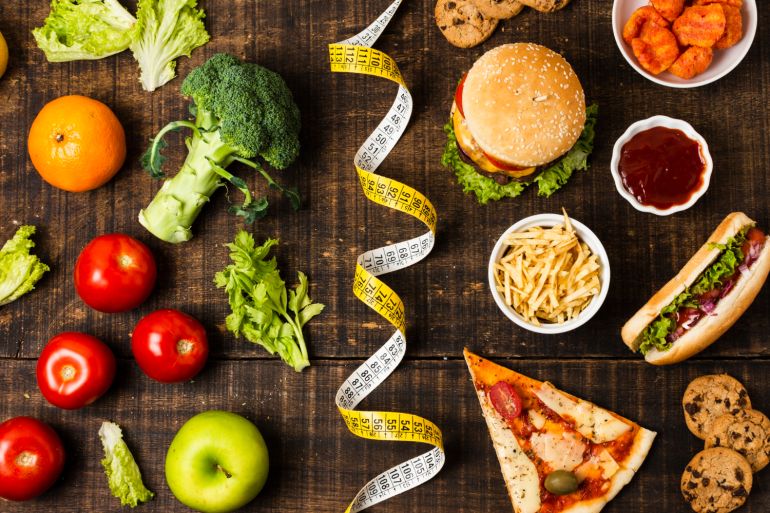
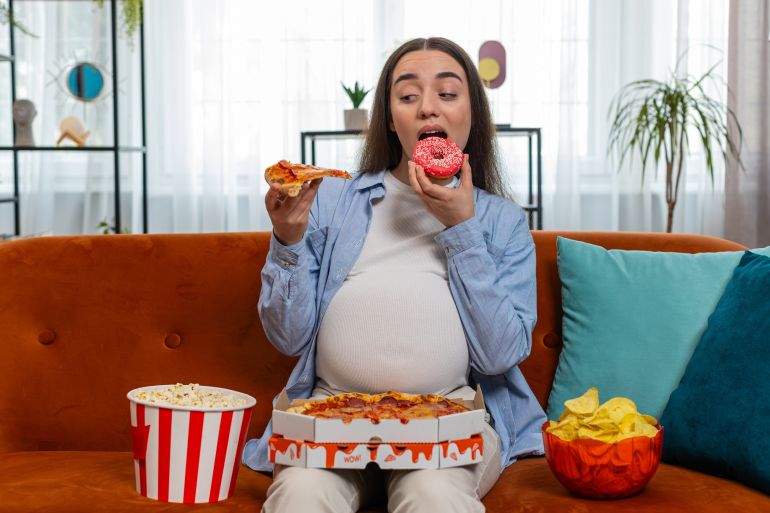
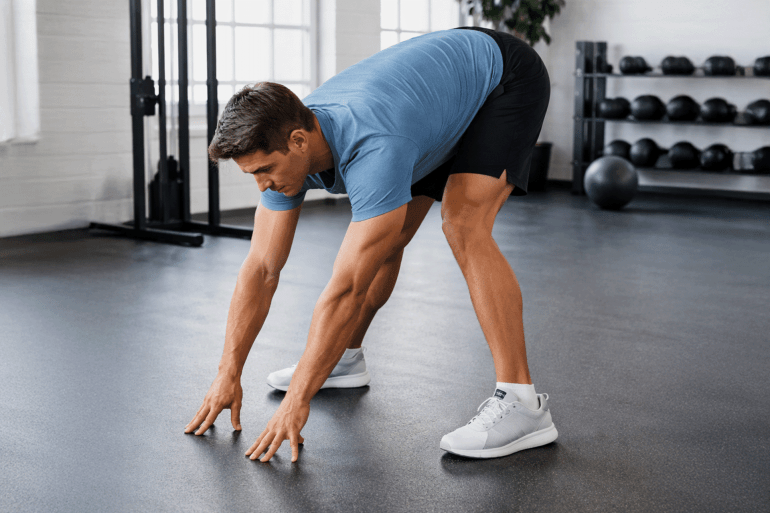
At a time when many diets are moving towards restricting or completely eliminating carbohydrates, specialists suggest that regulating their intake may be more effective for weight loss and enhancing fat burning. This is where “carb cycling” has emerged as a dietary approach that combines discipline and flexibility by changing the daily intake of carbohydrates according to a well-planned schedule that serves weight loss goals and physical activity levels.
