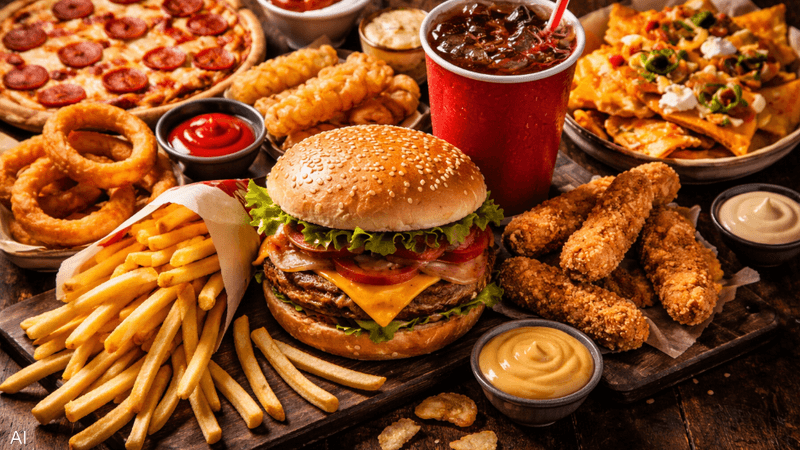
Eating fast food daily might seem like a practical choice to avoid missing meals, but multiple studies warn that this dietary pattern can have serious health consequences, including an increased risk of chronic diseases, malnutrition, and potentially a shorter life expectancy.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Research indicates a strong link between frequent fast food consumption and a higher Body Mass Index (BMI) and obesity.
These meals are often high in calories, saturated and trans fats, sugars, and sodium, while being low in fiber and essential nutrients, making them a major factor in weight gain.
Scientific reviews have concluded that people who regularly eat fast food face a 20% to 129% higher risk of obesity compared to others.
Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
Most fast food relies on refined carbohydrates, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar and the need for large insulin releases.
With repetition, insulin resistance can develop, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Studies indicate this risk can increase by up to 68% for those who eat fast food twice a week or more.
Cardiovascular Diseases
High consumption of fast food is linked to lipid disorders, elevated “bad” cholesterol (LDL), increased inflammation, all of which pave the way for heart disease.
The high sodium content also contributes to elevated blood pressure. Research suggests that frequent consumption of these meals may increase the risk of metabolic syndrome by up to 150%.
Poor Diet Quality
Fast food restaurant meals are often higher in calories, fats, and sodium, and lower in nutritional value compared to home-cooked meals.
Reviews have shown that most ready-made meals exceed recommended health guidelines, leading to deficiencies in essential elements like fiber and protein, despite exceeding daily calorie needs.
Effects on Physical and Mental Health
Daily reliance on fast food contributes to poor overall health, increased inflammation, digestive and sleep disorders, as well as feelings of fatigue and low energy.
Studies have also linked frequent consumption of fast food to a higher risk of depression and psychological stress by up to 16%, although debate continues about a direct causal relationship.
Accelerated Aging and Potential Shortened Lifespan
Research indicates that frequent fast food consumption is associated with higher hospitalization rates for cardiovascular events and a significantly increased risk of cardiac death.
Furthermore, the high fats and sugars promote chronic inflammation, which accelerates aging processes and increases the risk of chronic diseases that can lead to a loss of life years.