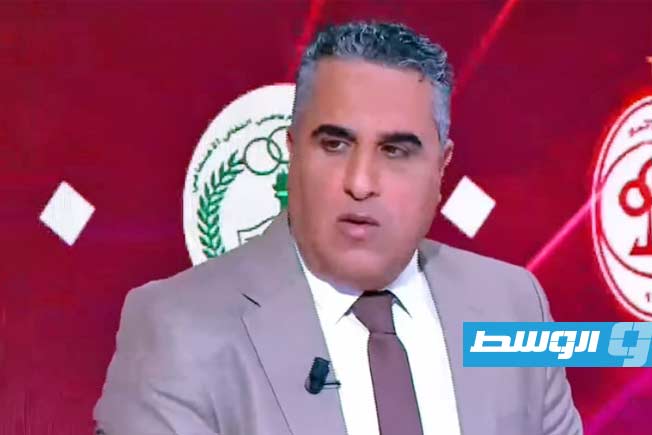
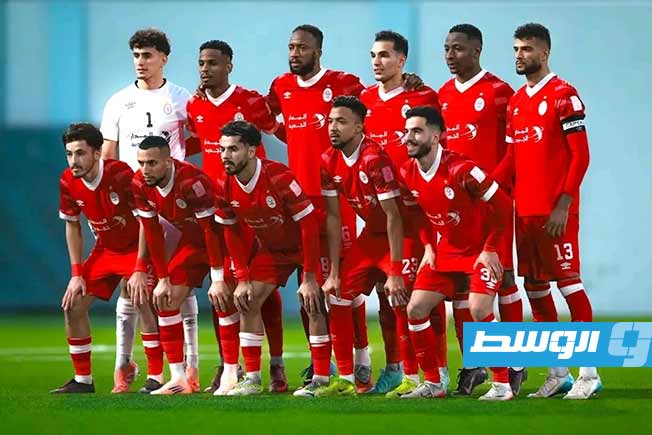
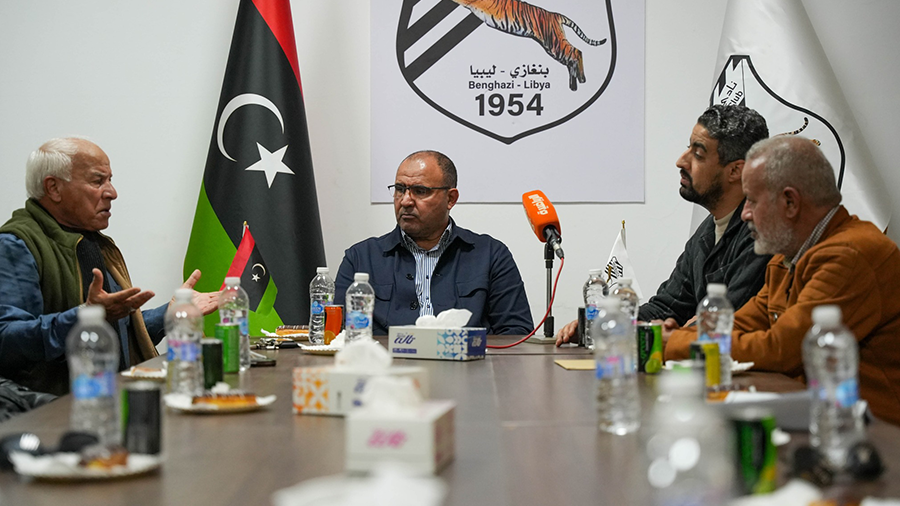
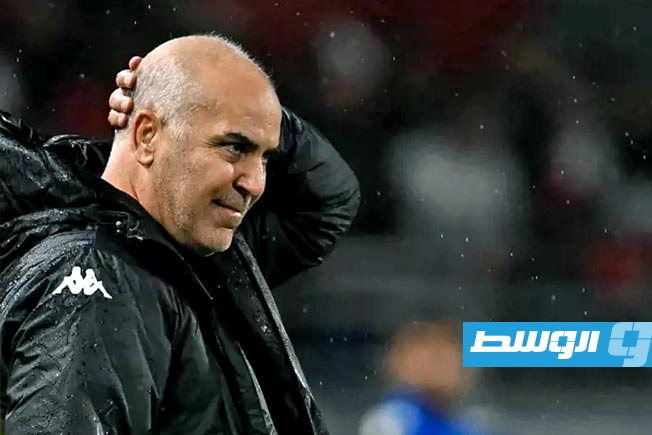
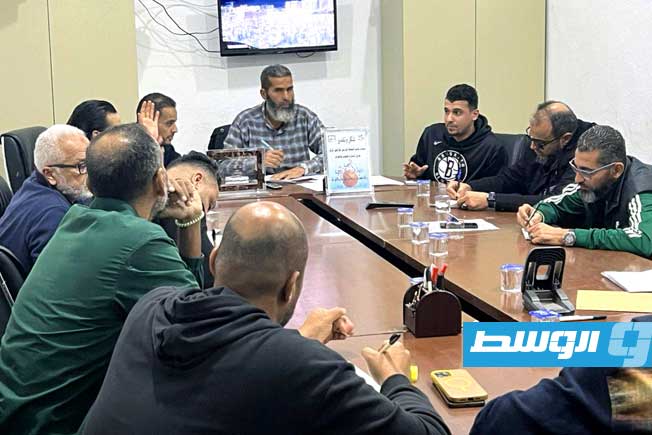
Al-Ahli Benghazi Club announced the mutual termination of its contract with Egyptian coach Tarek Mostafa and his accompanying technical staff.
The decision by Al-Ahli Benghazi’s management to terminate the contract with the Egyptian coach Tarek Mostafa came after he failed to meet the club’s ambitions at the start of the team’s journey in the Premier League, with the team drawing in the first and second rounds of the Premier League competition.