This system is popular among athletes and bodybuilders, but it can also be an ideal dietary strategy for those looking for a weight loss plan or to break the monotony of low-calorie diets. It is important to consult a nutrition specialist before starting to ensure a plan is developed that suits one’s lifestyle.
Some studies point to the effectiveness of this approach. A study published in 2024 revealed that carb cycling can be an effective option for weight loss and improving body composition, especially when combined with high-intensity exercise.
Another study published in 2014 showed that following this system for 6 weeks contributed to stabilizing the basal metabolic rate, lowering glucose, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, while reducing feelings of hunger and increasing satiety compared to those who followed traditional calorie-restricted diets.
What is Carb Cycling?
Also known as “intermittent carbohydrate dieting,” it is an eating pattern based on alternating between high-carbohydrate and low-carbohydrate days. The plan may include dedicating days that are almost carbohydrate-free while maintaining a consistent protein intake and incorporating healthy fats.
The core idea is that consuming carbohydrates at specific times stimulates the metabolic process, while following a low-carbohydrate diet for consecutive days encourages the body to consume its carbohydrate stores (glycogen) and switch to burning stored fat (ketones) as an energy source.
There is no fixed protocol for this system, but one common method is to consume larger amounts of carbohydrates on days with strenuous exercise to provide the body with energy, versus restricting intake on less active days. On high-carbohydrate days, a person might consume between 2 to 2.5 grams of carbohydrates per pound of body weight, while the amount drops to half a gram per pound on other days. An individual’s total carbohydrate consumption may reach less than 30 grams on some days.
