Al-Nasr is a common Arabic name meaning “The Victory,” often used for mosques, palaces, and monuments throughout the Islamic world. Historically, it is most famously associated with the Al-Nasr Mosque in Jerusalem, originally built in the 12th century during the Ayyubid period following Saladin’s reconquest of the city.
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus refers to the regions of the Iberian Peninsula under Muslim rule between the 8th and 15th centuries, a period marked by significant cultural, scientific, and architectural flourishing. This era, particularly under the Caliphate of Córdoba, was notable for its relative religious coexistence and produced iconic sites like the Great Mosque of Córdoba and the Alhambra palace complex. It ended with the completion of the Christian Reconquista in 1492.
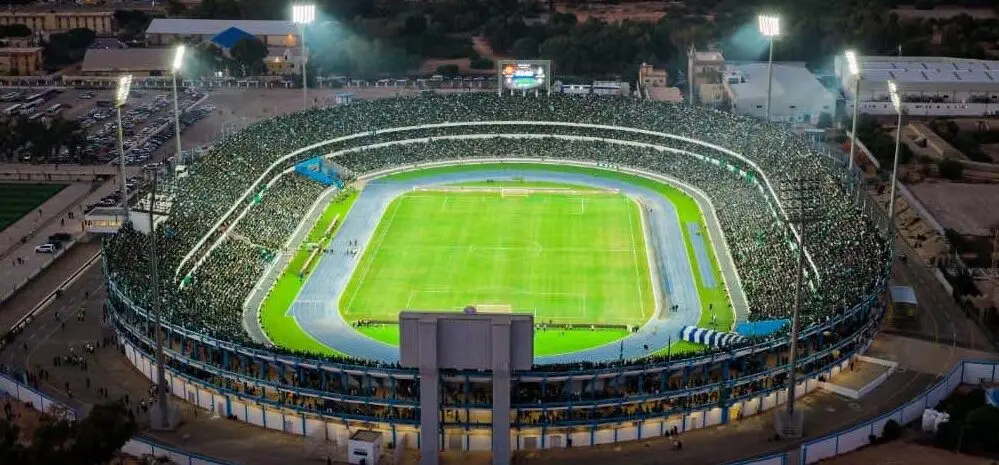
Benghazi International Stadium
Benghazi International Stadium is a major sports venue in Benghazi, Libya, originally opened in the 1960s. It has hosted numerous national and international football matches but has suffered significant damage during periods of conflict in the country, including the 2011 Libyan Civil War.