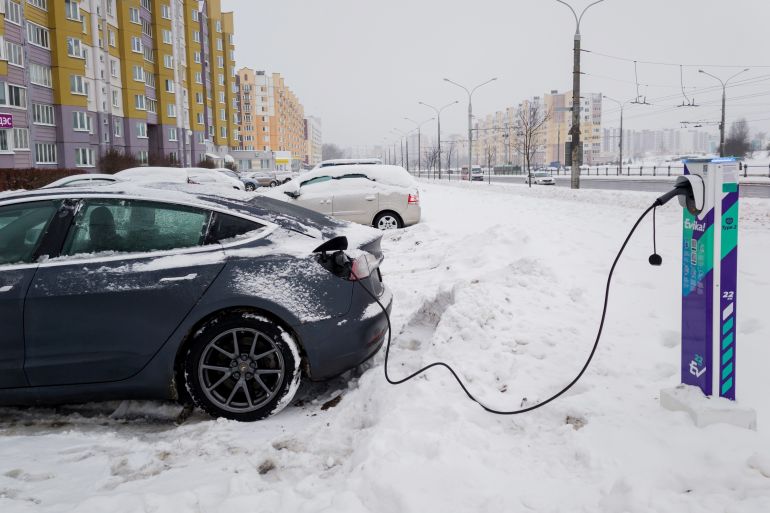
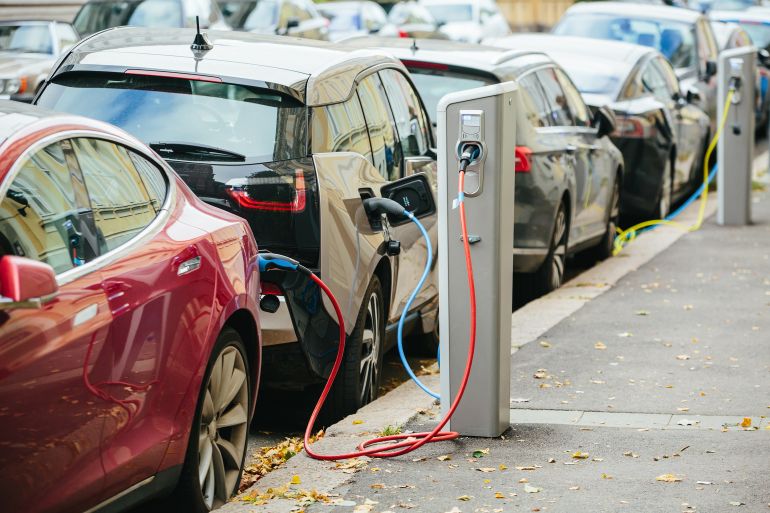
Electric vehicle users face a common challenge during winter: slow battery charging, especially when using fast chargers. Battery efficiency drops significantly as temperatures fall, losing its optimal ability to absorb energy after cooling overnight.
However, the impact of weather on an electric car’s performance can be reduced by following simple tips that help save time and money, and maintain the car’s efficiency during the cold months.
How much does cold weather affect an electric car?
Numerous studies indicate that this effect varies depending on conditions. At a temperature of -6.5°C, an electric car can lose about 12% of its charging efficiency. With the heater running at full power, the drop can reach 40%.
Tests have also shown that the efficiency of electric cars can decrease by about 39% in cold weather.
Reasons for reduced electric car battery performance in winter
There are several main reasons leading to the decline in electric car performance in cold weather, the most prominent of which are:
1. Reduced battery efficiency and charging speed due to low temperatures
A battery has an optimal operating range, typically between 20°C and 40°C, which varies depending on the car model. In winter—especially when the car is parked outdoors or in a cold garage—the battery temperature drops, approaching the ambient air temperature.
When charging begins in this state, a portion of the energy from the charger is allocated to heating the battery first until it reaches a safe operating temperature, instead of being stored directly. This leads to longer charging times and reduced speed.
Furthermore, the chemical reactions inside the battery become slower in cold weather, reducing its ability to receive or provide energy with the usual efficiency. This negatively affects both the driving range and charging speed.
2. Increased energy consumption from using various car systems
In cold weather, drivers rely more on the heating system, which is one of the most energy-consuming systems in an electric car.
In addition, the use of wipers to clear condensation from the windshield increases, and lights are used for longer periods due to shorter daylight hours. All of these consume additional battery power.
This increased consumption means a larger portion of the battery’s energy is allocated to powering auxiliary systems at the expense of the available driving range.
3. The impact of road conditions on energy consumption
Road conditions play an important role in reducing electric car efficiency during winter. Wet, snowy, or icy roads increase rolling resistance and force stability and traction control systems to work intensively to maintain vehicle grip.
This extra effort can raise energy consumption by up to 10% or more, especially when driving in harsh weather conditions or on unpaved roads.
4. Winter isn’t the only cause
Although slow charging is commonly linked to cold weather, it is not always solely due to low temperatures. When using two charging points at one station, the charging power is often shared between the two cars, leading to a decrease in charging speed for each. Some stations may also experience temporary drops in electrical capacity.
However, the most common cause remains a high battery charge level. Charging speed gradually decreases as the battery approaches a full 100% charge. This is normal behavior designed to protect the battery and extend its lifespan.
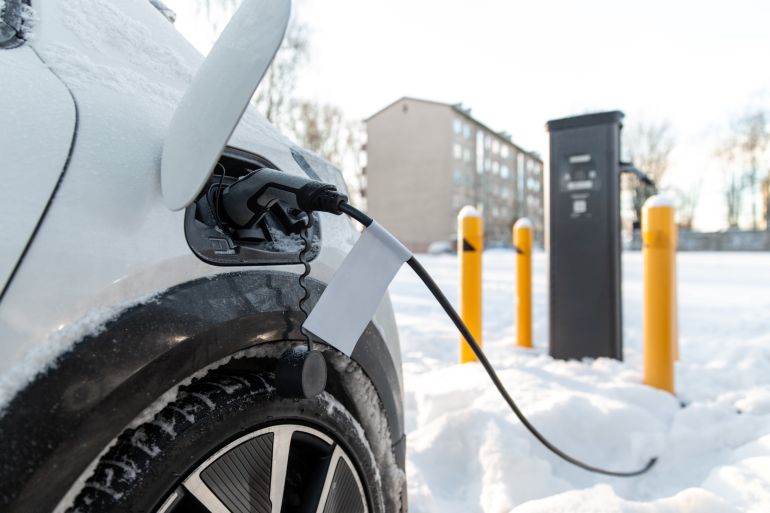

5 solutions to increase charging efficiency in cold weather
Although it is difficult to maintain the optimal performance of an electric car battery during the cold months, it is possible to improve charging speed by following a set of tips, the most prominent of which are:
First: Pre-heat the battery
Many electric cars offer a feature to pre-heat or precondition the