Another common method is “refeeding,” where an 8 to 12-hour window is dedicated to increasing carbohydrates, often once a week and sometimes once or twice a month.
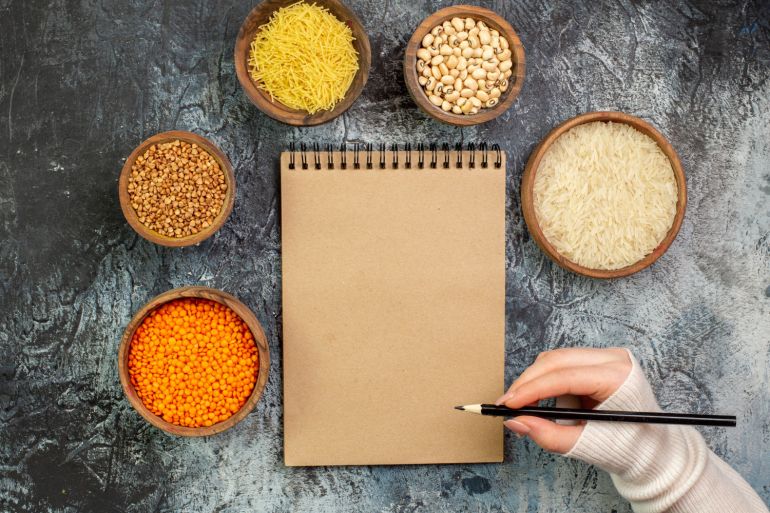
Healthy Choices
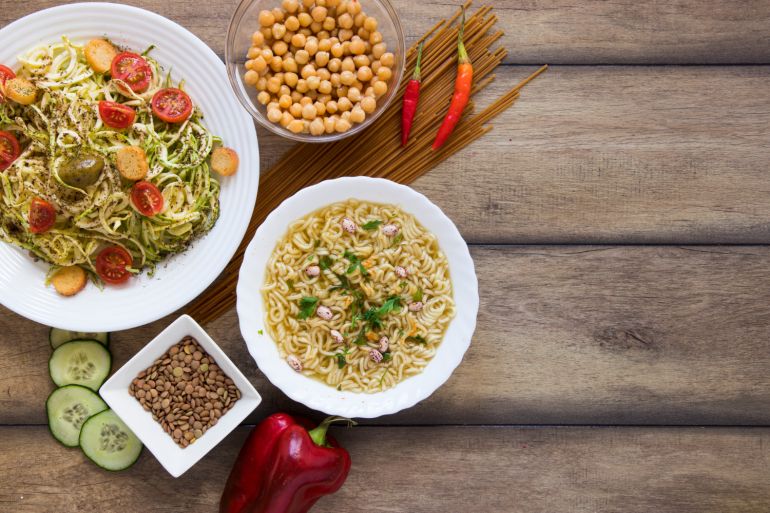
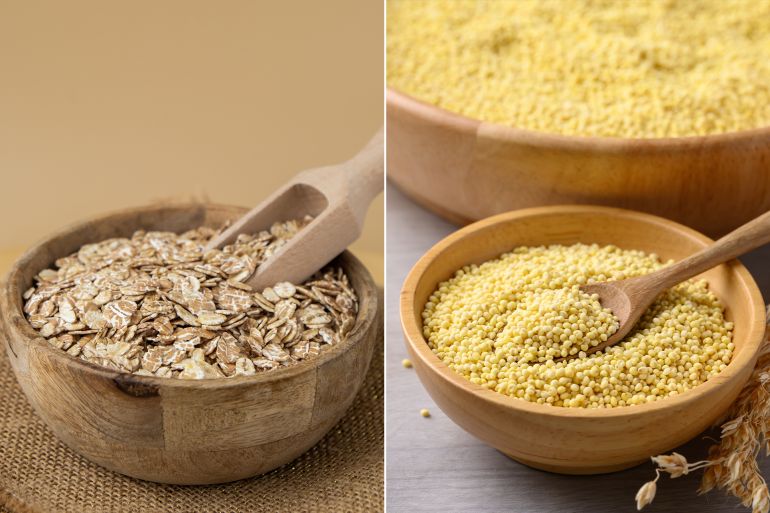
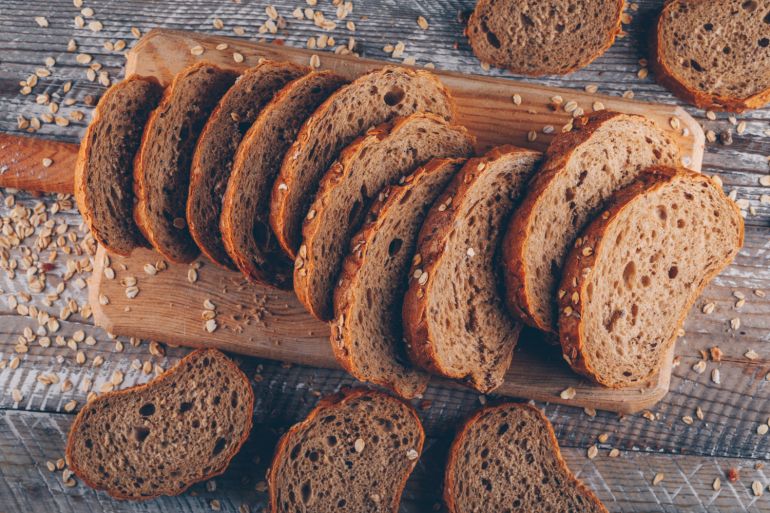
The success of this diet depends on the quality of carbohydrates. Therefore, it is advised to avoid white bread, pasta, and sugars, and replace them with whole foods like sweet potatoes, oats, lentils, chickpeas, whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and fruits. These choices are rich in fiber and have a more complex carbohydrate structure, requiring more energy for digestion.
On low-carbohydrate days, it is preferable to reduce fruits and starchy vegetables, and focus on low-carbohydrate vegetables like eggplant, tomatoes, broccoli, peppers, cauliflower, avocado, and leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach.

Potential Benefits
-
Enhancing Fat Burning
Consuming adequate amounts of carbohydrates at the right time stimulates hormones like leptin, which helps control appetite, raise metabolic rate, and the body’s ability to burn fat as an energy source, unlike excessive consumption, which leads to opposite results and causes weight gain.
-
Preserving Muscle Mass
This diet helps regulate the entry of amino acids and glucose into muscle cells. According to results from a 2013 study, carbohydrates help restore energy and supply muscles with glucose for rebuilding or glycogen for storage, which in turn improves endurance, strength, and overall performance.
-
More Sustainable
Some people find it difficult to adhere to a low-carbohydrate diet permanently, so they resort to alternating their carbohydrate consumption to enjoy foods rich in them or