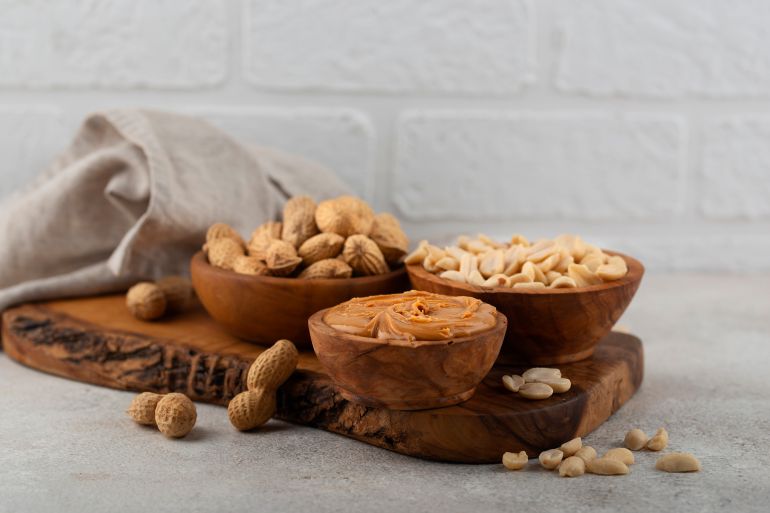
Researchers at the Maastricht University Medical Center in the Netherlands have revealed that peanuts “are not just a snack for entertainment in front of the TV, but can play a role in improving brain function and memory.”
Many tend to classify peanuts as nuts, but in fact they belong to the legume family, the same family that includes chickpeas, lentils, peas, and soybeans.
Peanuts enjoy widespread popularity around the world and are a staple component in vegetarian diets, thanks to their richness in healthy fats, protein, and a range of vitamins and minerals.
They also contribute to lowering cholesterol levels, aiding weight loss, and maintaining stable blood sugar levels, as explained when discussing their health benefits.
The new development is that in late 2025, researchers at the Maastricht University Medical Center in the Netherlands revealed that peanuts can play a role in improving brain function and memory. In light of these findings, we review what the researchers found regarding the potential benefits of daily peanut consumption…
Consuming 60 Roasted, Unsalted Peanuts
Researchers found that consuming about 60 grams of peanuts (equivalent to 60 shelled peanuts) daily for 4 months—unsalted, roasted, in the morning or evening, all at once or spread throughout the day, alone or added to meals—was effective in improving the function of blood vessels in the brain.
The research involved 31 healthy individuals aged between 60 and 75 years. An analysis of the participants’ cognitive performance was conducted, studying the effects of peanut consumption on their brain health.
Consuming 60 peanuts was also effective in “increasing overall cerebral blood flow” and enhancing participants’ ability to “remember spoken or written information.” Blood flow to the brain increased by up to 4.5%, memory improved by 5.8%, and a decrease in participants’ blood pressure was observed.

The Essence of the Study and Its Implications
The core of the study lies in its potential to limit the deterioration of blood vessel function in the brain and reduce the risk of dementia, a risk that increases with age.
Dementia is one of the most prominent growing global health problems; more than 7 million Americans suffer from Alzheimer’s disease, while Alzheimer’s Disease International predicts that the number of people with dementia will rise to 78 million by 2030 and reach 139 million by 2050.
In this context, it was explained that “cerebral blood flow is an extremely important indicator of the efficiency of the blood vessels responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients necessary to maintain brain health.”
It was added: “We found that long-term consumption of unsalted, roasted peanuts with their skin improves overall cerebral blood flow, which indicates a comprehensive improvement in the function of blood vessels within the brain.”
To confirm the importance of these results, it was noted that “the rate of overall cerebral blood flow decreases by about 0.37% annually with advancing age,” highlighting the preventive value of any dietary intervention capable of slowing this decline.
The Secret of Peanuts
The research team suggested that the secret may lie in peanuts containing an amino acid known as “L-arginine,” which helps the body build protein. It has also been proven important for vascular health and increases overall cerebral blood flow by 9.5% when injected intravenously.
It was explained: “In this study, peanuts roasted with their skin were chosen because they are a valuable source of unsaturated fats and polyphenols, both known to support vascular function.”
The choice was also made “for their content of additional dietary fiber, natural plant compounds, and anti-inflammatory antioxidants; including ‘resveratrol,’ which enhances blood flow in the brain during cognitive tasks in healthy young people.”
It was confirmed that “all these elements together may help explain the beneficial health effects of skin-on roasted peanuts observed in the study.”