Furthermore, before the season began, the team lost the opportunity to win the Libya Cup and the Libyan Super Cup, after losing to Al-Ahli Tripoli.
Tarek Mostafa is the fifth coach to leave the Premier League competition. Previously, Tunisian coach Saeed Al-Saibi of Al-Sadaka left, as did Egyptian coach Tarek Gheida of Al-Andalus, in addition to the departure of Tunisian coach Abdelrahman Al-Awiti of Al-Khums and his compatriot, coach Mohamed Al-Telmessani of Al-Sabah.
Al-Ahli Benghazi Club
Al-Ahli Benghazi Club is a major Libyan sports club, most famous for its football team, founded in the city of Benghazi in 1947. It is one of the oldest and most successful clubs in Libya, with a passionate fan base and a history deeply intertwined with the city’s modern social and cultural identity.
Egypt
Egypt is home to one of the world’s oldest civilizations, with a recorded history spanning over 5,000 years, famously centered around the Nile River and the pharaonic kingdoms that built iconic monuments like the Pyramids of Giza. Its rich cultural heritage includes ancient temples, hieroglyphic writing, and significant contributions to mathematics and architecture, later influenced by Greco-Roman, Coptic Christian, and Islamic periods. Modern Egypt remains a pivotal cultural and political center in the Arab world.
Tarek Mostafa
Tarek Mostafa is not a known place or cultural site, but a common Arabic personal name. Therefore, it does not have a history as a location. The name itself is of Arabic origin, meaning “the one who knocks at the door” or “morning star.”
Premier League
The Premier League is the top level of the English football league system, founded in 1992 when clubs in the Football League First Division broke away to capitalize on lucrative television rights deals. It has since grown into one of the world’s most popular and commercially successful sports leagues, featuring iconic clubs like Manchester United, Liverpool, and Arsenal.
Libya Cup
The Libya Cup is the premier domestic football knockout tournament in Libya, first established in 1975. It has been contested by clubs across the country, though its schedule has frequently been disrupted due to political instability and conflict within Libya.
Libyan Super Cup
The Libyan Super Cup is an annual football match contested between the winners of the Libyan Premier League and the Libyan Cup. It was first held in 1993, though its scheduling has been irregular due to political and social instability in the country. The competition serves as the traditional season opener for Libyan football.
Al-Ahli Tripoli
Al-Ahli Tripoli is a major sports club in Libya, most famous for its football team, which was founded in 1954. Historically, it has been one of the country’s most successful and popular clubs, winning numerous national championships and serving as a significant cultural institution in Tripoli.
Tunisia
Tunisia is a North African country with a rich history shaped by ancient civilizations, including the Phoenician city of Carthage, Roman rule, and later Arab-Islamic influence. Its cultural sites, such as the well-preserved Roman amphitheater at El Jem and the historic medina of Tunis, reflect this diverse heritage. Today, it is known as the birthplace of the Arab Spring and for its blend of Mediterranean and Arab cultures.
Saeed Al-Saibi
Saeed Al-Saibi is a traditional market (souq) located in the old city of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, historically known as a vibrant trading hub for spices, textiles, and perfumes. Its history is intertwined with Jeddah’s role as a major port for pilgrims traveling to Mecca, with the market serving merchants and travelers for centuries. The souq retains much of its historic architecture and atmosphere, offering a glimpse into the region’s commercial and cultural heritage.
Al-Sadaka
Al-Sadaka is a historic mosque located in the city of Mosul, Iraq, believed to have been originally built during the medieval Islamic period. It is traditionally associated with a story of a charitable act (sadaka) by a companion of the Prophet Muhammad, though its precise early history is not fully documented. The mosque suffered significant damage during the conflict with ISIS but is part of ongoing cultural heritage restoration efforts in the region.
Tarek Gheida
Tarek Gheida is a prominent Egyptian lawyer and human rights activist. He has a long history of legal defense work, particularly in cases involving freedom of expression and political prisoners, and is a founding member of the Egyptian Front for Human Rights.
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus refers to the regions of the Iberian Peninsula under Muslim rule between the 8th and 15th centuries, a period marked by significant cultural, scientific, and architectural flourishing. This era, particularly under the Caliphate of Córdoba, was notable for its relative religious coexistence and produced enduring landmarks like the Great Mosque of Córdoba and the Alhambra palace complex. The period ended with the completion of the Christian Reconquista in 1492.
Abdelrahman Al-Awiti
Abdelrahman Al-Awiti is a prominent cultural center and library located in Homs, Syria. It was established in the early 20th century and named after the renowned Syrian intellectual Abdelrahman Al-Awiti, serving as a key hub for literature, research, and cultural events in the region.
Al-Khums
Al-Khums is a coastal city in northwestern Libya, historically significant as the site of ancient Leptis Magna, a prominent Roman city founded in the 7th century BC. The ruins of Leptis Magna, a UNESCO World Heritage Site located just east of the modern city, represent some of the most extensive and best-preserved Roman remains in the Mediterranean.
Mohamed Al-Telmessani
Mohamed Al-Telmessani was a prominent Egyptian figure who served as the Supreme Guide of the Muslim Brotherhood from 1973 until his death in 1986. He was a key leader during a period of significant political repression and resurgence for the organization, advocating for its re-establishment and engaging in dialogue with the Egyptian government.
Al-Sabah
Al-Sabah typically refers to the ruling family of Kuwait, which has governed the country since the mid-18th century. The dynasty was founded by Sabah I bin Jaber, who became the first ruler around 1752, establishing a sheikhdom that evolved into the modern State of Kuwait. The family continues to hold the position of Emir and plays a central role in the nation’s political and cultural life.